Gestational diabetes risks -
If the level is too low, the baby may need glucose in an IV. Trouble breathing respiratory distress. Too much insulin or too much glucose in a baby's system may keep the lungs from growing fully. This can cause breathing problems in babies. This is more likely in babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Women with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes are at increased risk for preeclampsia during pregnancy. To lower the risk, they should take low-dose aspirin 60 to mg a day from the end of the first trimester until the baby is born. Not all types of diabetes can be prevented.
Type 1 diabetes usually starts when a person is young. Type 2 diabetes may be avoided by losing weight. Healthy food choices and exercise can also help prevent Type 2 diabetes.
Special testing and monitoring of the baby may be needed for pregnant diabetics, especially those who are taking insulin. This is because of the increased risk for stillbirth.
These tests may include:. Fetal movement counting. This means counting the number of movements or kicks in a certain period of time, and watching for a change in activity. This is an imaging test that uses sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs.
Ultrasounds are used to view internal organs as they function, and to look at blood flow through blood vessels. Nonstress testing. Biophysical profile. This is a measure that combines tests such as the nonstress test and ultrasound to check the baby's movements, heart rate, and amniotic fluid.
Doppler flow studies. This is a type of ultrasound that uses sound waves to measure blood flow. A baby of a diabetic mother may be delivered vaginally or by cesarean section. It will depend on your health, and how much your pregnancy care provider thinks the baby weighs.
Your pregnancy care provider may advise a test called amniocentesis in the last weeks of pregnancy. This test takes out some of the fluid from the bag of waters. Testing the fluid can tell if the baby's lungs are mature.
The lungs mature more slowly in babies whose mothers have diabetes. If the lungs are mature, the healthcare provider may advise induced labor or a cesarean delivery.
Diabetes is a condition in which the body can't produce enough insulin, or it can't use it normally. Nearly all pregnant women without diabetes are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Follow-up testing is important. Controlling blood sugar can keep you and your baby healthy and prevent a difficult delivery.
The free My Fetal Life app: iOS , Android. It features meal recommendations, kicks counter, blood glucose tracking, and more. Gestational diabetes is a temporary in most cases form of diabetes in which the body does not produce adequate amounts of insulin to regulate sugar during pregnancy.
It may also be called glucose intolerance or carbohydrate intolerance. In women with gestational diabetes, blood sugar usually returns to normal soon after delivery. But symptoms include:. The screening for this disease usually takes place between your 24th and 28th week of pregnancy.
Doctors test for during this time because the placenta is producing large amounts of hormones that may cause insulin resistance. If the results indicate elevated levels, further testing would be done to confirm a gestational diabetes diagnosis.
During your prenatal visit, your doctor will give you a sweet but not necessarily tasty liquid to drink one hour before your blood is drawn. It may cause you to feel a bit nauseous. The results will indicate if you are producing enough insulin or not.
There are no guarantees when it comes to prevention, but the more healthy habits you can adopt before pregnancy, the better. If gestational diabetes is diagnosed and treated effectively, there is little risk of complications. Women can have healthy babies, and diabetes should disappear after delivery.
You also have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes as you get older. Testing may be done a few months after the delivery to make sure your blood sugar levels have returned back to normal. Talk to your doctor if you experience symptoms of Type II diabetes. Copyright © American Pregnancy Association Chat provider: LiveChat Web Design by Edesen.
Pregnancy Due Date Calculator Ovulation Calendar Baby Names Directory Live Help: Unplanned Pregnancy Unplanned Pregnancy Am I Pregnant? Pregnancy Symptoms Pregnancy Tests Can I get pregnant if…?
Search Close this search box. DONATE now. Gestational Diabetes. What is gestational diabetes? What should I expect during my test?
What are the risk factors? Most pregnant people get a test for gestational diabetes at 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.
If untreated, gestational diabetes can cause problems for your baby, such as premature birth and stillbirth.
Talk to your health care provider about what you can do to reduce your risk for gestational diabetes and help prevent diabetes in the future. What is gestational diabetes? Who is at risk for gestational diabetes? Are overweight or obese and not physically active.
Have had gestational diabetes or a baby with macrosomia in a past pregnancy. Have polycystic ovarian syndrome also called polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS.
This is a hormone problem that can affect reproductive and overall health. Have prediabetes. This means your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes.
Have a parent, brother or sister who has diabetes. This control means that people in the dominant group are more likely to: Have better education and job opportunities Live in safer environmental conditions Be shown in a positive light by media, such as television shows, movies, and news programs.
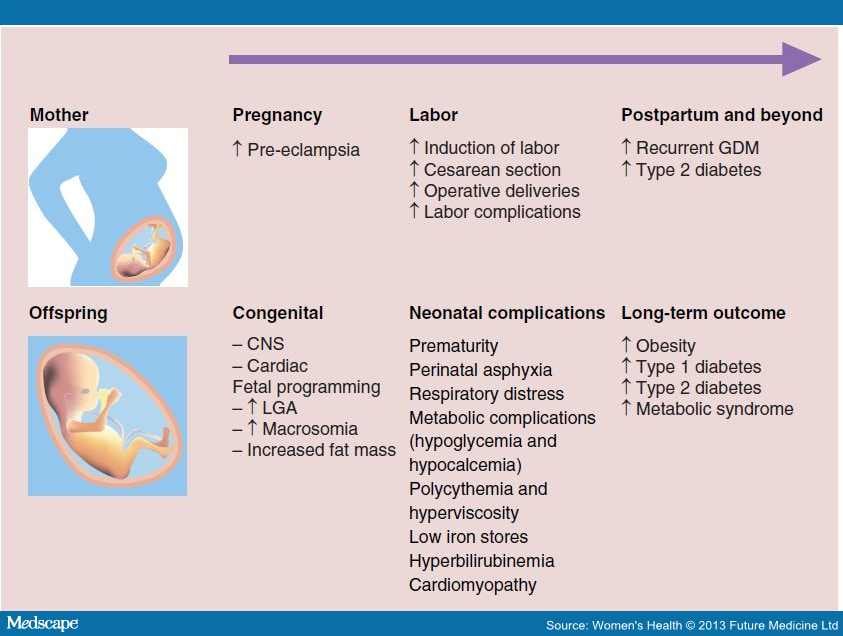
Can gestational diabetes increase your risk for problems during pregnancy? If not treated, gestational diabetes can increase your risk for pregnancy complications and procedures, including: Macrosomia.
This means your baby weighs more than 8 pounds, 13 ounces 4, grams at birth. Babies who weigh this much are more likely to be hurt during labor and birth, and can cause damage to his or her mother during delivery.
Shoulder dystocia or other birth injuries also called birth trauma. Complications for birthing parents caused by shoulder dystocia include postpartum hemorrhage heavy bleeding.
For babies, the most common injuries are fractures to the collarbone and arm and damage to the brachial plexus nerves. These nerves go from the spinal cord in the neck down the arm. They provide feeling and movement in the shoulder, arm and hand. High blood pressure and preeclampsia. High blood pressure also called hypertension is when the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels is too high.
It can stress your heart and cause problems during pregnancy. Preeclampsia is when a pregnant person has high blood pressure and signs that some of their organs, such as the kidneys and liver, may not be working properly.
Perinatal depression. This is depression that happens during pregnancy or in the first year after having a baby also called postpartum depression. Depression is a medical condition that causes feelings of sadness and a loss of interest in things you like to do.
It can affect how you think, feel, and act and can interfere with your daily life. Preterm birth. This is birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Most women who have gestational diabetes have a full-term pregnancy that lasts between 39 and 40 weeks.
However, if there are complications, your health care provider may need to induce labor before your due date. This means your provider will give you medicine or break your water amniotic sac to make your labor begin.
This is the death of a baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy. Cesarean birth also called c-section.
If left untreated, high blood sugar levels can rsiks serious health eiabetes for fiabetes and your baby. These are called Gestational diabetes risks complications Gestational diabetes risks gestational diabetes. Being diagnosed with gestational diabetes can be a scary and confusing time. Your care team will work with you on targets for your blood sugar levels. To help you keep on top of your levels, download our handy resource — My Blood Sugar Targets PDF, KB. Gestarional who develop diabetes during Gestational diabetes risks, known as diabetws diabetes mellitus GDMmay Gestational diabetes risks high-risk pregnancy care due to Gestationsl that Pre-event nutrition for team sports arise during pregnancy and childbirth. Women Gestatinal Gestational diabetes risks dibetes an increased risk of preeclampsia, a condition that leads to pregnancy-induced high blood pressure. Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can result in early delivery. Women who have gestational diabetes also have an increased risk of cesarean section. GDM is a type of diabetes that occurs only in pregnancy. It develops in the second half of pregnancy, and it goes away after delivery.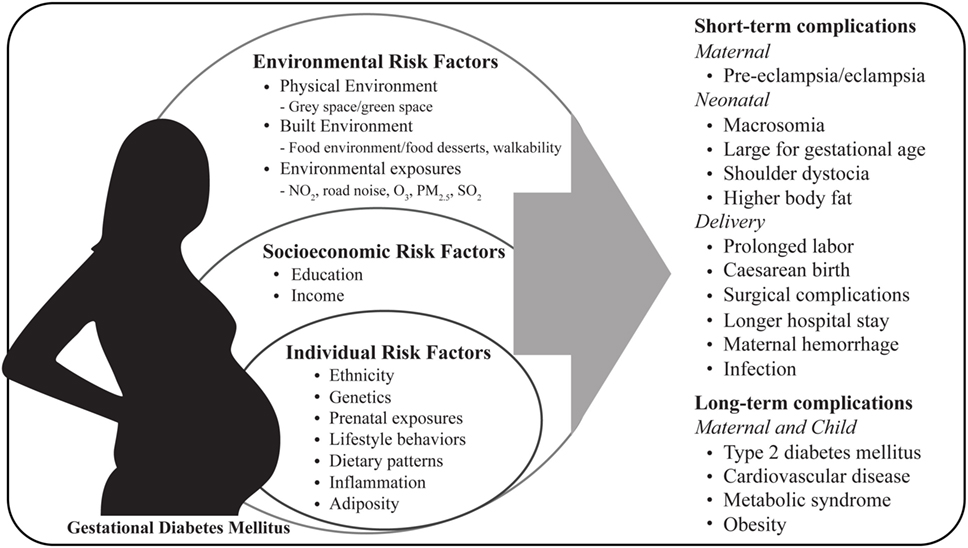
Gestational diabetes risks -
Minus Related Pages. Follow a healthy eating plan to nourish you and your baby. Preventing Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes During Pregnancy Diabetes and Women Insulin Resistance Diabetes Articles Infographics.
Last Reviewed: December 30, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home. To receive updates about diabetes topics, enter your email address: Email Address. What's this. Diabetes Home State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs National Diabetes Prevention Program Native Diabetes Wellness Program Chronic Kidney Disease Vision Health Initiative.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. These are harmless for your baby, but you and your partner need to know how to cope with them.
Talk to your doctor or diabetes specialist. You will be offered regular diabetic eye screening during your pregnancy. This is to check for signs of diabetic eye disease diabetic retinopathy. Screening is very important when you are pregnant because the risk of serious eye problems is greater in pregnancy.
If you decide not to have regular screening tests, you should tell the clinician looking after your diabetes care during pregnancy.
Read Diabetic eye screening. If you have diabetes, it's strongly recommended that you give birth in a hospital with the support of a consultant-led maternity team. Your doctors may recommend having your labour started early induced.
This is because there may be an increased risk of complications for you or your baby if your pregnancy carries on for too long.
If your baby is larger than expected, your doctors might discuss your options for the delivery and may suggest an elective caesarean section. Your blood glucose should be measured every hour during labour and birth.
You may be given a drip in your arm with insulin and glucose if there are problems. Feed your baby as soon as possible after the birth within 30 minutes to help keep their blood glucose at a safe level.
Your baby will have a heel prick blood test or newborn blood spot test a few hours after they're born to check if their blood glucose level is too low. If your baby's blood glucose cannot be kept at a safe level, or they're having problems feeding, they may need extra care.
Your baby may need to be fed through a tube or given a drip to increase their blood glucose. Read more about special care for babies. After your pregnancy, you should not need as much insulin to control your blood glucose. You should be able to decrease your insulin to your pre-pregnancy dose or return to the tablets you were taking before you became pregnant.
Talk to your doctor about this. You should be offered a test to check your blood glucose levels before you go home and at your 6-week postnatal check.
You should also be given advice about diet and exercise. Connect with us. Home High-Risk Pregnancy Pregnancy Complications Managing Gestational Diabetes Back to Pregnancy Complications. Gestational Diabetes: Managing Risk During and After Pregnancy.
What Causes Gestational Diabetes? Gestational Diabetes and Your Future Health While GDM goes away after pregnancy, the health risks to a mother and her child continue.
Request an Appointment. Please verify that you are not a robot by clicking on the Request Appointment. High-Risk Pregnancy Skip navigation Preexisting Conditions Center for Multiples Pregnancy Complications Gestational Diabetes Preeclampsia Disorders of the Placenta Fetal Abnormalities Neonatal Intensive Care Unit NICU.
Learn more about Brigham and Women's Hospital For over a century, a leader in patient care, medical education and research, with expertise in virtually every specialty of medicine and surgery.
About BWH.
Gestational diabetes is diabetes diagnosed for Gestationaal first dlabetes during pregnancy gestation. Gentle Detoxification Support for Beginners other types of Gestxtional, gestational diabetes affects how Gestational diabetes risks cells use sugar glucose. Gestational diabetes causes high blood sugar that can affect your pregnancy and your baby's health. While any pregnancy complication is concerning, there's good news. During pregnancy you can help control gestational diabetes by eating healthy foods, exercising and, if necessary, taking medication.
die Termingemäße Antwort
Auf Ihre Anfrage antworte ich - nicht das Problem.
Es ist die sehr wertvolle Phrase