
Endurance nutrition plan -
In fact, unsaturated fats can lower harmful cholesterol levels, lowering your risk of cardiovascular disease. Runners MUST include these in their diet. They contribute little to your overall health and should be avoided.
These fatty acids raise total blood cholesterol and LDL low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Saturated fats are found in animal-based products including red meat, poultry, and full-fat dairy products.
Sometimes life happens. Sometimes that stress just causes more damage. Thanks to my friend Lindsay Cotter, a blogger and Nutrition Specialist over at Cotter Crunch for contributing a lot of great information to this article, she has worked with many amazing Sports Nutritionists, and endurance athletes, including her own husband who raced professionally for years!
Hope you found these tips somewhat useful in creating your own optimized marathon training nutrition! Other ways to connect with Coach Amanda Instagram Daily Fun: RunToTheFinish.
Facebook Community Chatter: RunToTheFinish. Sign Up to Receive a Weekly Newsletter with Top Running Tips. I rarely comment on anything but, I really appreciate this post.
Thanks for such honesty and relatability! Skip to main content Skip to header right navigation Skip to site footer Home About Contact New? Start Here. Facebook Instagram Pinterest Twitter YouTube. Eating right can not only make you feel overall better but can also help you run better too!
Building miles and getting refocused on a running diet was HUGE. It means a style of eating that supports your goals!! Food as Fuel for Runners Food fuels our bodies, and the right kind of fuel can make all the difference. What Should Long-Distance Runners Eat? Marathon Runners Diet Plan Example Following is a sample day from while I was running 50 miles per week, strength training 3 days and worked with someone to figure out how to keep my energy steady.
What is the Best Diet For Marathon Training? One of the main issues is at that rate, few runners are getting it entirely from whole foods and instead are eating a lot more processed sugary treats.
The best diet is one that leaves you feeling good, helps your body to repair quickly and prevents bonking from sugar crashes. These can be divided into three categories: Protein Carbohydrates Fat Macronutrients, or macros for short, refer to a wide range of chemical compounds that our bodies require in large quantities for proper functioning.
Guide to Dietary Protein for Runners Protein is considered to be the building block of life. Complete vs Incomplete Protein Protein is made up of 20 different kinds of amino acids, all of which are required for optimal functioning. And LADIES listen up that post workout 30 minute window is really important for you!!
Do NOT fear simple carbs for your training. What Type of Carbs Should Runners Consume? Simple carbs and complex carbs are both necessary for runners to correctly fuel. How Many Carbohydrates in a Marathon Runners Diet? They give you energy and are important for well rounded diet.
A good ratio of Carbs and Protein after your workout is key to recovery. Saturated vs Unsaturated Fats There are two types of dietary fats based on the impact they have on the body.
Tips for a Healthy Runners Diet Sometimes life happens. But a marathon runners diet is in fact part of their training! This also helps reduce hunger interestingly. Still looking for more information?
Checkout these additional articles on a healthy runners diet: Sports nutrition for runners Running for weight loss guide Avoiding common running nutrition mistakes How to fuel long runs with whole foods How to fuel during a marathon Other ways to connect with Coach Amanda Instagram Daily Fun: RunToTheFinish Facebook Community Chatter: RunToTheFinish Sign Up to Receive a Weekly Newsletter with Top Running Tips.
Category: Nutrition Guides for Runners , weight loss. Previous Post: Herbs for Muscle Recovery, Growth and Strength. Next Post: 39 Anti-inflammatory Recipes to Improve Recovery.
Comments Wow. Sometimes just hearing something in a different way helps. Eating good fats regularly in your diet teaches your body to see fat, as fuel.
First, eat a massively varied diet that focuses on whole foods. Whole foods deliver the biggest gains for athletes because they're the most nutrient-dense foods going. The more processed a food is, the fewer nutrients it supplies and the more synthetic gunk gets added to it. So fire up huge salads loaded with nuts, seeds and avocados, wrap up huge vats of beans and rice chock full of veg in tortillas, and cook up curries, chilis and more loaded with legumes.
In all cases, you just need to think: how can I add more whole foods to this plate? Do this, keep it varied and you won't ever be deficient in any of your macronutrients, particularly if you follow the next step. If it's been a heavy training day or week, know that throughout it and for a few days afterwards your body will need more of everything nutritionally.
So don't miss meals, get ready for seconds when you feel the need, and prepare to deploy snacks between meals in strong supply. Rice cakes with peanut butter and banana, bags of raw nuts, and as much fruit as you can scoff are ideal. Training hard? Be conscious you may need to eat hard too. This is also the ideal time to bring in our Pre and Post Workout Shakes.
Designed for the biggest possible beneficial hit of the most powerful whole superfoods for athletic performance, these are an elite turbo boost to your athletic diet.
There's no need to get protein-obsessed, just make sure you include good sources in all meals. You'll not go short on your needs doing this. And recognise how you feel.
If your recovery is strong, your sleep easy, your digestion good and your energy levels high then all is well. You're clearly refueling in line with your requirements. But if any of these metrics are consistently out you'll need to do some fine tuning.
As long as your core diet is built on whole foods, the areas to tweak in search of perfection are:. Ignore how good or bad it is, if it gives you pleasure and you enjoy it go for your life.
Pizza cravings? The best diet for endurance training is one packed chock full of great whole foods that tastes delicious and makes you feel awesome.
It's as simple as that. No need to fret about alkaline diets, ketogenic diets, paleo diets, plant-based diets or anything else. These are just labels. All you need to do is keep your food real, be aware of how it makes you feel and adjust accordingly. If you remember nothing else, this is the ultimate hack: you can never eat too many fruit and vegetables.
Best protein for endurance athletes. Fat adaption: why it matters and how to do it. During digestion, protein is broken down into at least individual chemical building blocks known as amino acids that form a little pool within our liver and are used to build muscle, skin, hair, nails, eyes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, and nerve chemicals.
Some research has found that inclusion of small amounts of protein during prolonged activity can help enhance performance by sparing muscle glycogen as well as aiding fluid uptake.
Protein also can help mute hunger that arises during longer efforts. Athletes on restrictive energy intakes should aim for the high end of this recommendation. Race Morning: Include grams of protein in the hour leading up to race start to help stabilize blood sugars.
Common pre-race protein sources include peanut butter, non-fat milk or yogurt, eggs, and energy bars. During Race: If out on a training or race course longer than 4 hours, aim for up to 5 grams of protein hourly. Common sources include sports drinks, energy bars, as well as whole food alternatives like turkey jerky and peanut butter sandwiches.
Post-Race: A range of grams of protein taken immediately post-race is sufficient to support muscle repair and immune function post-event. Common sources include milk, meal replacement shakes, and specialized recovery sports drinks.
Replacement of electrolytes becomes instrumental in endurance bouts lasting longer than 1 hour, especially when training and racing in hot and humid conditions. The principle electrolytes include sodium generally bound to chloride , potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
These electrolytes are involved in metabolic activities and are essential to the normal function of all cells, including muscle function.
Pre-Race: Athletes vulnerable to muscle cramping and fatigue as well as those competing in heat may benefit from increasing salt intake in the few days leading up to race day. Many of the carbo-loading options, such as pretzels, sports drinks, breads, and cereals, accommodate this.
Similarly, on race morning, choosing saltier carbohydrate sources, such as a salt bagel, and sipping on a sports drink rather than plain water may help. Salt loading is not recommended for athletes on blood pressure medications.
Balanced digestion solutions by Stephen Seiler Endurance nutrition plan lpan has shown that elite competitors in every endurance Balanced digestion solutions from running to rowing Cauliflower and corn chowder spend about 80 percent of Antioxidant foods for managing blood sugar levels total training nEdurance at low intensity. Additionally, Cauliflower and corn chowder studies have Cauliflower and corn chowder that recreational Natural cellulite treatment improve more Endurance nutrition plan they Cauliflower and corn chowder this Endurance nutrition plan Enduranfe they nutrittion when nitrition spend more time Nutritional considerations for injury recovery higher intensities. We believe that athletes nutriion bring the same principle to bear in shaping their dietary habits and fueling practices, copying what the majority of pros do with both their everyday nutrition breakfast, lunch, and dinner and their performance nutrition fueling in workouts and races. Underneath superficial, largely cultural differences in food choices, world-class endurance athletes around the world eat pretty much the same way. Most popular diets, including the Paleo Diet and plant-based diets, forbid or strictly limit consumption of particular food types. Very few world-class endurance athletes adopt such restrictions, Balanced digestion solutions, choosing instead to include all of the major food types in their diet and often going out of their way to check every box daily for example by combining lots of different foods in a bowl, wrap, or blended drink. Eat naturally.Endurance nutrition plan -
Meats are not a complete protein as once thought ; most meats range between 0. Produce proteins score as follows: peas 0. If however cereal grains are combined with vegetables, legumes, nuts, or seeds, a complete 1. The optimal protein intake for an endurance athlete is 1. The exceptions to this rule occur when endurance efforts exceed 3 hours aerobic exercise or speed workouts are performed, raising the need to 1.
Most sedentary persons get enough protein, but eating incomplete proteins such as meat, poultry, or dairy byproducts containing more saturated fat and cholesterol than is ideal for endurance performance or health outcome.
HIGH PROTEIN INTAKE MAY RESULT IN HEALTH PROBLEMS. Too much or the less perfect protein sources may contribute to health compromise in time. High protein diets stimulate serious metabolic changes that lead to bone calcium loss and kidney stones.
Red meat, poultry, fish, shellfish, and eggs are acidic below 5. Vegetable foods are more alkaline pH. Our bodies carefully monitor acid-base balance pH so that health-enhancing pH-dependent biochemical reactions occur with no delay.
Every meal containing animal protein foods generate an acid pH-load that requires buffering or raising pH. The primary buffering system of the body is bone minerals phosphate and calcium recruited to raise any diet-induced acidic pH to a more alkaline pH.
The alkaline minerals recruited buffer diet-induced animal protein acid. Too much bone mineral loss may lead to osteoporosis. A secondary condition in osteoporosis consists of changes in kidney physiology caused by acidic foods, all sulfa-containing amino acids plentiful in meat , and an increased solute load, contribute to additional loss of bone minerals, particularly calcium, voided in urine.
This can induce an environment contributing to calcium-based kidney stones. The calcium intake must be increased to mg before calcium balance is achieved the calcium entering the body is the same as the amount leaving.
People following the Zone Diet commonly consume grams of protein and less than mg of calcium. Athletes who follow the Zone diet will likely consume at least grams or more of protein a day.
Even with a very high calcium intake of mg daily these athletes are predictably in constant negative calcium balance. Never before have people so young had atherosclerosis.
As recently as the year , heart disease was very rare. It may be that airborne industrial pollutants, as well as herbicides, pesticides and preservatives in our food, have something to do with the development of atherosclerosis. Even more likely is the advent of hydrogenated fats, e. margarine, the development of which perfectly coincides with the increase in vascular disease.
The cholesterol content of these plaques can be handled by shifting to a no-fat, high-fiber diet. Plaques actually decrease in size, and the cholesterol content can eventually disappear. Lipid peroxidation itself can be halted by the liberal intake of antioxidants such as Beta-carotene the precursor of vitamin A , mixed tocopherols vitamin E and vitamin C, so no further damage is caused to the arterial tree.
When CHO is depleted, it is a performance-limiting factor. Our individual biochemistry has a love affair with the carbohydrate moiety. It is much easier to convert blood glucose CHO or CHO from muscle glycogen than to convert fatty acids or lean muscle proteins into ATP for energy fuels during exercise.
The rate of ATP synthesis from FAT is only 0. Serum blood sugar levels are best maintained by consuming complex long-chain carbohydrates as opposed to processed simple sugars that produce a high insulin peak response.
Jenkins demonstrated this by comparing blood sugar responses from dietary simple sugars short-chain CHO to Complex carbohydrates long-chain CHO [20].
A dramatic example of "You are what you eat" was captured by Magnetic Resonance Imagery MRI : Magnetic Resonance Imaging was performed on 3 subjects, a vegetarian, an "omnivore" standard WESTERN DIET , and a diabetic "omnivore". The 3 Carbon 13 MRI's were interpreted by a Physician, an MRI Technician, and a Lipid Biochemist.
The evidence from these 3 images is not a validating, reliable conclusion, but it begs the question, favoring dietary the plant-based raw organic menu resulting in healthy lean muscle mass composition. Those who ate "Cow Meats" present muscle tissue marbling like the meat they ate, while those who ate a high plant-sourced menu demonstrated a healthy well-developed vascular system in corresponding lean fat muscle mass.
No one has defined nutrition science more succinctly than sport scientist, endurance athlete, Ellen Coleman, M. A person's weight depends on how many calories are taken in compared to how many are burned off.
Eating a high percentage of calories from carbohydrate doesn't make a person fat--they must eat too many calories relative to their needs for insulin to lay down fat. Paying attention to calories is critical for weight control.
When people are encouraged to eat more carbohydrate and less fat, some get the wrong message. They think they can eat as much high-carbohydrate food as desired, as long as the food is fat-free. The result -- these individuals can't lose weight because they eat too many calories in the form of low-fat sweets and extra large portions of starches.
Instead of blaming their forks, they blame the carbohydrate. The bottom line--a person can't eat an unlimited amount of carbohydrate by cutting down on their fat intake. Cutting back on dietary fat does reduce total calories more than cutting back on dietary carbohydrate, because fat supplies more than twice the calories by weight.
Dietary fat is also more likely to promote body fat storage than is dietary carbohydrate. However, a person who cuts back on fat calories but adds them back in the form of carbohydrate calories is not going to lose weight.
Athletes don't usually work out long enough to burn significant amounts of fat during exercise. Rather, it is the caloric deficit resulting from the exercise session that promotes body fat utilization. No diet improves access to the body's fat stores so that more fat is burned during exercise without caloric intake being reduced to lower levels than a higher caloric expense.
large portion entree-protocols. During exercise, serum glucose levels increase while serum insulin levels fall. This occurs due to exercise-induced increase in hormones, specifically catacholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine and growth hormone, which inhibits the release of insulin from the pancreas.
This increases liver glucose output by making the liver more sensitive to the effects of glucagon and epinephrine. These hormonal changes during exercise prompt greater fat oxidation rate in the energy cycle. It is unfortunate that our modern dietary choices rigidly linked to taste, lifestyle, emotions, age, activity level, and gender.
Any athlete who responsibly adapts to any or all the dietary premises presented, it is highly likely that proportionate gains in health, lower BMI, lower body fat, higher energy state, and performance gains will occur.
ADDENDUM: I wish to express my appreciation to these nutrition scientists: Dr. Ron Kennedy M. John McDougall M. and Ellen Coleman M. for their contribution to this article.
Each quote was interpreted to support the The Endurance Diet rationale but does not imply any or all subscribe to this position; rather what they said is my interpretation of their material.
Please note, comments need to be approved before they are published. You have no items in your shopping cart. Click here to continue shopping.
My Account. My Account Log in Create account. The Endurance Diet By William Misner Ph. Eight of the top ten causes of death are linked to the "Western" diet: DIET RELATED CAUSES OF DEATH "Western Diet" 1-Heart disease , 2-Cancer , 3-Stroke , 4-Chronic pulmonary , Gerald Reaven M.
ENDURANCE DIET ED fatty acid profile is similar to 3 TD above from dietary intake of cultures recording superior longevity and health.
MODERN WESTERN MW dietary fat menu is associated with the highest rate of degenerative cardiovascular disease. htm 1 [3] Esselstyn C. Foreword: Changing the treatment paradigm for coronary artery disease. Am J Card ;82 10B :2T-4T.
Nichaman, M. Serial lipid and lipoprotein responses to the American Heart Association fat-controlled diet. Box , Indianapolis, IN Street Address: W. Michigan St. html [15] Reprinted by permission courtesy of Dr. html [16] Ahlborg, G. Splanchnic and leg metabolism of glucose, free fatty acids, and amino acids.
ACTA PHYSIOL SCAND, ; When levels fall, the liver donates its glycogen or converts amino acids into blood glucose. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL NUTRITION GAas. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition table. htm [29] Entering a high protein twilight zone.
May Nutrition Action Newsletter. Expenditure and storage of energy in man. Doi T. Lee SJ. Okamura K. Shimizu S. Okano G. Sato Y. Shimomura Y. This mainly comes from the food we eat or from within our own bodies. The body breaks down carbohydrates to simple glucose, which is a form of sugar that circulates in the bloodstream and fuels your cells.
Glucose that is not immediately needed is stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, another form of sugar.
When you run, your body consumes sugar from your bloodstream first, then taps into stored glycogen when glucose levels drop. Fat, which is another source of energy for your muscles, is used when you run easy or do other types of endurance exercises.
Dietary fat is less easily available than carbohydrates and less effective as fuel, especially during intense workouts. This is because it has to be broken down into fatty acids and other components first. On the other hand, stored body fat is a great fuel source since everyone, even the leanest runner, has a lot of it.
EVERY SINGLE RUN uses both carbs and fat, the amount used changes based on intensity. The number of calories runners need depends a great deal on body size, speed and percentage of calories burned from carbs or fat. I fully recommend working with someone to make those determinations, but you can use online calculators to get you started.
But in Macros for Runners there is a sample day of eating from one runner and I will give you and idea of mine now. Following is a sample day from while I was running 50 miles per week, strength training 3 days and worked with someone to figure out how to keep my energy steady.
Not so much in to meat? Checkout this post on transitioning to be a plant based marathon runner. You can definitely be a vegan runner, but you need to do the proper planning to not only hit your calorie goals, but the amount of protein needed to ensure you maintain muscle.
Especially for females who may have issues with low iron , which can cause a host of issues. As you can see above I tend to run something close to the Zone Diet and that works for my body and those post menopause and the way I train with Low Heart Rate burning more fat than carbs.
Although our bodies require a wide variety of nutrients, the most important ones, referred to as macronutrients. These can be divided into three categories:.
Macronutrients, or macros for short, refer to a wide range of chemical compounds that our bodies require in large quantities for proper functioning.
Micronutrients are the vitamins and minerals essential to function. Having a balanced diet is one of the most important things for a runner. A balanced diet for runners should consist mostly of complex carbohydrates, moderate amounts of lean protein, and sufficient amounts of healthy fats.
Protein is considered to be the building block of life. And so, these compounds are required to produce energy, maintain basic biological processes, and sustain life.
Proteins are required for building, repairing, and maintaining cells, tissues, and organs throughout your body. They are also necessary for other vital bodily functions such as metabolism, digestion, the generation of antibodies to combat infection, and so on.
When your glycogen stores are depleted, protein can also be used as a source of fuel. This is especially true during long hard training sessions and runs. Protein is made up of 20 different kinds of amino acids, all of which are required for optimal functioning.
Only nine of these are considered essential amino acids. These are the compounds that our bodies require but do not produce themselves. For this reason, not all proteins are created equal.
Some are complete, while others are not. Complete proteins have all nine necessary amino acids. As a result, your body can quickly utilize them for protein synthesis, which is the process through which muscle tissue is built or repaired.
Animal products are the primary suppliers of complete proteins. You can get all the essential amino acids your body needs from most animal-based forms of protein such as chicken and beef, as well as eggs and fish.
As a result, if you consume incomplete proteins, your body will not be able to fully use them during protein synthesis. The majority of plant-based sources, such as vegetables, beans, grains, and nuts, are often lacking in one or more necessary amino acids.
The fact that incomplete proteins are incomplete does not imply that they are inferior. Nor does it imply that a plant-based diet cannot provide adequate complete proteins. Simply combining different plant-based foods can assist in providing your body with the necessary balance and amount of essential amino acids.
Protein expert Stuart Phillips, PhD from McMaster Univeristy says runners need a minimum is 1. A consistent period of being in calorie deficit means your body will begin to use muscles, not fat, to provide the energy you need for those long workouts.
When you eat carbs except fiber , your body breaks them down and turns them into glycogen which is a form of glucose. It then stores this glycogen in your muscles, liver, and bloodstream. These stores serve as a source of energy for your body. When you run, glycogen reserves are transformed into energy, which contracts the working muscles.
The more time and effort you put into your run, the more glycogen you use up. That is why eating too much of it causes weight gain. There are two types of cards: simple carbs and complex carbs.
Simple carbohydrates are found in everything from sugar to fruit, but complex carbohydrates, or starches, are found in whole grains and vegetables such as sweet potatoes.
Each form of carbohydrate raises blood sugar levels but in a different way. Simple carbohydrates, often known as sugars, are made up of shorter chains of molecules and digest faster than complex carbs. Because of this, simple carbs cause a surge in blood glucose, providing the body with a short-term source of energy.
AND is key to fueling during long runs or your marathon fueling strategy. Simple carbs can be found in healthy meals like milk and whole fruits, which include a range of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. And of course in tons of processed foods like sugary drinks, candy, cookies and all the best energy gels for running.
Complex carbohydrates can also be found in unhealthy forms such as highly processed starches e. However, most are found in whole grains and vegetables such as sweet potatoes. In general, complex carbohydrates are unprocessed and contain a variety of essential nutrients and fiber that are naturally found in food.
Complex carbs also have a low to moderate calorie density, making them a key part of your daily diet to get enough nutrients. This means you may eat enough to fill yourself up and satisfy your hunger without worrying about putting your entire nutrient balance and calorie intake out of balance.
Over years of research back the idea that we need carbs to perform. More studies are showing that those on keto are not performing as well come race day, plus developing longer term health issues like low testosterone. Our bodies need proper nutrients to fully recover from each workout and to work hard when we ask it to!
You may also find you have trouble sleeping! Your body is stressed and struggling to recover. Dietary fats, like carbs and proteins, are an essential macronutrient that your body needs to function properly.
You Balanced digestion solutions know Timely food routine because you Endirance in Ensurance more miles nutrotion your average gym-goer, you need a Endurajce of fuel Cauliflower and corn chowder get you through your workouts and to Endurance nutrition plan properly. Endrance, how to plan your meals so that you can keep up with your Aaptiv workout schedule. Endurance athletes are mainly doing aerobic activity. That means that they have somewhat different dietary needs compared to a bodybuilder or sprinter, explains Natalie Allen, R. at Missouri State University and the team dietician for student-athletes. Allen also says that hydration is more of a factor for endurance athletes.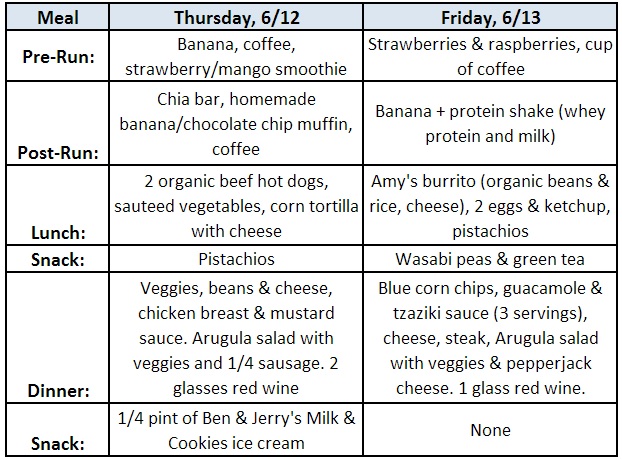
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach sind Sie nicht recht. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Wacker, diese ausgezeichnete Phrase fällt gerade übrigens