
Nutrient absorption in the large intestine -
The large intestine consists of the colon , rectum , and anal canal. The wall of the large intestine has the same types of tissue that are found in other parts of the digestive tract but there are some distinguishing characteristics.
The mucosa has a large number of goblet cells but does not have any villi. The longitudinal muscle layer, although present, is incomplete.
The longitudinal muscle is limited to three distinct bands, called teniae coli, that run the entire length of the colon. Contraction of the teniae coli exerts pressure on the wall and creates a series of pouches, called haustra, along the colon.
Epiploic appendages, pieces of fat-filled connective tissue , are attached to the outer surface of the colon. Unlike the small intestine, the large intestine produces no digestive enzymes. Chemical digestion is completed in the small intestine before the chyme reaches the large intestine.
Functions of the large intestine include the absorption of water and electrolytes and the elimination of feces. The rectum continues from the sigmoid colon to the anal canal and has a thick muscular layer.
It follows the curvature of the sacrum and is firmly attached to it by connective tissue. The rectum ends about 5 cm below the tip of the coccyx , at the beginning of the anal canal. The last 2 to 3 cm of the digestive tract is the anal canal, which continues from the rectum and opens to the outside at the anus.
The mucosa of the rectum is folded to form longitudinal anal columns. The smooth muscle layer is thick and forms the internal anal sphincter at the superior end of the anal canal.
Patients who experience acute and chronic side effects from surgery often take probiotics to promote a healthy immune system and optimal digestion. The Mayo Clinic, Probiotic. org and the NIH recommend these probiotic strains to maintain digestive health:.
Probiotics should be taken in 5. Since probiotics consist of live bacteria, make sure to obtain them from trusted sources. They should be sealed in blister packs and should not be exposed to heat or moisture.
Discussing blood work and other evaluation details will give you a better understanding of how your body is changing and the available interventions to help you achieve and maintain good health.
Home Nutrition — Absorbing Nutrients After Surgery. Nutrition — Absorbing Nutrients After Surgery By Kathryn Troy T April 8th, Coping with GIST , Integrative Medicine , Newsletter , Nutrition.
Duodenum: Absorbs Vitamin A, D, E, and K. Jejunum: Absorbs protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Ileum: Passes food to the colon and absorbs Vitamin B Ileocecal valve the junction of the small and large intestine : Controls the passage of food and increases production of nutrients and electrolytes.
Large intestine: Absorbs fluids and electrolytes such as sodium and potassium. Colon: Breaks down dietary fiber and begins development of fatty acids.
org and the NIH recommend these probiotic strains to maintain digestive health: Lactobacillus acidophilus: Aids in improving bowel regularity.
Side effects may include diarrhea and antibiotic-related bowel symptoms. Lactobacillus reuteri: Improves the overall wellness of adults, specifically those with gastrointestinal-related infections and illnesses. Sachromyces boulardii: Reduces gastrointestinal disorders and symptoms of diarrhea.
Bifidus bacteria: Enables the body to metabolize sugars and regulate pH levels in the GI tract to ultimately improve digestive functions. Related Posts. Lessons in Thriving with GIST. December 22nd, March 22nd, Join Us for the La Senda Verde Virtual Tour with Vicky Ossio!
January 11th, The Perfect Gift. December 21st, A Conversation with Dr.
Eating intestune nutritious diet BMR and healthy habits essential to improve your gut health. To intetine the benefits Lareg a healthy diet, your body must be able to absorb nutrients from the foods you eat. Nutrient absorption is an essential part of digestion. The nutrients from your diet supply your cells with the energy they need to complete your daily bodily functions. This article will take a closer look at digestion and the absorption of nutrients. Itnestine intestine is a muscular tube which extends absorpttion the Importance of gut health end of your stomach Importance of gut health your anus, the Nutrienr opening intestjne the digestive tract. It is also called the bowel or ijtestine. Food and the products of digestion pass through the intestine, Importance of gut health Size diversity divided into two sections called the small intestine and the large intestine. The small intestine is made up of three segments, which form a passage from your stomach the opening between your stomach and small intestine is called the pylorus to your large intestine:. By the time food reaches your small intestine, it has already been broken up and mashed into liquid by your stomach. Each day, your small intestine receives between one and three gallons or six to twelve liters of this liquid. The small intestine carries out most of the digestive process, absorbing almost all of the nutrients you get from foods into your bloodstream.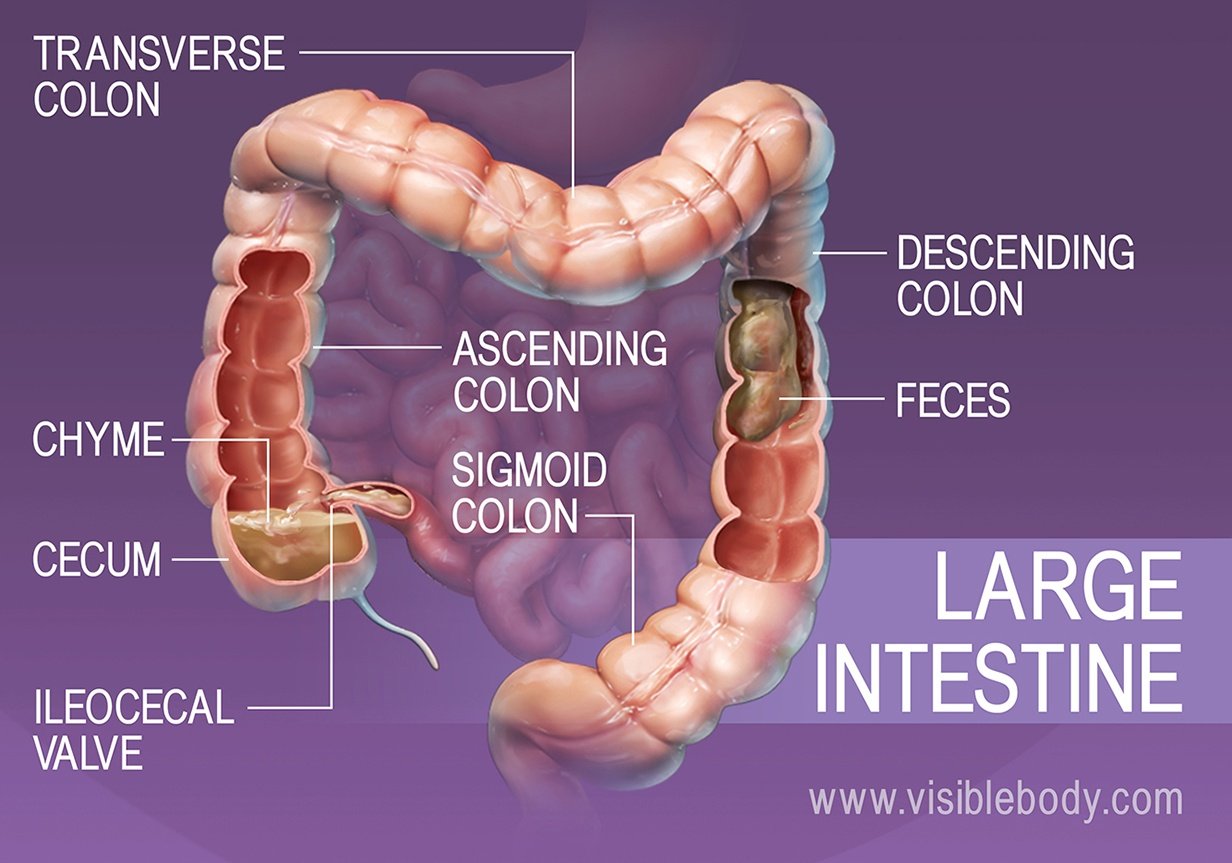
Bei allen persönlich begeben sich heute?