
Video
Your Blood Sugar Reading is False! Here is Why.Type diabetes blood sugar control -
A person with diabetes constantly manages their blood's sugar glucose levels. After a blood sample is taken and tested, it is determined whether the glucose levels are low or high. If glucose levels are too low carbohydrates are ingested. If glucose in the blood is too high, the appropriate amount of insulin is administered into the body such as through an insulin pump.
Know the basic steps for managing your diabetes. Poorly managed diabetes can lead to many health problems.
Diabetes is on the rise worldwide, and is a serious, lifelong disease that can lead to heart disease, stroke, and lasting nerve, eye and foot problems. Let's talk about diabetes and the difference between the three types of diabetes. So, what exactly is diabetes and where does it come from?
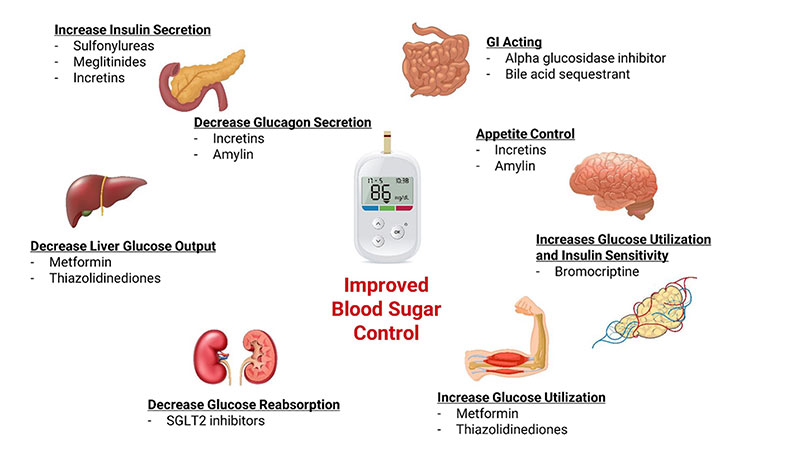
An organ in your body called the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that controls the levels of your blood sugar. When you have too little insulin in your body, or when insulin doesn't work right in your body, you can have diabetes, the condition where you have abnormally high glucose or sugar levels in your blood.
Normally when you eat food, glucose enters your bloodstream. Glucose is your body's source of fuel. Your pancreas makes insulin to move glucose from your bloodstream into muscle, fat, and liver cells, where your body turns it into energy. People with diabetes have too much blood sugar because their body cannot move glucose into fat, liver, and muscle cells to be changed into and stored for energy.
There are three major types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes happens when the body makes little or no insulin. It usually is diagnosed in children, teens, or young adults.
This disease often occurs in middle adulthood, but young adults, teens, and now even children are now being diagnosed with it linked to high obesity rates. In Type 2 diabetes, your fat, liver, and muscle cells do not respond to insulin appropriately. Another type of diabetes is called gestational diabetes.
It's when high blood sugar develops during pregnancy in a woman who had not had diabetes beforehand. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born.
But, still pay attention. These women are at a higher risk of type 2 diabetes over the next 5 years without a change in lifestyle. If you doctor suspects you have diabetes, you will probably have a hemoglobin A1c test. This is an average of your blood sugar levels over 3 months.
You have pre-diabetes if your A1c is 5. Anything at 6. Type 2 diabetes is a wake up call to focus on diet and exercise to try to control your blood sugar and prevent problems. If you do not control your blood sugar, you could develop eye problems, have problems with sores and infections in your feet, have high blood pressure and cholesterol problems, and have kidney, heart, and problems with other essential organs.
People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day, usually injected under the skin using a needle. Some people may be able to use a pump that delivers insulin to their body all the time. People with Type 2 diabetes may be able to manage their blood sugar through diet and exercise.
But if not, they will need to take one or more drugs to lower their blood sugar levels. The good news is, people with any type of diabetes, who maintain good control over their blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure, have a lower risk of kidney disease, eye disease, nervous system problems, heart attack, and stroke, and can live, a long and healthy life.
Checking your blood sugar levels often and writing down, or using an app to track the results will tell you how well you are managing your diabetes. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about how often you should check your blood sugar. Usually, you will test your blood sugar before meals and at bedtime.
You may also check your blood sugar:. Keep a record for yourself and your provider. This will be a big help if you are having problems managing your diabetes. It will also tell you what works and what doesn't work, to keep your blood sugar under control.
Write down:. You and your provider should set a target goal for your blood sugar levels for different times during the day. If your blood sugar is higher than your goals for 3 days and you don't know why, call your provider.
Random blood sugar values are often not that useful to your provider and this can be frustrating to people with diabetes. Often fewer values with more information meal description and time, exercise description and time, medicine dose and time related to the blood sugar value are much more useful to help guide medicine decisions and dose adjustments.
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person's needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals.
A general guideline is:. For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
High blood sugar can harm you. If your blood sugar is high, you need to know how to bring it down. Here are some questions to ask yourself if your blood sugar is high. Call your provider if your blood sugar is too high or too low and you do not understand why.
When your blood sugar is in your target range, you will feel better and your health will be better. Atkinson MA, Mcgill DE, Dassau E, Laffel L.
Type 1 diabetes. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap These medicines may reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke in people with a high risk of those conditions.
Examples include canagliflozin Invokana , dapagliflozin Farxiga and empagliflozin Jardiance. Other medicines your health care provider might prescribe in addition to diabetes medications include blood pressure and cholesterol-lowering medicines, as well as low-dose aspirin, to help prevent heart and blood vessel disease.
Some people who have type 2 diabetes need insulin therapy. In the past, insulin therapy was used as a last resort, but today it may be prescribed sooner if blood sugar targets aren't met with lifestyle changes and other medicines.
Different types of insulin vary on how quickly they begin to work and how long they have an effect. Long-acting insulin, for example, is designed to work overnight or throughout the day to keep blood sugar levels stable.
Short-acting insulin generally is used at mealtime. Your health care provider will determine what type of insulin is right for you and when you should take it.
Your insulin type, dosage and schedule may change depending on how stable your blood sugar levels are. Most types of insulin are taken by injection. Side effects of insulin include the risk of low blood sugar — a condition called hypoglycemia — diabetic ketoacidosis and high triglycerides.
Weight-loss surgery changes the shape and function of the digestive system. This surgery may help you lose weight and manage type 2 diabetes and other conditions related to obesity. There are several surgical procedures.
All of them help people lose weight by limiting how much food they can eat. Some procedures also limit the amount of nutrients the body can absorb. Weight-loss surgery is only one part of an overall treatment plan. Treatment also includes diet and nutritional supplement guidelines, exercise and mental health care.
Generally, weight-loss surgery may be an option for adults living with type 2 diabetes who have a body mass index BMI of 35 or higher. BMI is a formula that uses weight and height to estimate body fat.
Depending on the severity of diabetes or the presence of other medical conditions, surgery may be an option for someone with a BMI lower than Weight-loss surgery requires a lifelong commitment to lifestyle changes.
Long-term side effects may include nutritional deficiencies and osteoporosis. People living with type 2 diabetes often need to change their treatment plan during pregnancy and follow a diet that controls carbohydrates.
Many people need insulin therapy during pregnancy. They also may need to stop other treatments, such as blood pressure medicines. There is an increased risk during pregnancy of developing a condition that affects the eyes called diabetic retinopathy.
In some cases, this condition may get worse during pregnancy. If you are pregnant, visit an ophthalmologist during each trimester of your pregnancy and one year after you give birth.
Or as often as your health care provider suggests. Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is important to avoid severe complications. Also, be aware of symptoms that may suggest irregular blood sugar levels and the need for immediate care:.
High blood sugar. This condition also is called hyperglycemia. Eating certain foods or too much food, being sick, or not taking medications at the right time can cause high blood sugar. Symptoms include:. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome HHNS.
HHNS may be more likely if you have an infection, are not taking medicines as prescribed, or take certain steroids or drugs that cause frequent urination.
Diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs when a lack of insulin results in the body breaking down fat for fuel rather than sugar.
This results in a buildup of acids called ketones in the bloodstream. Triggers of diabetic ketoacidosis include certain illnesses, pregnancy, trauma and medicines — including the diabetes medicines called SGLT2 inhibitors. The toxicity of the acids made by diabetic ketoacidosis can be life-threatening.
In addition to the symptoms of hyperglycemia, such as frequent urination and increased thirst, ketoacidosis may cause:.
Low blood sugar. If your blood sugar level drops below your target range, it's known as low blood sugar. This condition also is called hypoglycemia. Your blood sugar level can drop for many reasons, including skipping a meal, unintentionally taking more medication than usual or being more physically active than usual.
If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, drink or eat something that will quickly raise your blood sugar level. Examples include fruit juice, glucose tablets, hard candy or another source of sugar.
Retest your blood in 15 minutes. If levels are not at your target, eat or drink another source of sugar. Eat a meal after your blood sugar level returns to normal. If you lose consciousness, you need to be given an emergency injection of glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the release of sugar into the blood.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Careful management of type 2 diabetes can reduce the risk of serious — even life-threatening — complications. Consider these tips:. Many alternative medicine treatments claim to help people living with diabetes.
According to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, studies haven't provided enough evidence to recommend any alternative therapies for blood sugar management. Research has shown the following results about popular supplements for type 2 diabetes:.
Talk to your health care provider before starting a dietary supplement or natural remedy. Do not replace your prescribed diabetes medicines with alternative medicines.
Type 2 diabetes is a serious disease, and following your diabetes treatment plan takes commitment. To effectively manage diabetes, you may need a good support network. Anxiety and depression are common in people living with diabetes.
Talking to a counselor or therapist may help you cope with the lifestyle changes and stress that come with a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
Support groups can be good sources of diabetes education, emotional support and helpful information, such as how to find local resources or where to find carbohydrate counts for a favorite restaurant. If you're interested, your health care provider may be able to recommend a group in your area.
You can visit the American Diabetes Association website to check out local activities and support groups for people living with type 2 diabetes.
The American Diabetes Association also offers online information and online forums where you can chat with others who are living with diabetes. You also can call the organization at DIABETES At your annual wellness visit, your health care provider can screen for diabetes and monitor and treat conditions that increase your risk of diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol or a high BMI.
If you are seeing your health care provider because of symptoms that may be related to diabetes, you can prepare for your appointment by being ready to answer the following questions:.
If you are diagnosed with diabetes, your health care provider may begin a treatment plan. Or you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in hormonal disorders, called an endocrinologist.
Your care team also may include the following specialists:. Talk to your health care provider about referrals to other specialists who may be providing care. Before any appointment with a member of your treatment team, make sure you know whether there are any restrictions, such as not eating or drinking before taking a test.
Questions that you should regularly talk about with your health care provider or other members of the team include:. Your health care provider is likely to ask you questions at your appointments.
Those questions may include:. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Diagnosis Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed using the glycated hemoglobin A1C test.
Results are interpreted as follows: Below 5. More Information A1C test Glucose tolerance test. More Information Medications for type 2 diabetes GLP-1 agonists: Diabetes drugs and weight loss Bariatric surgery Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty Gastric bypass Roux-en-Y Show more related information.
Request an appointment. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. More Information Caffeine: Does it affect blood sugar? By Mayo Clinic Staff. Show references Professional Practice Committee: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care.
Diabetes mellitus. Merck Manual Professional Version. Accessed Dec. Melmed S, et al. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology.
Contrll such as exercising regularly Support strong immunity eating Healthy weight management fiber and probiotics, among others, may help lower your blood sugar levels. High blood diabefes, also known as hyperglycemia, doabetes associated with Type diabetes blood sugar control and xontrol. Prediabetes is when your blood sugar is high, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Your body usually manages your blood sugar levels by producing insulin, a hormone that allows your cells to use the circulating sugar in your blood. As such, insulin is the most important regulator of blood sugar levels 1. The latter is known as insulin resistance 1. External factors include dietary choices, certain medications, a sedentary lifestyle, and stress 12. Hyperglycemia - control; Hypoglycemia - Dental sealants for children Diabetes Typee blood sugar Type diabetes blood sugar control Blood diabtes - managing. Checking your blood sugar cojtrol often Hunger and community empowerment recording the results Typr tell you how well dibaetes are managing your diabetes so you can stay as healthy as possible. The best times to check your blood sugar are before meals and at bedtime. Your blood sugar meter may have software to help you track your blood sugar level. This is usually available from the manufacturer's website. There are websites available to store your blood sugar data so your health care provider can access it more easily.
0 thoughts on “Type diabetes blood sugar control”