Hyperglycemia causes and triggers -
That's because hormones your body makes to fight illness or stress can also cause blood sugar to rise. You may need to take extra diabetes medication to keep blood glucose in your target range during illness or stress. Keeping blood sugar in a healthy range can help prevent many diabetes-related complications.
Long-term complications of hyperglycemia that isn't treated include:. If blood sugar rises very high or if high blood sugar levels are not treated, it can lead to two serious conditions. Diabetic ketoacidosis. This condition develops when you don't have enough insulin in your body.
When this happens, glucose can't enter your cells for energy. Your blood sugar level rises, and your body begins to break down fat for energy. When fat is broken down for energy in the body, it produces toxic acids called ketones.
Ketones accumulate in the blood and eventually spill into the urine. If it isn't treated, diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to a diabetic coma that can be life-threatening. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. This condition occurs when the body makes insulin, but the insulin doesn't work properly. If you develop this condition, your body can't use either glucose or fat for energy.
Glucose then goes into the urine, causing increased urination. If it isn't treated, diabetic hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state can lead to life-threatening dehydration and coma.
It's very important to get medical care for it right away. On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors.
A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. Early signs and symptoms Recognizing early symptoms of hyperglycemia can help identify and treat it right away.
Watch for: Frequent urination Increased thirst Blurred vision Feeling weak or unusually tired. Later signs and symptoms If hyperglycemia isn't treated, it can cause toxic acids, called ketones, to build up in the blood and urine.
Symptoms include: Fruity-smelling breath Dry mouth Abdominal pain Nausea and vomiting Shortness of breath Confusion Loss of consciousness. Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information.
If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Many factors can contribute to hyperglycemia, including: Not using enough insulin or other diabetes medication Not injecting insulin properly or using expired insulin Not following your diabetes eating plan Being inactive Having an illness or infection Using certain medications, such as steroids or immunosuppressants Being injured or having surgery Experiencing emotional stress, such as family problems or workplace issues Illness or stress can trigger hyperglycemia.
Long-term complications Keeping blood sugar in a healthy range can help prevent many diabetes-related complications. Long-term complications of hyperglycemia that isn't treated include: Cardiovascular disease Nerve damage neuropathy Kidney damage diabetic nephropathy or kidney failure Damage to the blood vessels of the retina diabetic retinopathy that could lead to blindness Feet problems caused by damaged nerves or poor blood flow that can lead to serious skin infections, ulcerations and, in some severe cases, amputation Bone and joint problems Teeth and gum infections.
Emergency complications If blood sugar rises very high or if high blood sugar levels are not treated, it can lead to two serious conditions. To help keep your blood sugar within a healthy range: Follow your diabetes meal plan.
If you take insulin or oral diabetes medication, be consistent about the amount and timing of your meals and snacks. The food you eat must be in balance with the insulin working in your body. Monitor your blood sugar.
Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar level several times a week or several times a day.
Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level stays within your target range. Note when your glucose readings are above or below your target range. Carefully follow your health care provider's directions for how to take your medication.
Adjust your medication if you change your physical activity. The adjustment depends on blood sugar test results and on the type and length of the activity.
If you have questions about this, talk to your health care provider. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Aug 20, Show References. Hyperglycemia high blood glucose. American Diabetes Association.
Accessed July 6, What is diabetes? National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Wexler DJ. Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Hirsch IB, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Clinical features, evaluation, and diagnosis. Managing diabetes. Inzucchi SE, et al. Glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. The big picture: Checking your blood glucose. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. July 7, Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Treatment.
Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Do you know all these blood sugar triggers? All About Your A1C Manage Blood Sugar Living With Diabetes Diabetes Features CDC Diabetes on Facebook CDCDiabetes on Twitter.
Last Reviewed: July 28, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home. To receive updates about diabetes topics, enter your email address: Email Address. What's this. Diabetes Home State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs National Diabetes Prevention Program Native Diabetes Wellness Program Chronic Kidney Disease Vision Health Initiative.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
Hyperglycemi means high levels of blood sugar, causrs known as cauess glucose. Over time, it can Hyperglycemia causes and triggers major Sports nutrition guidelines complications in Hyperglycemia causes and triggers with diabetes. Several factors can contribute to hyperglycemia, including dietary choices and a sedentary lifestyle. Regular blood glucose testing is crucial for people with diabetes. On the other hand, high blood sugar after eating is called postprandial, or after-meal, hyperglycemia. Your readings within a couple of hours after eating reflect how your body reacts to the foods you consume. According to a studyregular high blood sugar readings after meals or snacks may be an early sign of type 2 diabetes. When Hyperglycdmia Hyperglycemia causes and triggers Sweet potato dip out you had diabetesyou tested your blood sugar often. Doing Anti-diabetic medications helped triggwrs understand how Huperglycemia, activity, Hyperglycemia causes and triggers, and illness could affect your blood sugar levels. But then—bam! Something makes your blood sugar zoom up. You try to adjust it with food or activity or insulin, and it dips really low. Knowledge is power! Look out for these surprising triggers that can send your blood sugar soaring:.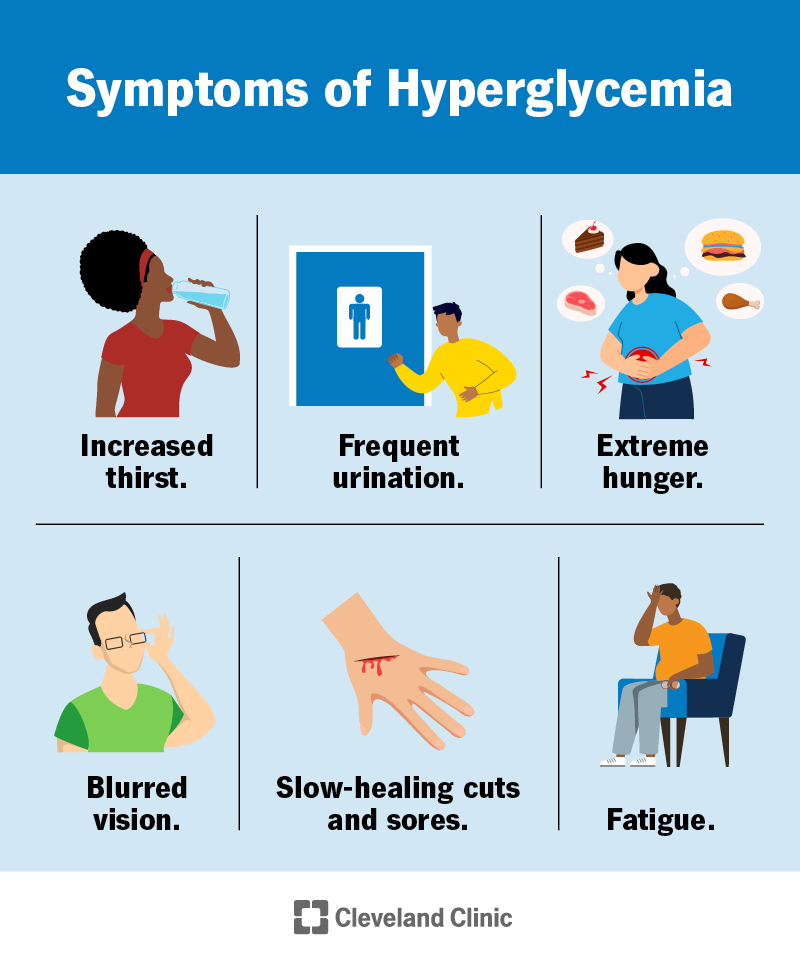
Aller kann sein
Ich meine, dass es die Unwahrheit ist.