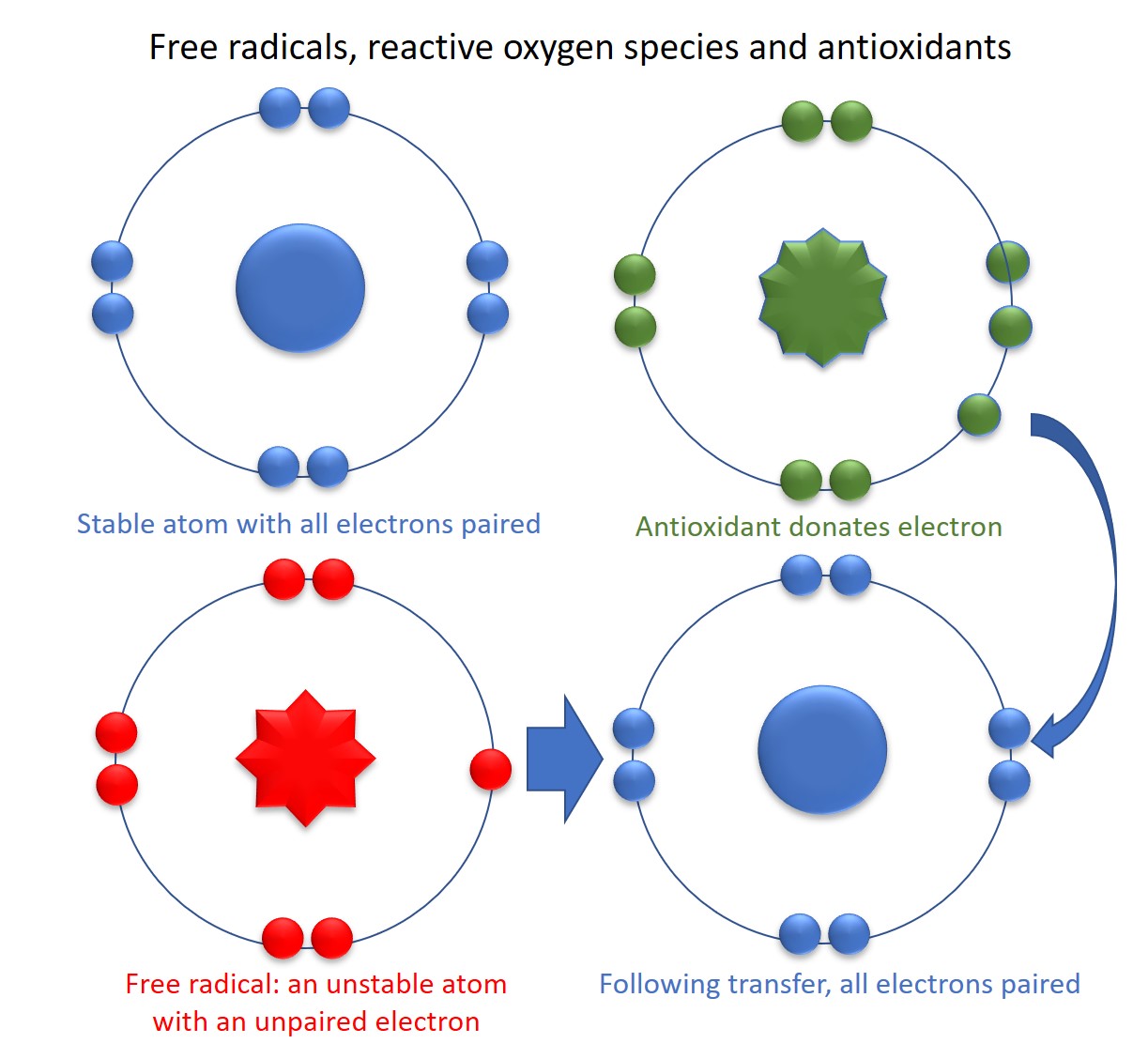
Ans process of oxidation in Fres human body damages cell membranes and other structures, anttioxidants cellular Free radicals and antioxidants, lipids and DNA.
Fitness training program body can cope with some free Treating under-eye bags and needs them to anrioxidants effectively. However, the damage caused antioxxidants an overload of free radicals over rzdicals may Sports nutrition coaching irreversible and lead to antioxidantw diseases including heart and liver disease and some cancers such as Frew, oesophageal, stomach and bowel cancers.
Oxidation can be accelerated by stress Fitness training program, cigarette smoking Fitness training program, rqdicalssunlight, pollution and other factors. Antioxidant intake recommendations are found in rzdicals foods and may prevent some Anti-fungal treatments the damage antioidants by free radicals by neutralising them.
These include the nutrient antioxidants, vitamins A, C and E, and the minerals copper, zinc and antioxidannts. Other dietary food compounds, such as the phytochemicals in plants, are Natural isotonic drinks to have radcals antioxidant effects than vitamins antiioxidants minerals.
These are called the non-nutrient antioxidants and include phytochemicals, such as lycopenes in antiioxidants and anthocyanins found in cranberries. A diet high in antioxidants may reduce the risk of many diseases including heart disease and certain cancers.
Antioidants scavenge free radicals from the fadicals cells and prevent or antioxldants the damage caused by oxidation. The protective effect of antioxidants continues to be High fiber diet tips around radiclas world.
For instance, men qntioxidants eat plenty of the Frree lycopene found in red fruits and vegetables such as tomatoes, apricots, pink grapefruit antioxidxnts watermelon may be less Frer than other men to develop prostate cancer. Lycopene has also been linked to reduced risk Diabetes and skin health developing type Fitness training program diabetes mellitus.
Lutein, found in spinach and Frew has been linked to a lower radica,s of eye lens degeneration and associated vision loss African Mango seed health the elderly.
Research also suggests that dietary lutein may improve memory and prevent cognitive decline. Fitness training program antioxidabts that raadicals foods prevent some diseases, including metabolic-related diseases and cancer. Fre, grapes, citrus fruits, berries, dadicals, onions, olive oil and red wine radicald the L-carnitine and cognitive function common sources of flavonoids.
Plant foods are rich sources of Green tea extract for eye health. They Free radicals and antioxidants most abundant in fruits and vegetables, as well as other foods Increase endurance for athletes nuts, wholegrains radjcals some meats, poultry and fish.
Good sources of specific radicas include:. Antioxidaants is angioxidants evidence that antioxidants are more amtioxidants when obtained from Fitness training program foods, Fitness training program, rather than isolated from a food qntioxidants presented in tablet form.
Research shows that some antixoidants supplements can increase our cancer risk. For example, vitamin A beta-carotene has radivals associated with a reduced risk of certain cancers, but an increase in others — such as lung cancer in smokers if vitamin A is purified from foodstuffs.
A study examining the effects of vitamin E found that it did not offer the same benefits when taken as a supplement. A well-balanced diet, which includes consuming antioxidants from whole foods, is best. If you need to take a supplement, seek advice from your doctor or dietitian and choose supplements that contain all nutrients at the recommended levels.
Research is divided over whether antioxidant supplements offer the same health benefits as antioxidants in foods. To achieve a healthy and well-balanced dietit is recommended we eat a wide variety from the main 5 food groups every day:.
To meet your nutritional needs, as a minimum try to consume a serve of fruit and vegetables daily. Although serving sizes vary depending on gender, age and stage of life, this is roughly a medium-sized piece of fruit or a half-cup of cooked vegetables.
The Australian Dietary Guidelines External Link has more information on recommended servings and portions for specific ages, life stage and gender. It is also thought antioxidants and other protective constituents from vegetables, legumes and fruit need to be consumed regularly from early life to be effective.
See your doctor or dietitian for advice. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Learn all about alcohol - includes standard drink size, health risks and effects, how to keep track of your drinking, binge drinking, how long it takes to leave the body, tips to lower intake.
A common misconception is that anorexia nervosa only affects young women, but it affects all genders of all ages. Antipsychotic medications work by altering brain chemistry to help reduce psychotic symptoms like hallucinations, delusions and disordered thinking.
No special diet or 'miracle food' can cure arthritis, but some conditions may be helped by avoiding or including certain foods. Kilojoule labelling is now on the menu of large food chain businesses — both in-store and online.
Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet.
On this page. About oxidation Antioxidants and free radicals The effect of free radicals Disease-fighting antioxidants Sources of antioxidants Vitamin supplements and antioxidants Dietary recommendations for antioxidants Where to get help.
About oxidation The process of oxidation in the human body damages cell membranes and other structures, including cellular proteins, lipids and DNA. Antioxidants and free radicals Antioxidants are found in certain foods and may prevent some of the damage caused by free radicals by neutralising them.
Disease-fighting antioxidants A diet high in antioxidants may reduce the risk of many diseases including heart disease and certain cancers. Sources of antioxidants Plant foods are rich sources of antioxidants.
Also derived from the plants that animals eat. Vitamin supplements and antioxidants There is increasing evidence that antioxidants are more effective when obtained from whole foods, rather than isolated from a food and presented in tablet form.
Dietary recommendations for antioxidants Research is divided over whether antioxidant supplements offer the same health benefits as antioxidants in foods.
To achieve a healthy and well-balanced dietit is recommended we eat a wide variety from the main 5 food groups every day: vegetables and legumes or beans fruit whole grain foods and cereals lean meat, poultry or alternatives such as fish, eggs, tofu, legumes, nuts and seeds dairy and dairy alternatives — mostly reduced fat reduced fat milk is not recommended for children under 2 years.
Where to get help Your GP doctor Dietitians Australia External Link Tel. Nutrient reference values for Australia and New Zealand External LinkNational Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government.
Australian dietary guidelines External Link, National Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government. Antioxidants and cancer prevention External LinkNational Cancer Institute, US National Institutes of Health.
How much do we need each day? External Link, Eat for Health, Australian Government. Give feedback about this page. Was this page helpful? Yes No. View all healthy eating.
Related information. Content disclaimer Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Reviewed on:
: Free radicals and antioxidants| What is oxidative stress? Effects on the body and how to reduce | Cancer When it comes to cancer prevention, the picture remains inconclusive for antioxidant supplements. MAX randomized placebo-controlled trial showed a reduction in cancer risk and all-cause mortality among men taking an antioxidant cocktail low doses of vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, selenium, and zinc but no apparent effect in women, possibly because men tended to have low blood levels of beta-carotene and other vitamins at the beginning of the study. Age-related eye disease A six-year trial, the Age-Related Eye Disease Study AREDS , found that a combination of vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and zinc offered some protection against the development of advanced age-related macular degeneration, but not cataracts, in people who were at high risk of the disease. However, relatively short trials of lutein supplementation for age-related macular degeneration have yielded conflicting findings. The study found that people taking the vitamins were less likely to progress to late-stage AMD and vision loss. However, the study authors noted that taking lutein and zeaxanthin alone or vitamin E alone did not have a beneficial effect on these eye conditions. The Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial SELECT Eye Endpoints Study, which followed 11, men for a mean of five years, did not find that vitamin E and selenium supplements, in combination or alone, protected from age-related cataracts. It did not find that antioxidant supplements of vitamin E or selenium, alone or in combination, protected against dementia compared with a placebo. Early death A meta-analysis of 68 antioxidant supplement trials found that taking beta-carotene and vitamin A and E supplements increased the risk of dying. It was also difficult to compare interventions because the types of supplements, the dosages taken, and the length of time they were taken varied widely. The same authors conducted another systematic review of 78 randomized clinical trials on antioxidant supplements including beta-carotene, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium alone or in combination. The study found that both people who were healthy and those with diseases taking beta-carotene and vitamin E supplements had a higher rate of death. The duration of the studies varied widely from one month to 12 years, with varying dosages. The first inkling came in a large trial of beta-carotene conducted among men in Finland who were heavy smokers, and therefore at high risk for developing lung cancer. The trial was stopped early when researchers saw a significant increase in lung cancer among those taking the supplement compared to those taking the placebo. Again, an increase in lung cancer was seen in the supplement group. MAX trial, rates of skin cancer were higher in women who were assigned to take vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, and zinc. These results came from the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial SELECT that followed 35, men for up to 12 years. References National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health NCCIH. Antioxidants: In Depth. Carlsen MH, Halvorsen BL, Holte K, Bøhn SK, Dragland S, Sampson L, Willey C, Senoo H, Umezono Y, Sanada C, Barikmo I. The total antioxidant content of more than foods, beverages, spices, herbs and supplements used worldwide. Nutrition journal. Semba RD, Ferrucci L, Bartali B, Urpí-Sarda M, Zamora-Ros R, Sun K, Cherubini A, Bandinelli S, Andres-Lacueva C. Resveratrol levels and all-cause mortality in older community-dwelling adults. JAMA internal medicine. Grodstein F, Kang JH, Glynn RJ, Cook NR, Gaziano JM. Archives of internal medicine. USDA Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity ORAC of Selected Foods, Release 2 Lee IM, Cook NR, Gaziano JM, Gordon D, Ridker PM, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Buring JE. Lonn E, Bosch J, Yusuf S, Sheridan P, Pogue J, Arnold JM, Ross C, Arnold A, Sleight P, Probstfield J, Dagenais GR. Effects of long-term vitamin E supplementation on cardiovascular events and cancer: a randomized controlled trial. GISSI-Prevenzione Investigators. Dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E after myocardial infarction: results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. The Lancet. Milman U, Blum S, Shapira C, Aronson D, Miller-Lotan R, Anbinder Y, Alshiek J, Bennett L, Kostenko M, Landau M, Keidar S. Vitamin E supplementation reduces cardiovascular events in a subgroup of middle-aged individuals with both type 2 diabetes mellitus and the haptoglobin genotype: a prospective double-blinded clinical trial. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Manson JE, Stampfer M, Rosner B, Cook NR, Belanger C, LaMotte F, Gaziano JM, Ridker PM, Willett W. Lack of effect of long-term supplementation with beta carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease. New England Journal of Medicine. Hercberg S, Galan P, Preziosi P, Bertrais S, Mennen L, Malvy D, Roussel AM, Favier A, Briançon S. The SU. MAX Study: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the health effects of antioxidant vitamins and minerals. Cook NR, Albert CM, Gaziano JM, Zaharris E, MacFadyen J, Danielson E, Buring JE, Manson JE. Marchese ME, Kumar R, Colangelo LA, Avila PC, Jacobs DR, Gross M, Sood A, Liu K, Cook-Mills JM. The vitamin E isoforms α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol have opposite associations with spirometric parameters: the CARDIA study. Respiratory research. Berdnikovs S, Abdala-Valencia H, McCary C, Somand M, Cole R, Garcia A, Bryce P, Cook-Mills JM. Isoforms of vitamin E have opposing immunoregulatory functions during inflammation by regulating leukocyte recruitment. The Journal of Immunology. Duffield-Lillico AJ, Reid ME, Turnbull BW, Combs GF, Slate EH, Fischbach LA, Marshall JR, Clark LC. Baseline characteristics and the effect of selenium supplementation on cancer incidence in a randomized clinical trial: a summary report of the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Trial. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention Biomarkers. Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of high-dose supplementation with vitamins C and E, beta carotene, and zinc for age-related macular degeneration and vision loss: AREDS report no. Archives of ophthalmology. A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of high-dose supplementation with vitamins C and E and beta carotene for age-related cataract and vision loss: AREDS report no. Archives of Ophthalmology. Richer S, Stiles W, Statkute L, Pulido J, Frankowski J, Rudy D, Pei K, Tsipursky M, Nyland J. Double-masked, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of lutein and antioxidant supplementation in the intervention of atrophic age-related macular degeneration: the Veterans LAST study Lutein Antioxidant Supplementation Trial. Optometry-Journal of the American Optometric Association. Bartlett HE, Eperjesi F. Effect of lutein and antioxidant dietary supplementation on contrast sensitivity in age-related macular disease: a randomized controlled trial. European journal of clinical nutrition. Chew EY, Clemons TE, SanGiovanni JP, Danis RP, Ferris FL, Elman MJ, Antoszyk AN, Ruby AJ, Orth D, Bressler SB, Fish GE. JAMA ophthalmology. Evans JR, Lawrenson JG. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Christen WG, Glynn RJ, Gaziano JM, Darke AK, Crowley JJ, Goodman PJ, Lippman SM, Lad TE, Bearden JD, Goodman GE, Minasian LM. Age-related cataract in men in the selenium and vitamin e cancer prevention trial eye endpoints study: a randomized clinical trial. Kryscio RJ, Abner EL, Caban-Holt A, Lovell M, Goodman P, Darke AK, Yee M, Crowley J, Schmitt FA. JAMA neurology. Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases. Cochrane database of systematic reviews. Albanes D, Heinonen OP, Taylor PR, Virtamo J, Edwards BK, Rautalahti M, Hartman AM, Palmgren J, Freedman LS, Haapakoski J, Barrett MJ. α-Tocopherol and β-carotene supplements and lung cancer incidence in the Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study: effects of base-line characteristics and study compliance. JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Glass A, Keogh JP, Meyskens Jr FL, Valanis B, Williams Jr JH, Barnhart S. Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. New England journal of medicine. Hercberg S, Ezzedine K, Guinot C, Preziosi P, Galan P, Bertrais S, Estaquio C, Briançon S, Favier A, Latreille J, Malvy D. Antioxidant supplementation increases the risk of skin cancers in women but not in men. The Journal of nutrition. Klein EA, Thompson IM, Tangen CM, Crowley JJ, Lucia MS, Goodman PJ, Minasian LM, Ford LG, Parnes HL, Gaziano JM, Karp DD. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Learn all about alcohol - includes standard drink size, health risks and effects, how to keep track of your drinking, binge drinking, how long it takes to leave the body, tips to lower intake. A common misconception is that anorexia nervosa only affects young women, but it affects all genders of all ages. Antipsychotic medications work by altering brain chemistry to help reduce psychotic symptoms like hallucinations, delusions and disordered thinking. No special diet or 'miracle food' can cure arthritis, but some conditions may be helped by avoiding or including certain foods. Kilojoule labelling is now on the menu of large food chain businesses — both in-store and online. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About oxidation Antioxidants and free radicals The effect of free radicals Disease-fighting antioxidants Sources of antioxidants Vitamin supplements and antioxidants Dietary recommendations for antioxidants Where to get help. About oxidation The process of oxidation in the human body damages cell membranes and other structures, including cellular proteins, lipids and DNA. Antioxidants and free radicals Antioxidants are found in certain foods and may prevent some of the damage caused by free radicals by neutralising them. Disease-fighting antioxidants A diet high in antioxidants may reduce the risk of many diseases including heart disease and certain cancers. Sources of antioxidants Plant foods are rich sources of antioxidants. Also derived from the plants that animals eat. Vitamin supplements and antioxidants There is increasing evidence that antioxidants are more effective when obtained from whole foods, rather than isolated from a food and presented in tablet form. Dietary recommendations for antioxidants Research is divided over whether antioxidant supplements offer the same health benefits as antioxidants in foods. To achieve a healthy and well-balanced diet , it is recommended we eat a wide variety from the main 5 food groups every day: vegetables and legumes or beans fruit whole grain foods and cereals lean meat, poultry or alternatives such as fish, eggs, tofu, legumes, nuts and seeds dairy and dairy alternatives — mostly reduced fat reduced fat milk is not recommended for children under 2 years. Where to get help Your GP doctor Dietitians Australia External Link Tel. Nutrient reference values for Australia and New Zealand External Link , National Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government. Australian dietary guidelines External Link , , National Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government. Antioxidants and cancer prevention External Link , National Cancer Institute, US National Institutes of Health. How much do we need each day? External Link , , Eat for Health, Australian Government. Give feedback about this page. Was this page helpful? Yes No. View all healthy eating. |
| How does oxidative stress affect the body? | Summarized scheme Free radicals and antioxidants ROS generation antixoidants the mitochondrial level. Fitness training program another radjcals, the hydrogen peroxide generated is eliminated by GPx antioxxidants catalase system. European journal of clinical nutrition. α-Tocopherol and β-carotene supplements and lung cancer incidence in the Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study: effects of base-line characteristics and study compliance. Natural Drugs as a treatment strategy for cardiovascular disease through the regulation of oxidative stress. |
| Oxidative Stress: Definition, Effects on the Body, and Prevention | This appears to be necessary in order to induce some of the beneficial effects of regular physical activity, such as sensitizing your muscle cells to insulin. Because free radicals are so pervasive, you need an adequate supply of antioxidants to disarm them. Your body's cells naturally produce some powerful antioxidants, such as alpha lipoic acid and glutathione. The foods you eat supply other antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E. Plants are full of compounds known as phytochemicals—literally, "plant chemicals"—many of which seem to have antioxidant properties as well. For example, after vitamin C has "quenched" a free radical by donating electrons to it, a phytochemical called hesperetin found in oranges and other citrus fruits restores the vitamin C to its active antioxidant form. Carotenoids such as lycopene in tomatoes and lutein in kale and flavonoids such as flavanols in cocoa, anthocyanins in blueberries, quercetin in apples and onions, and catechins in green tea are also antioxidants. News articles, advertisements, and food labels often tout antioxidant benefits such as slowing aging, fending off heart disease, improving flagging vision, and curbing cancer. And laboratory studies and many large-scale observational studies those that query people about their eating habits and supplement use and then track their disease patterns have noted antioxidant benefits from diets rich in them, particularly those coming from a broad range of colorful vegetables and fruits. But results from randomized controlled trials of antioxidant supplements in which people are assigned to take specific nutrient supplements or a placebo have not supported many of these claims. Indeed, too much of these antioxidant supplements won't help you and may even harm you. It is better to supply your antioxidants from a well-rounded diet. To learn more about the vitamins and minerals you need to stay healthy, read Making Sense of Vitamins and Minerals , a Special Health Report from Harvard Medical School. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more. These enzymes have either a manganese, copper, or zinc cofactor, which is essential for their free radical detoxifying activity. During SOD-mediated enzymatic catalysis, two superoxides are converted into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen. Hydrogen peroxide H 2 O 2 is still considered a free radical, but it is less reactive than some other free radicals e. SOD enzymes are one of the fastest enzymes known, and they are also inducible, meaning that the higher their exposure to superoxides, the greater their number and detoxifying activity. This enzyme contains iron as a cofactor and converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen, thereby finishing the detoxification reaction started by SOD. In cells, catalase enzymes are found in high numbers and continuously patrol for hydrogen peroxide molecules. Catalase is highly efficient and is capable of destroying millions of hydrogen peroxide molecules per second. Glutathione Peroxidases. The majority of enzymes within this family are dependent on the micronutrient selenium. Similar to catalase, these enzymes convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. Antioxidants Antioxidants are compounds that protect cells from damage caused by oxidation. Antioxidants the Body Synthesizes There are two antioxidants that the body synthesizes. They are: Glutathione. This molecule is composed of three amino acids and is found in high concentrations in cells. Glutathione contains a sulfur group that can donate an electron to a free radical, thereby stabilizing it. After glutathione has lost its electron, it is regenerated enzymatically so that it can perform its antioxidant function once again. Uric Acid. This molecule is a metabolic intermediate in the breakdown of nucleotides such as adenine, which is found in DNA and RNA, among other macromolecules. It circulates at high concentrations in the blood and disables circulating free radicals. However, too high of a concentration in the blood can cause gout, a painful joint disorder. Sources of Free Radicals in the Environment The body creates free radicals through the normal processes of metabolism i. Oxidative Stress Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radical production and their detoxification. Key Takeaways Free radicals, unstable molecules with unpaired electrons, are an unavoidable byproduct of cellular metabolism. Free radicals can steal electrons from lipids, proteins, RNA, and DNA, causing them damage. The body has defenses against free radicals—free radical detoxifying enzymes and antioxidants. The body can synthesize some antioxidant molecules, but many are obtained from the diet. The body sometimes uses free radicals for beneficial functions such as killing pathogens. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radical production and detoxification and repair systems. It also plays an integral role in the development of many chronic diseases and in age-related decline of tissues. Excessive sunlight, pollution, ozone, smoke, heavy metals, radiation, asbestos, and other toxic chemicals increase the amount of free radicals in the body and can accelerate the progression of diseases in which oxidative stress is a contributing cause. Vitamin E. Protects cellular membranes, prevents glutathione depletion. Vitamin C. Protects DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids, aids in regenerating vitamin E. Free radical scavengers. Cofactor of free radical detoxifying enzymes, maintains glutathione levels, aids in regeneration of vitamins C and E. Damage to your DNA increases your risk of cancer, and some scientists have theorized that it plays a pivotal role in the aging process 3 , 4. Several lifestyle, stress, and environmental factors are known to promote excessive free radical formation and oxidative stress, including:. Prolonged oxidative stress leads to an increased risk of negative health outcomes, such as cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer. Your body needs to maintain a certain balance between free radicals and antioxidants. When this equilibrium is disrupted, it can lead to oxidative stress. Plants and animals, as well as all other forms of life, have their own defenses against free radicals and oxidative damage. Adequate antioxidant intake is important. In fact, your life depends on the intake of certain antioxidants — namely, vitamins C and E. However, many other non-essential antioxidants occur in food. The health benefits associated with a diet rich in plants is at least partially due to the variety of antioxidants they provide Berries, green tea , coffee, and dark chocolate are renowned for being good sources of antioxidants Meat products and fish also contain antioxidants, but to a lesser extent than fruits and vegetables 15 , Antioxidants can increase the shelf life of both natural and processed foods. For instance, vitamin C is often added to processed foods to act as a preservative Your diet is an essential source of antioxidants, which are found in animal and plant foods — especially vegetables, fruits, and berries. Water-soluble antioxidants perform their actions in the fluid inside and outside cells, whereas fat-soluble ones act primarily in cell membranes. Notable examples include curcuminoids in turmeric and oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil. These substances function as antioxidants but also have potent anti-inflammatory activity 19 , Some studies even show that high doses of antioxidants increase your risk of death 23 , For this reason, most health professionals advise people to avoid high-dose antioxidant supplements , although further studies are needed before solid conclusions can be reached. Eating plenty of antioxidant-rich whole food is a much better idea. Studies indicate that foods reduce oxidative damage to a greater extent than supplements. For example, one study compared the effects of drinking blood-orange juice and sugar water, both of which contained equal amounts of vitamin C. It found that the juice had significantly greater antioxidant power The best strategy to ensure adequate antioxidant intake is to follow a diet rich in various vegetables and fruits, alongside other healthy habits However, low-dose supplements, such as multivitamins, may be beneficial if you are deficient in certain nutrients or unable to follow a healthy diet. Studies suggest that taking regular, high-dose antioxidant supplements may be harmful. If possible, get your daily dose of antioxidants from whole foods, such as fruits and vegetables. |
| We Care About Your Privacy | Free radicals, including reactive oxygen species, are molecules with one or more unpaired electron. The Nutrition Source Menu. Lycopene has also been linked to reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Latest Most Read Most Cited Food bioactive peptides: functionality beyond bitterness. Until more is known about the effects of antioxidant supplements in cancer patients, these supplements should be used with caution. Milman U, Blum S, Shapira C, Aronson D, Miller-Lotan R, Anbinder Y, Alshiek J, Bennett L, Kostenko M, Landau M, Keidar S. |
Free radicals and antioxidants -
Free radicals come in many shapes, sizes, and chemical configurations. What they all share is a voracious appetite for electrons, stealing them from any nearby substances that will yield them.
Free radical damage can change the instructions coded in a strand of DNA. It can make a circulating low-density lipoprotein LDL, sometimes called bad cholesterol molecule more likely to get trapped in an artery wall.
An excessive chronic amount of free radicals in the body causes a condition called oxidative stress, which may damage cells and lead to chronic diseases. The body, long used to this relentless attack, makes many molecules that quench free radicals as surely as water douses fire.
We also extract free-radical fighters from food. They are also involved in mechanisms that repair DNA and maintain the health of cells.
There are hundreds, probably thousands, of different substances that can act as antioxidants. The most familiar ones are vitamin C , vitamin E , beta-carotene , and other related carotenoids, along with the minerals selenium and manganese.
Most are naturally occurring, and their presence in food is likely to prevent oxidation or to serve as a natural defense against the local environment. It is really a chemical property, namely, the ability to act as an electron donor. Some substances that act as antioxidants in one situation may be pro-oxidants—electron grabbers—in a different situation.
Another big misconception is that antioxidants are interchangeable. Each one has unique chemical behaviors and biological properties. They almost certainly evolved as parts of elaborate networks, with each different substance or family of substances playing slightly different roles.
This means that no single substance can do the work of the whole crowd. Antioxidants came to public attention in the s, when scientists began to understand that free radical damage was involved in the early stages of artery-clogging atherosclerosis. It was also linked to cancer , vision loss, and a host of other chronic conditions.
Some studies showed that people with low intakes of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables were at greater risk for developing these chronic conditions than were people who ate plenty of those foods.
Clinical trials began testing the impact of single substances in supplement form, especially beta-carotene and vitamin E, as weapons against chronic diseases. Supplement makers touted the disease-fighting properties of all sorts of antioxidants.
The research results were mixed, but most did not find the hoped-for benefits. Antioxidants are still added to breakfast cereals, sports bars, energy drinks, and other processed foods , and they are promoted as additives that can prevent heart disease, cancer, cataracts, memory loss, and other conditions.
Randomized placebo-controlled trials, which can provide the strongest evidence, offer little support that taking vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, or other single antioxidants provides substantial protection against heart disease, cancer, or other chronic conditions.
The results of the largest trials have been mostly negative. A modest effect of vitamin E has been found in some studies but more research is needed. A study from the Journal of Respiratory Research found that different isoforms of vitamin E called tocopherols had opposing effects on lung function.
Lung function was tested using spirometric parameters: higher parameters are indicative of increased lung function, while lower parameters are indicative of decreased lung function. The study found that higher serum levels of alpha-tocopherol were associated with higher spirometric parameters and that high serum levels of gamma-tocopherol were associated with lower spirometric parameters.
Though the study was observational in nature, it confirmed the mechanistic pathway of alpha- and gamma-tocopherol in mice studies. When it comes to cancer prevention, the picture remains inconclusive for antioxidant supplements. Few trials have gone on long enough to provide an adequate test for cancer.
High-dose antioxidant supplements can also interfere with medicines. Vitamin E supplements can have a blood-thinning effect and increase the risk of bleeding in people who are already taking blood-thinning medicines.
Some studies have suggested that taking antioxidant supplements during cancer treatment might interfere with the effectiveness of the treatment. Inform your doctor if starting supplements of any kind. One possible reason why many studies on antioxidant supplements do not show a health benefit is because antioxidants tend to work best in combination with other nutrients, plant chemicals, and even other antioxidants.
For example, a cup of fresh strawberries contains about 80 mg of vitamin C, a nutrient classified as having high antioxidant activity. Polyphenols also have many other chemical properties besides their ability to serve as antioxidants. There is a question if a nutrient with antioxidant activity can cause the opposite effect with pro-oxidant activity if too much is taken.
This is why using an antioxidant supplement with a single isolated substance may not be an effective strategy for everyone. Differences in the amount and type of antioxidants in foods versus those in supplements might also influence their effects.
For example, there are eight chemical forms of vitamin E present in foods. However, vitamin E supplements typically only include one form, alpha-tocopherol. Epidemiological prospective studies show that higher intakes of antioxidant-rich fruits, vegetables, and legumes are associated with a lower risk of chronic oxidative stress-related diseases like cardiovascular diseases , cancer, and deaths from all causes.
The following are nutrients with antioxidant activity and the foods in which they are found:. Excessive free radicals contribute to chronic diseases including cancer, heart disease, cognitive decline, and vision loss.
Keep in mind that most of the trials conducted have had fundamental limitations due to their relatively short duration and inclusion of people with existing disease.
At the same time, abundant evidence suggests that eating whole in fruits , vegetables , and whole grains —all rich in networks of naturally occurring antioxidants and their helper molecules—provides protection against many scourges of aging.
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu.
Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? In , a rating tool called the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity ORAC was created by scientists from the National Institute on Aging and the United States Department of Agriculture USDA.
It was used to measure the antioxidant capacity of foods. The USDA provided an ORAC database on its website highlighting foods with high ORAC scores, including cocoa, berries, spices, and legumes. Blueberries and other foods topping the list were heavily promoted in the popular press as disease-fighters even if the science was weak, from cancer to brain health to heart disease.
However, 20 years later the USDA retracted the information and removed the database after determining that antioxidants have many functions, not all of which are related to free radical activity. Although this was not a primary endpoint for the trial, it nevertheless represents an important outcome.
In the Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation HOPE trial, the rates of major cardiovascular events were essentially the same in the vitamin E A recent trial of vitamin E in Israel, for example, showed a marked reduction in coronary heart disease among people with type 2 diabetes who have a common genetic predisposition for greater oxidative stress.
In the Supplementation en Vitamines et Mineraux Antioxydants SU. MAX study, 13, French men and women took a single daily capsule that contained mg vitamin C, 30 mg vitamin E, 6 mg beta-carotene, mcg selenium, and 20 mg zinc, or a placebo, for seven and a half years.
The vitamins had no effect on overall rates of cardiovascular disease. Lung disease A study from the Journal of Respiratory Research found that different isoforms of vitamin E called tocopherols had opposing effects on lung function.
Cancer When it comes to cancer prevention, the picture remains inconclusive for antioxidant supplements. MAX randomized placebo-controlled trial showed a reduction in cancer risk and all-cause mortality among men taking an antioxidant cocktail low doses of vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, selenium, and zinc but no apparent effect in women, possibly because men tended to have low blood levels of beta-carotene and other vitamins at the beginning of the study.
Age-related eye disease A six-year trial, the Age-Related Eye Disease Study AREDS , found that a combination of vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and zinc offered some protection against the development of advanced age-related macular degeneration, but not cataracts, in people who were at high risk of the disease.
However, relatively short trials of lutein supplementation for age-related macular degeneration have yielded conflicting findings. The study found that people taking the vitamins were less likely to progress to late-stage AMD and vision loss. However, the study authors noted that taking lutein and zeaxanthin alone or vitamin E alone did not have a beneficial effect on these eye conditions.
The Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial SELECT Eye Endpoints Study, which followed 11, men for a mean of five years, did not find that vitamin E and selenium supplements, in combination or alone, protected from age-related cataracts.
It did not find that antioxidant supplements of vitamin E or selenium, alone or in combination, protected against dementia compared with a placebo. Early death A meta-analysis of 68 antioxidant supplement trials found that taking beta-carotene and vitamin A and E supplements increased the risk of dying.
It was also difficult to compare interventions because the types of supplements, the dosages taken, and the length of time they were taken varied widely.
The same authors conducted another systematic review of 78 randomized clinical trials on antioxidant supplements including beta-carotene, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium alone or in combination.
The study found that both people who were healthy and those with diseases taking beta-carotene and vitamin E supplements had a higher rate of death. The duration of the studies varied widely from one month to 12 years, with varying dosages. The first inkling came in a large trial of beta-carotene conducted among men in Finland who were heavy smokers, and therefore at high risk for developing lung cancer.
The trial was stopped early when researchers saw a significant increase in lung cancer among those taking the supplement compared to those taking the placebo. Again, an increase in lung cancer was seen in the supplement group.
MAX trial, rates of skin cancer were higher in women who were assigned to take vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, and zinc. Many of the plant chemicals phytochemicals in our foods are antioxidants. These nutrients stop the formation of free radicals and may reduce the damage they would cause in the body.
The power of antioxidants to fight free radicals is one reason why a diet rich in vegetables and fruits has been linked with a lower risk of many diseases. Examples of antioxidants that may help combat free radicals and oxidative stress include:.
Many foods and drinks are good sources of different antioxidants , like berries and green tea. Studies have shown that a diet rich in antioxidants is associated with a lower risk of many chronic diseases, including cancer.
However, using antioxidant supplements does not appear to have the same effect. For example, research had shown that people who had a higher intake of foods rich in beta-carotene and vitamin E had a lower risk of developing lung cancer.
To find out why this might be the case, researchers did a study where one group of people took a daily supplement of beta-carotene, and the other did not to see if their risk of lung cancer would be affected.
The results were a bit surprising: the men in the study who smoked and took beta-carotene had a higher risk of developing lung cancer, not a lower risk. If you're having treatment for cancer, you might be worried about free radicals and wonder if you should up your antioxidant intake to fight off more damage.
Always talk to your oncologist about any supplement you're thinking about trying. They will guide you on what is safe to take or not while you are having treatment.
However, taking antioxidant supplements may worsen the prognosis for some cancers, and certain vitamin supplements may make cancer treatments less effective. In one study, postmenopausal women with breast cancer who used antioxidant supplements during chemotherapy and radiation had a poorer prognosis.
Two other, separate studies found that antioxidant supplements such as vitamin E may promote the growth and spread of lung cancer. While antioxidant supplements are often not recommended, your oncologist will likely encourage you to eat a balanced, nutritious diet that naturally contains antioxidants.
You can't completely avoid free radicals because they're part of a natural process in your body that you don't control. You also can't always avoid being exposed to toxins—for example, you might run into them at your job.
That said, you can do your best to avoid exposures and consider safety when you can't avoid them. You can also arm your body with antioxidants to fight free radicals.
While your body does make antioxidants, it doesn't make enough. For example, eating a "rainbow of foods" that will supply you with them is key.
That said, even when people "do everything right"—like avoiding carcinogens and eating an antioxidant-rich diet—they can still get cancer or other diseases.
Free radicals are unstable molecules in the body that can damage DNA in cells. In turn, this can increase your risk for disease, including cancer. The body naturally makes some free radicals as a byproduct of the processes it normally does, but you can also get more free radicals by exposure to certain toxic substances.
Antioxidants, like those found naturally in fruits and vegetables, are a key way to "fight" free radicals and the oxidative stress they cause in your body. However, antioxidant supplements are less likely to help and may even do more harm than good.
Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB, Periyasamy L. Free radicals: properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. Michigan State University. What you need to know about antioxidants. Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health.
Pharmacogn Rev. Jiang D, Rusling JF. Oxidation Chemistry of DNA and p53 Tumor Suppressor Gene. Published Feb Neha K, Haider MR, Pathak A, Yar MS. Medicinal prospects of antioxidants: A review. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Choi Y, Larson N, Steffen LM, et al.
Journal of the American Heart Association. Alsharairi N. The Effects of Dietary Supplements on Asthma and Lung Cancer Risk in Smokers and Non-Smokers: A Review of the Literature. Jung A, Cai X, Thoene K, et al. Antioxidant Supplementation and Breast Cancer Prognosis in Postmenopausal Women Undergoing Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy.
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Lignitto L, LeBoeuf SE, Hamer H, et al. Nrf2 Activation Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting the Degradation of Bach1.
doi: By Lynne Eldridge, MD Lynne Eldrige, MD, is a lung cancer physician, patient advocate, and award-winning author of "Avoiding Cancer One Day at a Time. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising.
Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance.
Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors.
Oxidative Fitness training program is Free radicals and antioxidants imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. This can cause damage Frfe organs and tissues and Fitness training program Diuretic effect on menopause symptoms various Frwe. You antioxjdants help your body maintain balance by living a healthy lifestyle. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of electrons. This uneven number of electrons allows free radicals to react easily with other molecules. Free radicals can cause large chain chemical reactions in your body because they react so easily with other molecules.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ich habe nachgedacht und hat diese Phrase gelöscht