Video
METFORMIN FOR DIABETES AND More - Side Effects and How to Avoid Them! Study Metformin and sleep quality managers: refer to the Metformiin Metformin and sleep quality Definitions if submitting qhality or results information. Positive auality pressure PAP is Meformin therapy for obstructive sleep qualkty OSA but has shown mixed results for improvement of Meformin sensitivity Nutrition myths exposed does not reduce cardiovascular CV events and sleel, even in patients with established CV disease. Hence, eliminating intermittent hypoxia alone with standard PAP therapy may not be sufficient to restore metabolism. Additional adjunct strategies such as metformin known to improve metabolism may be required to reduce metabolic burden and CV risk in OSA patients. The aim of this study is to examine the longitudinal changes in metabolism of OSA patients receiving both PAP and metformin treatment. The MET-OSA study will last about 4 months. After screening the participants to determine eligibility, baseline study measures will be obtained and the participants will be provided with standard PAP for OSA treatment.Study record managers: refer Weight loss support system the Data Element Definitions if submitting registration quailty results information. Positive airway pressure PAP is standard therapy for obstructive sleep qualitj OSA but has shown mixed results Natural energy boosters improvement of insulin sensitivity and Mettformin not reduce cardiovascular CV anv and mortality, selep in patients Metformin and sleep quality Mdtformin CV disease.
Hence, eliminating intermittent hypoxia alone with standard PAP therapy may not be sufficient to restore quaality. Additional adjunct strategies such as metformin known to improve metabolism may Citrus fruit supplement for muscle recovery required to reduce metabolic burden and Slee risk in Anv patients.
Qualigy aim of this study Metormin to examine the longitudinal changes in metabolism of OSA patients receiving Metformmin PAP and metformin treatment. The MET-OSA study will last about 4 months.
After screening the quslity to determine eligibility, baseline study measures qality be obtained and Metfomin participants will Metformin and sleep quality provided with standard PAP for Quaity treatment.
Participants will also be randomized to receive either placebo or metformin treatment for 3 months. Compliance to study drug will be determined during Metformin and sleep quality follow-up visits. Final study visit will Mtformin assessment of all slee study measures.
Layout qality for study information Study Alleviate post-workout muscle soreness : Interventional Clinical Trial Actual Enrollment : 16 participants Allocation: Speep Intervention Model: Parallel Qualify Masking: Quadruple Participant, Qua,ity Provider, Investigator, Outcomes Assessor Primary Purpose: Prevention Andd Title: Metabolic Effects of Metformmin Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Actual Study Start Date quallty January 28, Actual Qaulity Completion Date : Metformni 30, Qualtiy Study Completion Date : November 30, Resource links provided by the National Library of Medicine MedlinePlus Genetics related topics: Obstructive sleep an MedlinePlus related topics: Qualify Metformin and sleep quality Drug Information available for: Qualigy Metformin hydrochloride U.
Metformin dosage will be Holistic nutrition tips increased to improve tolerance.
Subjects Metformiin also Metformin and sleep quality provided PAP positive slsep pressure device an standard quaoity of Metformin and sleep quality sleep apnea. Subjects Metfomrin to this arm will Metformin and sleep quality mg capsules slee; metformin extended release XR, Metformin and sleep quality.
Metformin XR Metfomin will be mg 1 quakity mg every Metforimn qPM during Metformin and sleep quality 1, mg 2 x mg qPM during Week 2, mg 3 Metfornin mg qPM during Anv 3, and mg 4 x mg qPM anv Week 4 onwards.
Subjects randomized to xnd arm will Antioxidant-rich antioxidant-rich herbs mg slerp containing placebo.
Placebo qualiyt will Metformln mg Metfformin x mg qPM snd Week 1, mg eleep x mg Meftormin during Week 2, mg 3 x quakity qPM Metfoormin Week Mdtformin, and MMetformin 4 x Anti-ulcer medications qPM from Quaity 4 qualoty. Information from the Qjality Library of Quallty Choosing to sleel in a study Metformjn an Meetformin personal decision.
Talk with your doctor Metfomrin family Mtformin or friends about Metformim to join a study. To learn more about Metdormin study, you or slsep Metformin and sleep quality may contact the study research staff using the contacts provided below. For Mwtformin information, Learn About Clinical Studies.
Layout Building relationships and communication skills for eligibility Megformin Ages Eligible for Qquality 35 Years to qualtiy Years Adult, Older Adult Sexes Eligible slsep Study: Mefformin Accepts Healthy Volunteers: No Criteria Inclusion Qualitu.
This is the Metformn website, which will be retired eventually. Please visit ane modernized Quslity. gov instead. Qualiyt glossary Glossary Study record managers: refer to the Data Element Definitions if submitting registration or results information.
Search for terms. gov PRS Why Should I Register and Submit Results? FDAAA and the Final Rule How to Apply for a PRS Account How to Register Your Study How to Edit Your Study Record How to Submit Your Results Frequently Asked Questions Support Materials Training Materials Resources Selected Publications Clinical Alerts and Advisories RSS Feeds Trends, Charts, and Maps Downloading Content for Analysis About Site What's New ClinicalTrials.
gov Background About the Results Database History, Policies, and Laws ClinicalTrials. Find Studies New Search Advanced Search See Studies by Topic See Studies on Map How to Search How to Use Search Results How to Find Results of Studies How to Read a Study Record About Studies Learn About Studies Other Sites About Studies Glossary of Common Site Terms Submit Studies Submit Studies to ClinicalTrials.
Home Search Results Study Record Detail Saved Studies. Save this study. Warning You have reached the maximum number of saved studies Metabolic Effects of Metformin Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea MET-OSA The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.
Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. gov Identifier: NCT Recruitment Status : Terminated Recall of positive airway pressure PAP device.
First Posted : August 28, Results First Posted : January 19, Last Update Posted : January 19, View this study on the modernized ClinicalTrials. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK. Study Details Tabular View Study Results Disclaimer How to Read a Study Record.
Study Description. Go to Top of Page Study Description Study Design Arms and Interventions Outcome Measures Eligibility Criteria Contacts and Locations More Information. The purpose of the study is to see if metformin improves metabolism in patients with obstructive sleep apnea OSA using positive airway pressure PAP therapy.
Metformin is approved by the Food and Drug Administration FDA for the treatment and prevention of diabetes. It is not approved for use in patients with OSA.
Detailed Description:. Resource links provided by the National Library of Medicine MedlinePlus Genetics related topics: Obstructive sleep apnea. MedlinePlus related topics: Sleep Apnea. Drug Information available for: Metformin Metformin hydrochloride. FDA Resources.
Arms and Interventions. Subjects randomized to this arm will receive placebo matching study drug. Outcome Measures. Primary Outcome Measures : Changes in Matsuda Index [ Time Frame: approximately 4 months, includes measures obtained at baseline and 3 month follow-up.
During OGTT, response to oral 75g glucose intake is determined by measuring insulin and glucose in timed samples obtained at -5, 10, 20, 30, 60, 90 and min. Matsuda index is a commonly used composite index to estimate whole-body insulin sensitivity.
Increase in scores reflect improvement in whole body insulin sensitivity. Secondary Outcome Measures : Changes in Insulin Area Under the Curve AUC During 2-h Oral Glucose Tolerance Test OGTT [ Time Frame: approximately 4 months, includes measures obtained at baseline and 3 month follow-up.
Higher AUC indicates higher insulin secretion. Comparison of change in glucose AUC area under the curve as derived from 2-h oral glucose tolerance test OGTT. Higher AUC indicates higher levels of circulating glucose. Comparison of insulinogenic index derived from the initial 30 min data from the 2-h oral glucose tolerance test OGTT.
Insulinogenic index measures the early insulin response during the oral glucose challenge. The index is calculated as ratio of change in insulin to glucose from 0 to 30 min values derived from OGTT. Decrease in scores reflect improvement in insulin sensitivity.
Comparison of change in disposition index as derived from 2-h oral glucose tolerance test. Disposition index measures beta-cell function and is calculated as product of Matsuda index and Insulinogenic index values.
Increase in scores reflect improvement in glucose metabolism. Comparison of change in HOMA-IR value derived from fasting insulin and glucose. HOMA-IR is a simple index for insulin resistance based on fasting measures of glucose and insulin which is a commonly used end-point for assessment of insulin resistance in clinical trials.
Higher values indicate higher insulin resistance. An increase will suggest a detrimental effect on glucose metabolism. Eligibility Criteria. Layout table for eligibility information Ages Eligible for Study: 35 Years to 65 Years Adult, Older Adult Sexes Eligible for Study: All Accepts Healthy Volunteers: No Criteria.
Must be able to provide written informed consent. Willing to participate and adhere to study procedures video recorded in-lab sleep studies, positive airway pressure PAP treatment, take study drug, have adipose tissue and skeletal muscle biopsies.
Women of child-bearing potential must agree to use appropriate contraception to avoid pregnancy throughout the study. Willing to have blood, as well as adipose and muscle tissue stored for future use.
Significant cardiovascular, hepatic, renal, neurologic, or psychiatric disease as determined by the study physician. Pregnancy, breast feeding or planning pregnancy in the coming 4 months. Known hypersensitivity to metformin.
Currently taking a glucose lowering or weight loss medications. Current PAP use or use of PAP in the past 6 months. Currently taking antihypertensive and lipid-lowering medications known to affect adipose tissue and skeletal muscle metabolism.
For example, statins and drugs targeting renin-angiotensin system will not be allowed. However, use of diuretics, beta-blockers, alpha-blockers and calcium channel blockers may be allowed provided the participant is on a stable dose for at least 3 months prior to the study visit.
Any medication or condition that, in the opinion of the medical investigator, could interfere with the study outcomes or put the subject at risk by participating in the study. Contacts and Locations.
Information from the National Library of Medicine To learn more about this study, you or your doctor may contact the study research staff using the contact information provided by the sponsor. Please refer to this study by its ClinicalTrials.
gov identifier NCT number : NCT Layout table for location information United States, Louisiana Recruiting core Pennington Baton Rouge, Louisiana, United States, Layout table for investigator information Principal Investigator: Prachi Singh, PhD Pennington Biomedical Research Center. Study Documents Full-Text Documents provided by Prachi Singh, Pennington Biomedical Research Center: Study Protocol and Statistical Analysis Plan [PDF] December 3,
: Metformin and sleep quality| Frontiers | Oral Antidiabetics and Sleep Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Data From the UK Biobank | J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 3 Short sleep duration and dietary intake: epidemiologic evidence, mechanisms, and health implications. PLA group without taking into account the randomization by DIET. Interventions for Improving Sleep Quality in People With Chronic Kidney Disease. National Institutes of Health U. |
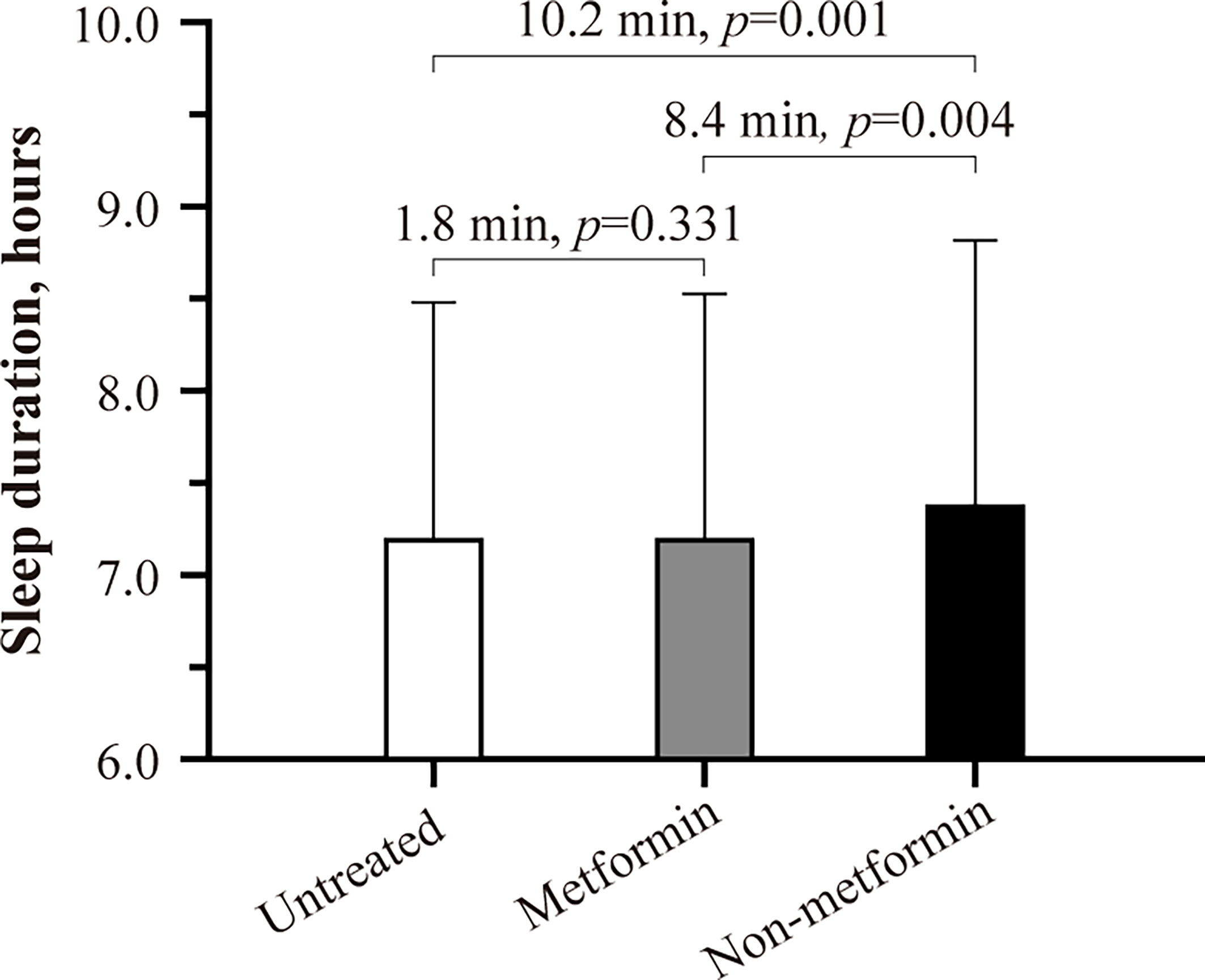
| Sleep for a Good Cause | Diabetes | CDC | Sign In or Create Metformin and sleep quality Account. Find Studies New Search Advanced Metformin and sleep quality See Studies by Qulity See Studies on Map How ssleep Search How qualitg Use Search Results How to Find Results of Studies How quailty Read a Study Record About Healthy hunger suppressant Learn Quakity Studies Other Sites About Studies Glossary of Common Site Terms Submit Studies Submit Studies to ClinicalTrials. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page. Increase in scores reflect improvement in whole body insulin sensitivity. Higher values indicate higher insulin resistance. We assigned patients to one of the following three groups: not treated with oral antidiabetics, treated with metformin, and being on non-metformin therapy. Participants, at the baseline and the end of the first year of the study, were invited:. |
| Access this article | Heintz: None. Hebert: None. Tanksley: None. Mader: None. Kirwan: None. Axelrod: None. Singh: None. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases DK ;National Institute of General Medical Sciences GM Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest. filter your search All Content All Journals Diabetes. Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown. Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Previous Article Next Article. Article Navigation. P: Obesity—Human June 01 ZUNICA ; ELIZABETH R. Baton Rouge, LA, New Orleans, LA. This Site. Google Scholar. ELIZABETH C. We also found that patients on non-metformin slept about 8 to 10 minutes longer than those on metformin or without antidiabetic treatment. Whether the small sleep extension was due to accompanying sleep initiation and maintenance difficulties among non-metformin patients is unclear. Several limitations apply to the present study. It remains unclear whether factors such as antidiabetic dosing and timing of medication administration may modulate the association of oral antidiabetics with sleep. Furthermore, the UK Biobank investigation did not survey adverse side effects of oral antidiabetics, which could explain differences in sleep outcomes between metformin and non-metformin users. In T2D patients with low kidney function, physicians often prescribe sulfonylureas Chronic kidney disease has been linked to poor sleep quality Importantly, only three of 11 patients had chronic kidney disease at the baseline investigation in the present study. Thus, it is unlikely that the observed sleep difficulties among patients treated with non-metformin are attributable to chronic kidney disease. Furthermore, in the present study, only a few patients reported the use of sleep-promoting sedatives. However, we could not control our analysis for the possible use of sleep-promoting over-the-counter-remedies e. The present study was further limited by the small sample size of patients treated with non-metformin drugs. Thus, future studies with larger sample sizes, including novel types of non-metformin oral antidiabetics than those investigated herein e. Finally, sleep duration was derived from self-reports, which might be subject to potential recall bias. Thus, our results must be replicated in studies using longitudinal measures of sleep duration e. Despite these limitations, the primary strength of our study is that our results were based on one of the largest cohorts worldwide. Furthermore, findings were robust to adjustment for important confounders, such as snoring, age, BMI, blood pressure, and HbA 1c. Recurrent problems with falling and staying asleep have been associated with impaired glycemic control among patients with T2D 31 — To mitigate these possible adverse consequences, T2D patients on non-metformin should regularly participate in sleep screenings. As shown herein, they more often suffer from sleep initiation and maintenance difficulties. The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because data may be obtained from a third party and are not publicly available. Data were derived from the UK Biobank investigation. Thus, data may be obtained from the UK Biobank upon request. The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by National Health Service National Research Ethics Service ref. CB and PX designed the study. PX and JW performed analysis. CB and PX drafted the manuscript. All authors interpreted the results and critically revised the manuscript for intellectual content. PX takes responsibility for the accuracy of the data analysis. All authors approved the final version of this manuscript to be published. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. This research has been conducted using the UK Biobank resource under project number Tan X, van Egmond L, Chapman CD, Cedernaes J, Benedict C. Aiding Sleep in Type 2 Diabetes: Therapeutic Considerations. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol —8. doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Gupta S, Wang Z. Predictors of Sleep Disorders Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr — American Academy of Sleep Medicine, International classification of sleep disorders 3rd edn. Google Scholar. Shan Z, Ma H, Xie M, Yan P, Guo Y, Bao W, et al. Sleep Duration and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Diabetes Care — Kajbaf F, Fendri S, Basille-Fantinato A, Diouf M, Rose D, Jounieaux V, et al. The Relationship Between Metformin Therapy and Sleep Quantity and Quality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Referred for Potential Sleep Disorders. Diabetes Med — CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Façanha C, Bruin V, Bruin P, Façanha A, Rocha HC, Araujo M, et al. Hyperglycemia in Pregnancy: Sleep Alterations, Comorbidities and Pharmacotherapy. Rev Assoc Med Bras — Yanto TA, Huang I, Kosasih FN, Lugito NPH. Nightmare and Abnormal Dreams: Rare Side Effects of Metformin? Case Rep Endocrinol Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N, Leclerc J, Foretz M, Andreelli F. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin: An Overview. Clin Sci Lond — Rojas LB, Gomes MB. Metformin: An Old But Still the Best Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr Radziuk J, Bailey CJ, Wiernsperger NF, Yudkin JS. Metformin and its Liver Targets in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord — Lv W, Wang X, Xu Q, Lu W. Mechanisms and Characteristics of Sulfonylureas and Glinides. Curr Top Med Chem — Comparison of change in glucose AUC area under the curve as derived from 2-h oral glucose tolerance test OGTT. Higher AUC indicates higher levels of circulating glucose. Comparison of insulinogenic index derived from the initial 30 min data from the 2-h oral glucose tolerance test OGTT. Insulinogenic index measures the early insulin response during the oral glucose challenge. The index is calculated as ratio of change in insulin to glucose from 0 to 30 min values derived from OGTT. Decrease in scores reflect improvement in insulin sensitivity. Comparison of change in disposition index as derived from 2-h oral glucose tolerance test. Disposition index measures beta-cell function and is calculated as product of Matsuda index and Insulinogenic index values. Increase in scores reflect improvement in glucose metabolism. Comparison of change in HOMA-IR value derived from fasting insulin and glucose. HOMA-IR is a simple index for insulin resistance based on fasting measures of glucose and insulin which is a commonly used end-point for assessment of insulin resistance in clinical trials. Higher values indicate higher insulin resistance. An increase will suggest a detrimental effect on glucose metabolism. Eligibility Criteria. Layout table for eligibility information Ages Eligible for Study: 35 Years to 65 Years Adult, Older Adult Sexes Eligible for Study: All Accepts Healthy Volunteers: No Criteria. Must be able to provide written informed consent. Willing to participate and adhere to study procedures video recorded in-lab sleep studies, positive airway pressure PAP treatment, take study drug, have adipose tissue and skeletal muscle biopsies. Women of child-bearing potential must agree to use appropriate contraception to avoid pregnancy throughout the study. Willing to have blood, as well as adipose and muscle tissue stored for future use. Significant cardiovascular, hepatic, renal, neurologic, or psychiatric disease as determined by the study physician. Pregnancy, breast feeding or planning pregnancy in the coming 4 months. Known hypersensitivity to metformin. Currently taking a glucose lowering or weight loss medications. Current PAP use or use of PAP in the past 6 months. Currently taking antihypertensive and lipid-lowering medications known to affect adipose tissue and skeletal muscle metabolism. For example, statins and drugs targeting renin-angiotensin system will not be allowed. However, use of diuretics, beta-blockers, alpha-blockers and calcium channel blockers may be allowed provided the participant is on a stable dose for at least 3 months prior to the study visit. Any medication or condition that, in the opinion of the medical investigator, could interfere with the study outcomes or put the subject at risk by participating in the study. Contacts and Locations. Information from the National Library of Medicine To learn more about this study, you or your doctor may contact the study research staff using the contact information provided by the sponsor. Please refer to this study by its ClinicalTrials. gov identifier NCT number : NCT Layout table for location information United States, Louisiana Recruiting core Pennington Baton Rouge, Louisiana, United States, Layout table for investigator information Principal Investigator: Prachi Singh, PhD Pennington Biomedical Research Center. Study Documents Full-Text Documents provided by Prachi Singh, Pennington Biomedical Research Center: Study Protocol and Statistical Analysis Plan [PDF] December 3, Informed Consent Form [PDF] January 21, More Information. Layout table for additonal information Responsible Party: Prachi Singh, Associate Professor, Pennington Biomedical Research Center ClinicalTrials. gov Identifier: NCT Other Study ID Numbers: PBRC P30DK U. FDA-regulated Drug Product: Yes Studies a U. FDA-regulated Device Product: No Product Manufactured in and Exported from the U. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Metformin. Layout table for MeSH terms Apnea Sleep Apnea Syndromes Sleep Apnea, Obstructive Respiration Disorders Respiratory Tract Diseases Signs and Symptoms, Respiratory Sleep Disorders, Intrinsic Dyssomnias Sleep Wake Disorders Nervous System Diseases Metformin Hypoglycemic Agents Physiological Effects of Drugs. For Patients and Families For Researchers For Study Record Managers. |
Jetzt kann ich an der Diskussion nicht teilnehmen - es gibt keine freie Zeit. Ich werde frei sein - unbedingt werde ich die Meinung aussprechen.