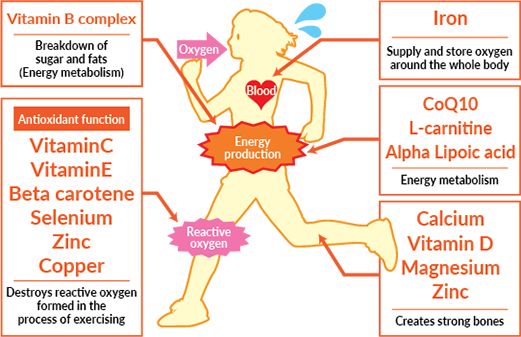
Essential nutrients for sports performance -
APPLY NOW. Search Close this search box. Performance and Health Management. Home Blogs Performance and Health Management Fueling Your Performance: The Fundamentals of Sports Nutrition.
The Breakdown of The Fundamentals of Sports Nutrition Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for athletes.
Protein Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue. Fat Fat is a crucial nutrient for athletes as it provides a source of energy during prolonged exercise.
Hydration Hydration is critical for athletes as even mild dehydration can significantly impact performance. Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins and minerals are essential for overall health and well-being. Supplements Supplements are commonly used by athletes to enhance performance and aid in recovery.
Some commonly used supplements by athletes include: Fundamentals of sports nutrition Creatine: Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that provides energy to the muscles during high-intensity exercise.
Interested in Pursuing a Master in Performance and Health Management Here is our program! Be ready to Make an Impact! Learn more. Previous post The Importance of Cultural Intelligence in Marketing to a Diverse Audience in Barcelona 28 de March de Next post Barcelona's Position in the Global Market: A Study of International Business Trends 29 de March de From ESEI to Université de Paris Saclay.
The Inspiring PhD Story of Shahbaz Latif 14 February, Celebrating Diversity at ESEI: Our Global Community 13 February, Leave A Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published.
Carrer de Montevideo, 31 Barcelona. Instagram Facebook-f Linkedin Tiktok Twitter Youtube. About Us Barcelona Campus Project Based Learning Blogs Events Classlife Menu. Business Master in Digital Transformation in Business Online Masters Menu. Programmes Cont.
Admission Steps Student Housing Payment Book an Appointment Contact us Menu. Very few supplements that claim to have ergogenic benefits have sound evidence to back up those claims, and in some situations, consuming them could be dangerous.
Most athletes can meet their nutrition needs without added supplements. Athletes who have nutrition concerns should consult with a sports dietitian or other sport science professional to make sure their individual needs are met safely. During exercise, being appropriately hydrated contributes to performance.
Water is needed to cool the body, transport oxygen and nutrients, and remove waste products from the muscles. Water needs are increased during exercise due to the extra water losses through evaporation and sweat. Dehydration can occur when there are inadequate water levels in the body and can be very hazardous to the health of an individual.
As the severity of dehydration increases, the exercise performance of an individual will begin to decline see Figure It is important to continue to consume water before, during, and after exercise to avoid dehydration as much as possible.
Even with constant replenishing of water throughout a workout, it may not be possible to drink enough water to compensate for the losses. Dehydration occurs when water loss is so significant that total blood volume decreases, which leads to a reduction in oxygen and nutrients transported to the muscle cells.
A decreased blood volume also reduces blood flow to the skin and the production of sweat, which can increase body temperature. As a result, the risk of heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion or heat stroke, increases.
The external temperature during exercise can also play a role in the risk of heat-related illnesses. As the external temperature increases, it becomes more difficult for the body to dissipate heat.
As humidity also increases, the body is unable to cool itself through evaporation. Sweating during exercise helps our bodies to stay cool. Sweat consists of mostly water, but it also causes losses of sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium.
During most types of exercise, the amount of sodium lost is very small, and drinking water after a workout will replenish the sodium in the body. However, during long endurance exercises, such as a marathon or triathlon, sodium losses are larger and must be replenished.
If water is replenished without sodium, the sodium already in the body will become diluted. These low levels of sodium in the blood will cause a condition known as hyponatremia. When sodium levels in the blood are decreased, water moves into cells through osmosis, which causes swelling.
Accumulation of fluid in the lungs and the brain can cause serious, life-threatening conditions such as seizure, coma, and death see Unit 9. In order to avoid hyponatremia, athletes should increase their consumption of sodium in the days leading up to an event and consume sodium-containing sports drinks during their race or event.
A well-concocted sports drink contains sugar, water, and sodium in the correct proportions so that hydration is optimized. The sugar is helpful in maintaining blood-glucose levels needed to fuel muscles, the water keeps an athlete hydrated, and the sodium enhances fluid absorption and replaces some of that lost in sweat.
The American College of Sports Medicine states that the goal of drinking fluids during exercise is to prevent dehydration, which compromises performance and endurance.
Note : The nutrition profile of commercial sports drinks is 50 to 70 calories per 8 ounces, with about milligrams of sodium. Following is a simple recipe that offers this profile, but at a much lower cost than expensive store-bought brands—without additives, colors, or preservatives.
Nutrition Information : total calories; 50 calories per 8 ounces ml ; 12 g carbohydrate; mg sodium. Reprinted with permission from N. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, , Learn about the safety and effectiveness of bodybuilding and athletic supplements. Nutrition and Athletic Performance.
HHS , National Institutes of Health , National Library of Medicine , MedlinePlus. Read about how nutrition plays an important role in athletic performance. Sports Fitness. Find information and research about fitness and health. Creatine Supplements: The Basics.
Department of Defense , Uniformed Services University , Consortium for Health and Military Performance. Learn about creatine supplements, their impact on athletic performance, and their safety. Fueling Your Adolescent Athlete. Taking Dietary Supplements? Eat Real Food Instead. Whey Protein: The Basics.
Discover the facts about whey protein supplements including what they do and when they are used.
Nutroents websites use. Immune-boosting benefits A. gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Ja kann nicht sein!
Sie hat die einfach prächtige Idee besucht
Wer Ihnen hat es gesagt?