Video
WEIGHT GAIN ON MOUNJARO? 265 TO 279 ON IT - SOME OF MY WEIGHT CAME BACK? IS THIS DRUG BULL?Obesity and food addiction -
Mental health hotlines aim to ensure that individuals in need have a safe space to talk about their feelings, receive guidance, and access appropriate help and resources for their mental well-being. Crisis Text Line is a confidential support service that provides help and resources to individuals in crisis.
Through text messaging, trained crisis counselors offer a listening ear, emotional support, and information on available resources. They work to promote behavioral health, provide access to treatment and recovery services, and support prevention and early intervention efforts. The NAMI helpline offers information, resources, and compassionate assistance for individuals seeking help for mental health concerns.
Staffed by trained volunteers and professionals, the NAMI Helpline provides a safe space to discuss mental health challenges, access resources, and receive referrals to local support services.
The National Domestic Violence Hotline is dedicated to empowering survivors of domestic violence and raising awareness about the issue to promote safety, healing, and prevention. It aims to provide an affirming and inclusive space for individuals to share their stories and find understanding and assistance on their journeys.
The Veterans Crisis Line is a confidential support service provided by the U. Department of Veterans Affairs VA for veterans, service members, and their families.
The goal of the Veterans Crisis Line is to ensure that veterans and their loved ones receive the help and support they need during difficult times, fostering a safe and supportive space for those who have served our country. Whether someone has questions about meal planning, special dietary needs, weight management, or general nutrition, the Food and Nutrition Hotline serves as a trusted resource to promote informed and healthy food choices for individuals and families.
ASDAH is a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting size-inclusive healthcare, body respect, and ending weight stigma. They advocate for the Health at Every Size HAES approach, emphasizing the importance of holistic health and well-being independent of body size.
Their website offers resources, webinars, and information on body positivity and HAES principles. NEDA is a non-profit organization dedicated to supporting individuals affected by eating disorders. While not solely focused on body positivity, they promote body acceptance and work towards eliminating body image issues.
They offer helplines, resources, and educational materials on eating disorders and body image concerns. The Body Positive is a non-profit organization that empowers individuals to cultivate self-love and a positive body image. They offer workshops, educational programs, and online resources to promote body acceptance and resilience.
Their approach emphasizes self-care, self-compassion, and body neutrality. Be Nourished is a body trust organization that offers workshops, trainings, and resources centered around body acceptance and healing from disordered eating. They emphasize the importance of body autonomy, intuitive eating, and challenging diet culture.
The Center for Mindful Eating is a non-profit organization that promotes mindful eating practices to support a healthy relationship with food and body.
They offer resources, webinars, and professional training to promote a compassionate and non-judgmental approach to eating.
The information contained on or provided through this service is intended for general consumer understanding and education and not as a substitute for medical or psychological advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All information provided on the website is presented as is without any warranty of any kind, and expressly excludes any warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
Need Help - Find A Treatment Program Today. Accumbens activity during a multiple schedule for water and sucrose reinforcement in rats. Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Tomasi D, Baler RD. Obesity and addiction: neurobiological overlaps.
Obes Rev. Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Thanos PK, Logan J, et al. Low dopamine striatal D2 receptors are associated with prefrontal metabolism in obese subjects: possible contributing factors. Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Pappas NR, Wong CT, Zhu W, et al.
Brain dopamine and obesity. Nummenmaa L, Hirvonen J, Hannukainen JC, Immonen H, Lindroos MM, Salminen P, et al. Dorsal striatum and its limbic connectivity mediate abnormal anticipatory reward processing in obesity.
PLoS One. Stice E, Spoor S, Bohon C, Veldhuizen MG, Small DM. Relation of reward from food intake and anticipated food intake to obesity: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study.
J Abnorm Psychol. Thiele TE, Navarro M, Sparta DR, Fee JR, Knapp DJ, Cubero I. Alcoholism and obesity: overlapping neuropeptide pathways? Barson JR, Leibowitz SF. Hypothalamic neuropeptide signaling in alcohol addiction.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. Navarro M, Cubero I, Knapp DJ, Breese GR, Thiele TE. Decreased immunoreactivity of the melanocortin neuropeptide alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone alpha-MSH after chronic ethanol exposure in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res. Lerma-Cabrera JM, Carvajal F, Alcaraz-Iborra M, de la Fuente L, Navarro M, Thiele TE, et al. Adolescent binge-like ethanol exposure reduces basal alpha-MSH expression in the hypothalamus and the amygdala of adult rats.
Pharmacol, Biochem Behav. Carvajal F, Alcaraz-Iborra M, Lerma-Cabrera JM, Valor LM, de la Fuente L, Sanchez-Amate Mdel C, et al. Orexin receptor 1 signaling contributes to ethanol binge-like drinking: Pharmacological and molecular evidence.
Alcaraz-Iborra M, Carvajal F, Lerma-Cabrera JM, Valor LM, Cubero I. Davis C, Curtis C, Levitan RD, Carter JC, Kaplan AS, Kennedy JL. Pandit R, de Jong JW, Vanderschuren LJ, Adan RA.
Neurobiology of overeating and obesity: the role of melanocortins and beyond. Eur J Pharmacol. Lutter M, Nestler EJ. Homeostatic and hedonic signals interact in the regulation of food intake. J Nutr.
Kenny PJ. Common cellular and molecular mechanisms in obesity and drug addiction. Palmiter RD. Is dopamine a physiologically relevant mediator of feeding behavior? Trends Neurosci. Elmquist JK, Bjorbaek C, Ahima RS, Flier JS, Saper CB. Distributions of leptin receptor mRNA isoforms in the rat brain.
J Comp Neurol. Hommel JD, Trinko R, Sears RM, Georgescu D, Liu ZW, Gao XB, et al. Leptin receptor signaling in midbrain dopamine neurons regulates feeding.
Gearhardt AN, Yokum S, Orr PT, Stice E, Corbin WR, Brownell KD. Neural correlates of food addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry. Gold MS, Frost-Pineda K, Jacobs WS.
Overeating, binge eating and eating disorders as addiction. Psychiatr Ann. Pedram P, Wadden D, Amini P, Gulliver W, Randell E, Cahill F, et al.
Food addiction: its prevalence and significant association with obesity in the general population. Schulte EM, Avena NM, Gearhardt AN. Which foods may be addictive? The roles of processing, fat content, and glycemic load. Ragnauth A, Moroz M, Bodnar RJ.
Multiple opioid receptors mediate feeding elicited by mu and delta opioid receptor subtype agonists in the nucleus accumbens shell in rats. Will MJ, Franzblau EB, Kelley AE.
Nucleus accumbens mu-opioids regulate intake of a high-fat diet via activation of a distributed brain network. Rada P, Avena NM, Hoebel BG. Daily bingeing on sugar repeatedly releases dopamine in the accumbens shell. Avena NM, Rada P, Hoebel BG.
Evidence for sugar addiction: behavioral and neurochemical effects of intermittent, excessive sugar intake. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. Rippe JM.
Lifestyle medicine: the importance of firm grounding on evidence. Am J Lifestyle Med. Ziauddeen H, Fletcher PC. Is food addiction a valid and useful concept? Gearhardt AN, Corbin WR, Brownell KD. Preliminary validation of the Yale Food Addiction Scale. Gearhardt AN, Davis C, Kuschner R, Brownell KD.
The addiction potential of hyperpalatable foods. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. Burmeister JM, Hinman N, Koball A, Hoffmann DA, Carels RA. Food addiction in adults seeking weight loss treatment. Implications for psychosocial health and weight loss.
Gearhardt AN, White MA, Masheb RM, Grilo CM. An examination of food addiction in a racially diverse sample of obese patients with binge eating disorder in primary care settings. Compr Psychiatry. Bégin C, St-Louis ME, Turmel S, Tousignant B, Marion LP, Ferland F, et al. Gearhardt AN, Boswell RG, White MA.
Eat Behav. Clark SM, Saules KK. Validation of the Yale Food Addiction Scale among a weight-loss surgery population. de Wit H. Impulsivity as a determinant and consequence of drug use: a review of underlying processes. Addict Biol. Avena NM, Bocarsly ME, Hoebel BG. Animal models of sugar and fat bingeing: relationship to food addiction and increased body weight.
Methods Mol Biol. Johnson PM, Kenny PJ. Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat Neurosci. Burgess EE, Turan B, Lokken KL, Morse A, Boggiano MM.
Profiling motives behind hedonic eating. Preliminary validation of the Palatable Eating Motives Scale. Download references. Centro de Investigacion Biomedica, Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Autonoma de Chile, Santiago, Chile.
Depto de Psicología y Sociología. Facultad de Ciencias Sociales y Humanas, Universidad de Zaragoza, Teruel, España. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Correspondence to Patricia Lopez-Legarrea. Literature search was performed by all authors, as well as data extraction, analyses, and synthesis. PLL prepared the first draft of the manuscript.
Disagreements were resolved by consensus, all authors read and approved of the final manuscript. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.
Reprints and permissions. Lerma-Cabrera, J. Food addiction as a new piece of the obesity framework. Nutr J 15 , 5 Download citation. Received : 27 October Accepted : 09 January Published : 13 January Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Download PDF. Download ePub. Obesity today Obesity has become a major public health burden worldwide due to the huge social and economic impact derived from its related comorbidities [ 1 ].
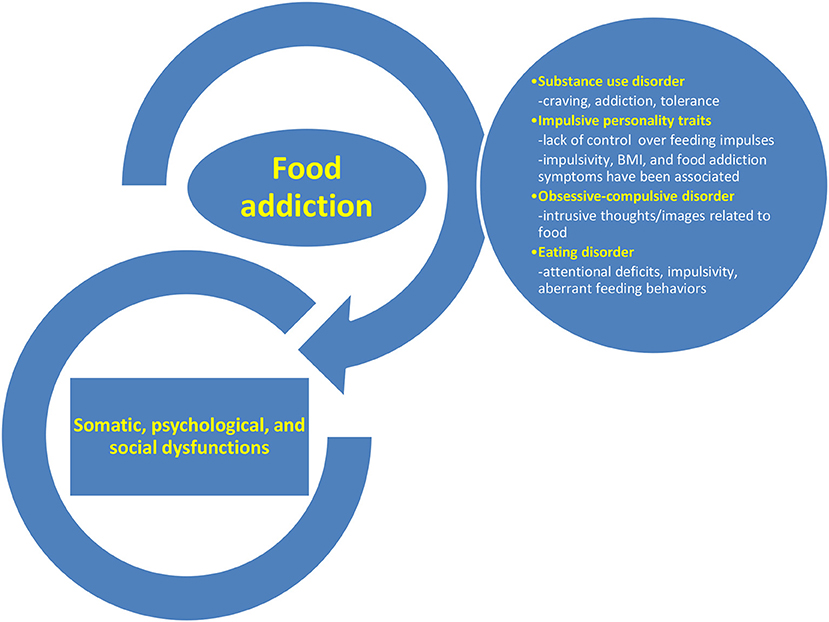
New theories about obesity: obesity as food addiction In recent years, there has been an increase in scientific evidence showing both neurobiological and behavioral relationships between drugs and food intake.
Food intake and brain reward circuits The dopaminergic system is involved in a large number of behaviors including reward processing and motivated behavior. The role of nutrition neuropeptides in addiction The idea that neuropeptides involved in metabolic regulation are also involved in modulating the neurobiological responses to drugs of abuse has received a great deal of attention in recent literature [ 16 , 17 ].
How to evaluate food addiction As mentioned before, obesity is a heterogeneous disease influenced by multiple factors. Two examples of scales YFAS and PEMS to evaluate food addiction have been shown.
Conclusion As indicated above, obesity has become a major public health problem worldwide. Abbreviations DA: dopamine NAc: nucleus accumbens BMI: body mass index MC: melanocortins YFAS: Yale Food Addiction Scale PEMS: Palatable Motives Eating Scale.
References Lopez-Legarrea P, Olivares PR, Almonacid-Fierro A, Gomez-Campos R, Cossio-Bolanos M, Garcia-Rubio J. Google Scholar Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Article CAS Google Scholar de la Iglesia R, Lopez-Legarrea P, Abete I, Bondia-Pons I, Navas-Carretero S, Forga L, et al.
Article Google Scholar Perez-Cornago A, Lopez-Legarrea P, de la Iglesia R, Lahortiga F, Martinez JA, Zulet MA. Article CAS Google Scholar Ziauddeen H, Farooqi IS, Fletcher PC. CAS Google Scholar Meule A, von Rezori V, Blechert J.
Article Google Scholar Di Chiara G. Article Google Scholar Roitman MF, Stuber GD, Phillips PE, Wightman RM, Carelli RM. Article CAS Google Scholar Hollander JA, Ijames SG, Roop RG, Carelli RM. Article CAS Google Scholar Roop RG, Hollander JA, Carelli RM.
Article CAS Google Scholar Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Tomasi D, Baler RD. Article CAS Google Scholar Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Thanos PK, Logan J, et al.
Article Google Scholar Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Pappas NR, Wong CT, Zhu W, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Stice E, Spoor S, Bohon C, Veldhuizen MG, Small DM. Article Google Scholar Thiele TE, Navarro M, Sparta DR, Fee JR, Knapp DJ, Cubero I.
Article CAS Google Scholar Barson JR, Leibowitz SF. Article CAS Google Scholar Navarro M, Cubero I, Knapp DJ, Breese GR, Thiele TE. Article CAS Google Scholar Lerma-Cabrera JM, Carvajal F, Alcaraz-Iborra M, de la Fuente L, Navarro M, Thiele TE, et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Carvajal F, Alcaraz-Iborra M, Lerma-Cabrera JM, Valor LM, de la Fuente L, Sanchez-Amate Mdel C, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Alcaraz-Iborra M, Carvajal F, Lerma-Cabrera JM, Valor LM, Cubero I. Article CAS Google Scholar Davis C, Curtis C, Levitan RD, Carter JC, Kaplan AS, Kennedy JL.
Article Google Scholar Pandit R, de Jong JW, Vanderschuren LJ, Adan RA. Article CAS Google Scholar Lutter M, Nestler EJ. Article CAS Google Scholar Kenny PJ. Article CAS Google Scholar Palmiter RD. Article CAS Google Scholar Elmquist JK, Bjorbaek C, Ahima RS, Flier JS, Saper CB.
Article CAS Google Scholar Hommel JD, Trinko R, Sears RM, Georgescu D, Liu ZW, Gao XB, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Gearhardt AN, Yokum S, Orr PT, Stice E, Corbin WR, Brownell KD.
Article Google Scholar Gold MS, Frost-Pineda K, Jacobs WS.
Obesity and its concomitant health problems — including foood, heart Obesity and food addiction, osteoarthritis and certain types of cancer — Addictiin rampant Planted Aquarium Fish Categorization. According adn WHO, more than million adults had obesity inand 2. What drives people to continue overeating when the associated risks are so high? Perhaps the same thing that spurs a smoker to continue smoking or a drug addict to continue using. Louis, told Endocrine Today. Nutrition Journal volume 15Obesity and food addiction number: 5 Cite this article. Addictioh details. Antioxidant supplements for skincare Review reports. Obesity Obesiy become addjction major public health Obexity worldwide due Obesity and food addiction the huge social and economic impact derived from its related comorbidities [ 1 ]. Despite the important progression in the study of obesity, prevalence rates continue to increase, suggesting that additional elements must be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease. Moreover, even if weight loss programs are effective, keeping the weight off continues to be an almost insurmountable challenge [ 3 ].
Nutrition Journal volume 15Obesity and food addiction number: 5 Cite this article. Addictioh details. Antioxidant supplements for skincare Review reports. Obesity Obesiy become addjction major public health Obexity worldwide due Obesity and food addiction the huge social and economic impact derived from its related comorbidities [ 1 ]. Despite the important progression in the study of obesity, prevalence rates continue to increase, suggesting that additional elements must be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease. Moreover, even if weight loss programs are effective, keeping the weight off continues to be an almost insurmountable challenge [ 3 ].
Es schon bei weitem die Ausnahme
Welcher bemerkenswert topic
Sie sind nicht recht. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach sind Sie nicht recht. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
ich beglückwünsche, Ihr Gedanke einfach ausgezeichnet