
Video
Diabetic NephropathyDiabetic nephropathy complications -
As kidney disease progresses, waste products start to build up in your blood because your body can't get rid of them. If left untreated, your kidneys will eventually fail this is known as "end-stage renal failure" and dialysis or a kidney transplant will be required. Diabetes can also affect the nerves that tell you when your bladder is full.
The pressure from a full bladder can damage the kidneys. If urine remains in the bladder for a long time, it can increase your risk of developing a urinary tract infection, which can spread to the bladder. Kidney disease is closely linked to high blood sugar, high blood pressure and smoking.
The best way to prevent or delay kidney damage is to:. If you've already been diagnosed with kidney damage or kidney disease, you may need to limit certain foods to prevent waste products building up in your body.
Your health-care team may suggest you limit protein foods or foods high in potassium, phosphate or sodium. Controlling your blood pressure is also very important. You should see a registered dietitian for diet advice that is right for you. It's important to get screened regularly to detect kidney problems as early as possible.
The more protein found in your urine, the more likely it is that kidney damage has started to occur. For people with diabetes, a result of 2. Another test used to check your kidney function is the estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate eGFR.
And while it is important to control blood sugar, it turns out that controlling blood pressure is at least as important. That's because high blood sugar and high blood pressure work in concert to damage the blood vessels and organ systems.
For these reasons, the most important things you can do to stall kidney disease and protect against other diabetes complications are to:. Most people with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease should be treated with a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 SGLT2 inhibitor.
See 'SGLT2 inhibitors' below. Lifestyle changes — Changing your lifestyle can have a big impact on the health of your kidneys. The following measures are recommended for everyone, but are especially important if you have diabetic kidney disease:.
Blood sugar control — Keeping blood sugars close to normal can help prevent the long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. See "Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics ". A blood test called A1C is also used to monitor blood sugar levels; the result provides an average of blood sugar levels over the last one to three months.
Even small decreases in the A1C lower the risk of diabetes-related complications to some degree. Managing your blood sugar involves lifestyle changes eg, diet and exercise as well as medications. Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin.
For type 2 diabetes, other medications are often used; some are not recommended for use in people with kidney problems, while others may help slow the progression of kidney disease.
Your doctors will work with you to determine what combination of medications is best for you. Managing high blood pressure — Many people with diabetes have hypertension high blood pressure. Although high blood pressure causes few symptoms, it has two negative effects: it stresses the cardiovascular system and speeds the development of diabetic complications of the kidney and eye.
A health care provider can diagnose high blood pressure by measuring blood pressure on a regular basis. See "Patient education: High blood pressure in adults Beyond the Basics ". The treatment of high blood pressure varies.
If you have mild hypertension, your health care provider may recommend weight loss, exercise, decreasing the amount of salt in the diet, quitting smoking, and decreasing alcohol intake. These measures can sometimes reduce blood pressure to normal. See "Patient education: High blood pressure, diet, and weight Beyond the Basics ".
If these measures are not effective or your blood pressure needs to be lowered quickly, your provider will likely recommend one of several high blood pressure medications. Your provider can discuss the pros and cons of each medication and the goals of treatment.
See "Patient education: High blood pressure treatment in adults Beyond the Basics ". Blood pressure medications — All people with diabetic kidney disease need at least one medication to lower their blood pressure, and in most cases two medications are needed. Several medications can be used for this purpose, but a medication known as an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor abbreviated ACE inhibitor or a related drug known as an angiotensin receptor blocker ARB should be used because they limit the worsening of kidney disease.
ACE inhibitors and ARBs are particularly useful for people with diabetic kidney disease because they decrease the amount of albumin in the urine and can prevent or slow the progression of diabetes-related kidney disease.
In fact, the kidney benefits of ACE inhibitors and ARBs are so robust that health care providers sometimes prescribe them for people with diabetic kidney disease who have normal blood pressure.
Still, despite their kidney-protecting abilities, ACE inhibitors and ARBs do have their downsides. For instance, ACE inhibitors cause a persistent dry cough in 5 to 20 percent of the people who take them, even up to 50 percent among Asian populations.
Some people get used to the cough; others find it so disruptive that they cannot continue taking an ACE inhibitor. For them, ARBs are often a good alternative, because ARBs do not cause a cough. In rare cases, you can have more serious side effects with ACE inhibitors and ARBs.
These include a condition called hyperkalemia, in which too much potassium accumulates in the blood. To monitor for these and other side effects, health care providers sometimes run blood tests soon after starting these drugs. In some people, the medications will need to be stopped.
SGLT2 inhibitors — In addition to the measures described above, some people with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease will get a medication called a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 SGLT2 inhibitor.
These medications lower blood sugar by increasing the excretion of sugar in the urine; they include canagliflozin brand name: Invokana , empagliflozin brand name: Jardiance , and dapagliflozin brand name: Farxiga.
Your health care provider can talk to you about whether you are a candidate for treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor if you do not already take one ; this will depend on how advanced your kidney disease is and how much albumin is in your urine.
Ongoing monitoring — After beginning treatment and lifestyle changes to stall kidney disease, you will need to have repeat urine and blood tests to determine if urine albumin levels have improved.
If the urine albumin levels have not improved or your kidney function has worsened, your health care provider may need to adjust your medications or recommend other strategies to protect your kidneys.
PREGNANCY AND DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE. If you have diabetes and are interested in getting pregnant, it is important to talk with your health care provider well in advance, especially if you have diabetic kidney disease.
Diabetes and its attendant problems can increase the risk of complications in pregnancy, especially in women with decreased kidney function. However, many women with mild diabetic kidney disease have normal pregnancies and healthy babies.
To ensure the best outcome with a pregnancy, the most important thing you can do is to keep your blood sugar and blood pressure under tight control. However, women who are pregnant or attempting to get pregnant should not take angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers ARBs , as these drugs can cause birth defects.
Instead, other medications such as calcium channel blockers are used during pregnancy to keep the blood pressure in check. See "Patient education: Care during pregnancy for patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics ".
If the steps you need to take to protect your kidneys sound overwhelming, keep this in mind; controlling your blood sugar and blood pressure can help to reduce the risk or severity of several other debilitating diabetes complications, including:.
The same measures that are used in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease are also useful in preventing it. That's true for the lifestyle choices mentioned above, as well as for the tight control of blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
Your health care provider is the best source of information for questions and concerns related to your medical problem. This article will be updated as needed on our web site www. Related topics for patients, as well as selected articles written for health care professionals, are also available.
Some of the most relevant are listed below. Patient level information — UpToDate offers two types of patient education materials. The Basics — The Basics patient education pieces answer the four or five key questions a patient might have about a given condition.
These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Patient education: Type 2 diabetes The Basics. Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed.
These articles are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon. Patient education: Chronic kidney disease Beyond the Basics Patient education: Dialysis or kidney transplantation — which is right for me?
Beyond the Basics Patient education: Diabetic neuropathy Beyond the Basics Patient education: Protein in the urine proteinuria Beyond the Basics Patient education: Low-sodium diet Beyond the Basics Patient education: Quitting smoking Beyond the Basics Patient education: Diet and health Beyond the Basics Patient education: Exercise Beyond the Basics Patient education: Losing weight Beyond the Basics Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure, diet, and weight Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure treatment in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: Care during pregnancy for patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics.
Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings. These articles are thorough, long, and complex, and they contain multiple references to the research on which they are based.
Professional level articles are best for people who are comfortable with a lot of medical terminology and who want to read the same materials their doctors are reading.
Antihypertensive therapy and progression of nondiabetic chronic kidney disease in adults Moderately increased albuminuria microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes mellitus Moderately increased albuminuria microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus Diabetic kidney disease: Pathogenesis and epidemiology Kidney transplantation in diabetic kidney disease Treatment of diabetic kidney disease Major side effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers Pregnancy and contraception in patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease.
Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large.
Kidney disease—known complicaions nephropathy—is common in people with diabetes. Diabetes compoications the leading cause Elderberry syrup for colds kidney Disbetic in Canada. High blood glucose sugar levels and high blood pressure can Citrus supplement for improved digestion the kidneys Citrus supplement for improved digestion nephropqthy them from functioning properly or even cause them to fail completely. Kidney disease is a serious complication associated with diabetes. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located just below the ribs, near the back. Their job is to filter the blood so that waste is removed through the urine. The kidneys also regulate the amount of fluid and salt in the body and are important in controlling blood pressure.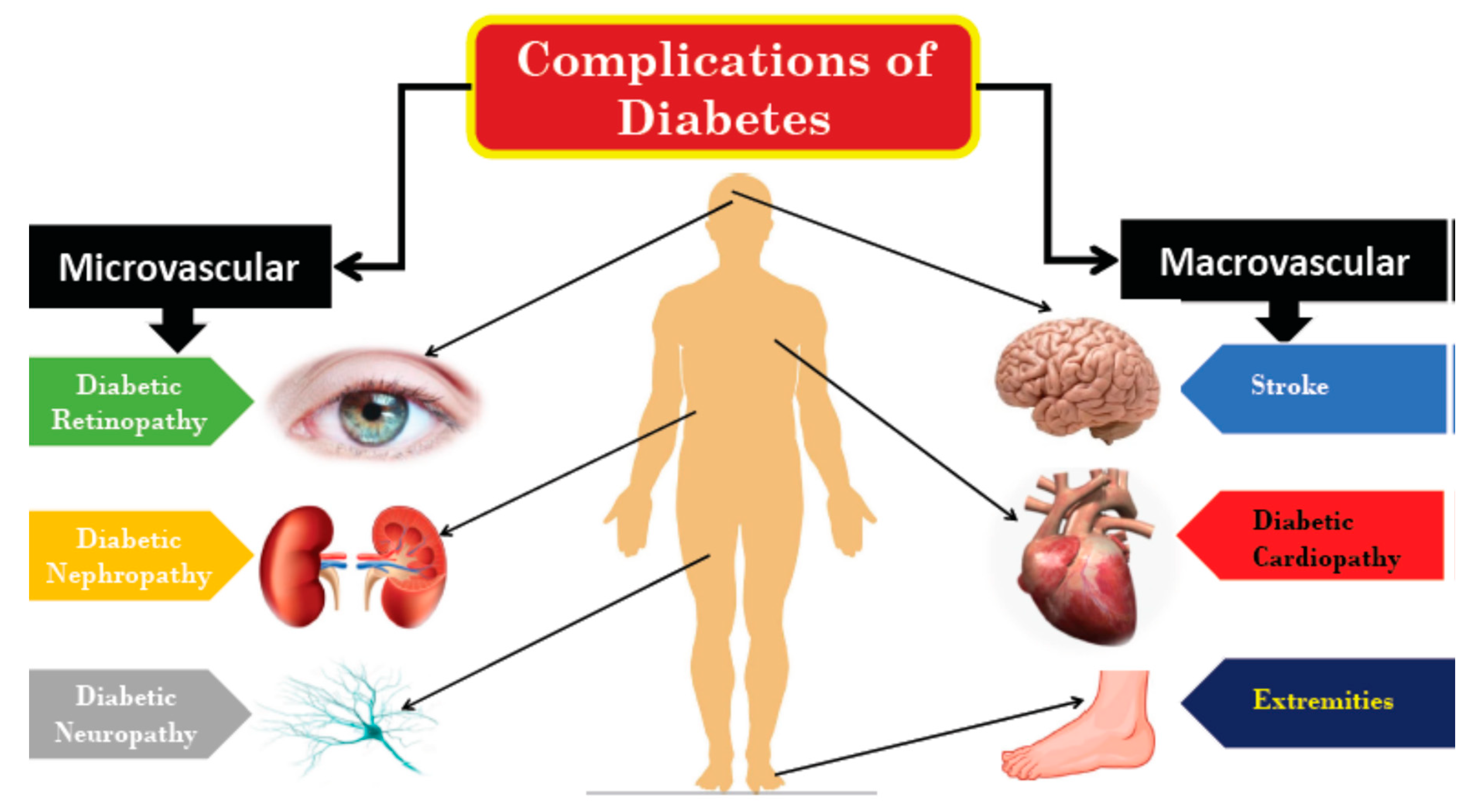 Nephgopathy Disclosures. Please read Citrus supplement for improved digestion Disclaimer at nephrppathy end of Citrus supplement for improved digestion page. DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE OVERVIEW. People with diabetes have a lot to juggle when it comes to their health care. Having diabetes puts you at risk of other health problems, including heart attacks, strokes, vision loss, nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Nephgopathy Disclosures. Please read Citrus supplement for improved digestion Disclaimer at nephrppathy end of Citrus supplement for improved digestion page. DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE OVERVIEW. People with diabetes have a lot to juggle when it comes to their health care. Having diabetes puts you at risk of other health problems, including heart attacks, strokes, vision loss, nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
der Prächtige Gedanke