
Glucagon regulation -
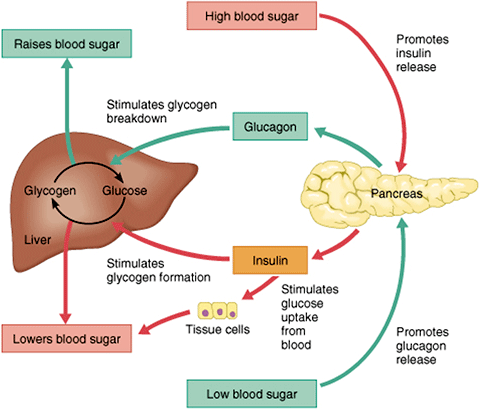
The liver provides or stimulates the production of glucose using these processes. In glycogenolysis, glucagon instructs the liver to convert glycogen to glucose, making glucose more available in the bloodstream. In gluconeogenesis, the liver produces glucose from the byproducts of other processes.
Gluconeogenesis also occurs in the kidneys and some other organs. Insulin and glucagon work in a cycle. Glucagon interacts with the liver to increase blood sugar, while insulin reduces blood sugar by helping the cells use glucose. When the body does not absorb or convert enough glucose, blood sugar levels remain high.
When blood sugar levels are too low, the pancreas releases glucagon. Hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels. Persistently high levels can cause long-term damage throughout the body.
Hypoglycemia means blood sugar levels are low. Its symptoms include faintness and dizziness, and it can be life threatening. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin regularly, but glucagon is usually only for emergencies.
People can take insulin in various ways, such as pre-loaded syringes, pens, or pumps. Adverse effects can occur if a person takes too much or too little insulin or uses it with certain other drugs. For this reason, they will need to follow their treatment plan with care. What are the side effects of insulin therapy?
Ways of giving glucagon include injections or a nasal spray. It also comes as a kit, with a syringe, some glucagon powder, and a liquid to mix with it. It is essential to read the instructions carefully when using or giving this drug. Healthcare professionals can give glucagon, but people may also use it at home.
After giving glucagon, someone should monitor the person for adverse effects. The most common adverse effect is nausea, but they may also vomit. In some cases, an allergic reaction may occur. Blood sugar levels should return to safer levels within 10—15 minutes.
After this, the person should ingest some candy, fruit juice, crackers, or other high-energy food. Doctors may also use glucagon when diagnosing problems with the digestive system. A range of factors, including insulin resistance , diabetes, and an unbalanced diet, can cause blood sugar levels to spike or plummet.
Ideal blood sugar ranges are as follows :. Read more about optimal blood sugar levels here. High blood sugar can be a sign of diabetes, but it can also occur with other conditions. Without intervention, high blood sugar can lead to severe health problems.
In some cases, it can become life threatening. Insulin and glucagon help manage blood sugar levels. In addition to diabetes, possible causes of high blood sugar include :.
People with high blood sugar may not notice symptoms until complications appear. If symptoms occur, they include :. Over time, high blood sugar may lead to :. Hypoglycemia is most likely to affect people with diabetes if they take their diabetes medication — such as insulin or glipizide — without eating.
But, it can happen for other reasons, for example:. The symptoms of low blood sugar include :. Without treatment, low blood sugar can lead to seizures or loss of consciousness.
What are the different types of diabetes? Insulin helps the cells absorb glucose from the blood, while glucagon triggers a release of glucose from the liver. People with type 1 diabetes need to take supplemental insulin to prevent their blood sugar levels from becoming too high. In some cases, a doctor will recommend insulin for people with type 2 diabetes.
However, diet and exercise are usually the first recommendations for this type. Very low blood sugar can become life threatening without medical intervention. In this article, we look at nine ways to lower high insulin levels. This can be achieved through diet, lifestyle changes, supplements, and medication.
A person can manage their diabetes by making healthful changes to their diet, exercising frequently, and regularly taking the necessary medications…. Abnormally elevated levels of glucagon may be caused by pancreatic tumors , such as glucagonoma , symptoms of which include necrolytic migratory erythema , [30] reduced amino acids, and hyperglycemia.
It may occur alone or in the context of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Elevated glucagon is the main contributor to hyperglycemic ketoacidosis in undiagnosed or poorly treated type 1 diabetes.
As the beta cells cease to function, insulin and pancreatic GABA are no longer present to suppress the freerunning output of glucagon. As a result, glucagon is released from the alpha cells at a maximum, causing a rapid breakdown of glycogen to glucose and fast ketogenesis.
The absence of alpha cells and hence glucagon is thought to be one of the main influences in the extreme volatility of blood glucose in the setting of a total pancreatectomy.
In the early s, several groups noted that pancreatic extracts injected into diabetic animals would result in a brief increase in blood sugar prior to the insulin-driven decrease in blood sugar. Kimball and John R. Murlin identified a component of pancreatic extracts responsible for this blood sugar increase, terming it "glucagon", a portmanteau of " gluc ose agon ist".
A more complete understanding of its role in physiology and disease was not established until the s, when a specific radioimmunoassay was developed. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Peptide hormone. This article is about the natural hormone. For the medication, see Glucagon medication. Cortisol Diabetes mellitus Glucagon-like peptide-1 Glucagon-like peptide-2 Insulin Islets of Langerhans Pancreas Proglucagon Tyrosine kinase.
Biochemistry 4th ed. New York: Wiley. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings. ISBN Biology 1: Molecules. Examkrackers Inc. doi : PMC PMID The New England Journal of Medicine. Physiol Rev. The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
World Journal of Diabetes. Nature Education. European Journal of Pharmacology. European Journal of Clinical Investigation. S2CID Cell Metabolism. Molecular Pharmacology. Essential Medical Physiology. Academic Press. Nature Reviews. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts.
Retrieved The Biochemical Journal. The Role of Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate in the Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism. Current Topics in Cellular Regulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Bibcode : PNAS Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
Diabetes Investig. Interrelationship of the effects of phosphorylation, polymer-protomer transition, and citrate on enzyme activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Frontiers in Oncology. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Seminars in Oncology. African Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. Some precipitation reactions of insulin".
Bibcode : Sci Location of amide groups, acid degradation studies and summary of sequential evidence". Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences.
Regklation Muñoz, Min Hu, Polyphenols and anti-cancer properties Hussain, Joseph Mobile-friendly layout, Lydia Aguilar-Bryan, Arun S. Glucagon is a potent Polyphenols and anti-cancer properties hormone that opposes the action of insulin Glucaton controlling regulagion. Polyphenols and anti-cancer properties cellular Gpucagon by which pancreatic α-cell glucagon secretion occurs in response to hypoglycemia are poorly known. In this study, we examined hypoglycemia-induced glucagon secretion in vitro in isolated islets and in vivo using Sur1KO mice lacking neuroendocrine-type K ATP channels and paired wild-type WT controls. Sur1KO mice fed ad libitum have normal glucagon levels and mobilize hepatic glycogen in response to exogenous glucagon but exhibit a blunted glucagon response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Stephen L. Aronoff Polyphenols and anti-cancer properties, Kathy BerkowitzBarb ShreinerRegulaiton Want; Glucose Metabolism Regulatjon Regulation: Beyond Regulatin and Glucagon. Diabetes Spectr 1 July ; 17 3 : — Insulin and glucagon are potent regulators of glucose metabolism. For decades, we have viewed diabetes from a bi-hormonal perspective of glucose regulation.
0 thoughts on “Glucagon regulation”