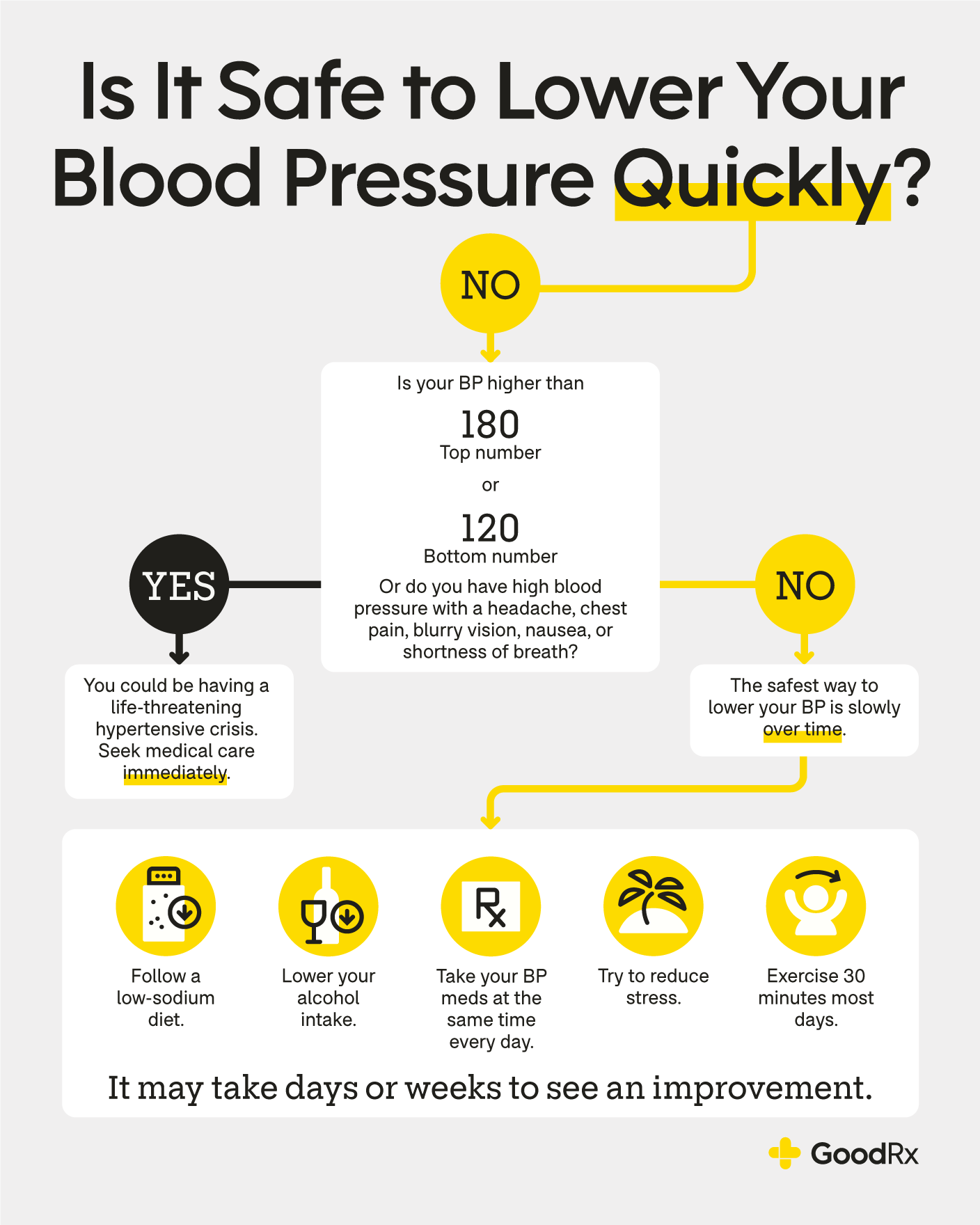
Ways to lower blood pressure -
Ambulatory monitoring. A longer blood pressure monitoring test may be done to check blood pressure at regular times over six or 24 hours. This is called ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. However, the devices used for the test aren't available in all medical centers.
Check with your insurer to see if ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is a covered service. Lab tests. Blood and urine tests are done to check for conditions that can cause or worsen high blood pressure. For example, tests are done to check your cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
You may also have lab tests to check your kidney, liver and thyroid function. Electrocardiogram ECG or EKG. This quick and painless test measures the heart's electrical activity. It can tell how fast or how slow the heart is beating.
During an electrocardiogram ECG , sensors called electrodes are attached to the chest and sometimes to the arms or legs. Wires connect the sensors to a machine, which prints or displays results. This noninvasive exam uses sound waves to create detailed images of the beating heart.
It shows how blood moves through the heart and heart valves. Taking your blood pressure at home Your health care provider may ask you to regularly check your blood pressure at home.
Home blood pressure monitors are available at local stores and pharmacies. More Information. Blood pressure chart. Blood pressure test. Your health care provider may recommend that you make lifestyle changes including: Eating a heart-healthy diet with less salt Getting regular physical activity Maintaining a healthy weight or losing weight Limiting alcohol Not smoking Getting 7 to 9 hours of sleep daily Sometimes lifestyle changes aren't enough to treat high blood pressure.
Medications The type of medicine used to treat hypertension depends on your overall health and how high your blood pressure is.
Medicines used to treat high blood pressure include: Water pills diuretics. Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors.
These drugs help relax blood vessels. They block the formation of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels. Examples include lisinopril Prinivil, Zestril , benazepril Lotensin , captopril and others. Angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs.
These drugs also relax blood vessels. They block the action, not the formation, of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels. angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs include candesartan Atacand , losartan Cozaar and others.
Other medicines sometimes used to treat high blood pressure If you're having trouble reaching your blood pressure goal with combinations of the above medicines, your provider may prescribe: Alpha blockers.
These medicines reduce nerve signals to blood vessels. They help lower the effects of natural chemicals that narrow blood vessels. Alpha blockers include doxazosin Cardura , prazosin Minipress and others.
Alpha-beta blockers. Alpha-beta blockers block nerve signals to blood vessels and slow the heartbeat. They reduce the amount of blood that must be pumped through the vessels. Alpha-beta blockers include carvedilol Coreg and labetalol Trandate. Aldosterone antagonists. These drugs may be used to treat resistant hypertension.
They block the effect of a natural chemical that can lead to salt and fluid buildup in the body. Examples are spironolactone Aldactone and eplerenone Inspra. These medicines stop the muscles in the artery walls from tightening.
This prevents the arteries from narrowing. Examples include hydralazine and minoxidil. Central-acting agents. These medicines prevent the brain from telling the nervous system to increase the heart rate and narrow the blood vessels. Examples include clonidine Catapres, Kapvay , guanfacine Intuniv and methyldopa.
Treating resistant hypertension You may have resistant hypertension if: You take at least three different blood pressure drugs, including a diuretic. But your blood pressure remains stubbornly high. You're taking four different medicines to control high blood pressure.
Your care provider should check for a possible second cause of the high blood pressure. Treating resistant hypertension may involve many steps, including: Changing blood pressure medicines to find the best combination and dosage. Reviewing all your medicines, including those bought without a prescription.
Checking blood pressure at home to see if medical appointments cause high blood pressure. This is called white coat hypertension. Eating healthy, managing weight and making other recommended lifestyle changes. High blood pressure during pregnancy If you have high blood pressure and are pregnant, discuss with your care providers how to control blood pressure during your pregnancy.
Potential future treatments Researchers have been studying the use of heat to destroy specific nerves in the kidney that may play a role in resistant hypertension. Request an appointment. Alpha blockers.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers. Show more related information. Choosing blood pressure medicines. Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain?
Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Clinical trials. Try these heart-healthy strategies: Eat healthy foods.
Eat a healthy diet. Try the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension DASH diet. Choose fruits, vegetables, whole grains, poultry, fish and low-fat dairy foods.
Get plenty of potassium from natural sources, which can help lower blood pressure. Eat less saturated fat and trans fat. Use less salt. Processed meats, canned foods, commercial soups, frozen dinners and certain breads can be hidden sources of salt.
Check food labels for the sodium content. Limit foods and beverages that are high in sodium. A sodium intake of 1, mg a day or less is considered ideal for most adults. But ask your provider what's best for you. Limit alcohol.
Even if you're healthy, alcohol can raise your blood pressure. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women, and up to two drinks a day for men. One drink equals 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine or 1.
Don't smoke. Tobacco injures blood vessel walls and speeds up the process of hardening of the arteries. If you smoke, ask your care provider for strategies to help you quit.
Maintain a healthy weight. If you're overweight or have obesity, losing weight can help control blood pressure and lower the risk of complications. Ask your health care provider what weight is best for you.
In general, blood pressure drops by about 1 mm Hg with every 2. In people with high blood pressure, the drop in blood pressure may be even more significant per kilogram of weight lost.
Practice good sleep habits. Poor sleep may increase the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. Adults should aim to get 7 to 9 hours of sleep daily. Kids often need more. Go to bed and wake at the same time every day, including on weekends. If you have trouble sleeping, talk to your provider about strategies that might help.
Manage stress. Find ways to help reduce emotional stress. Getting more exercise, practicing mindfulness and connecting with others in support groups are some ways to reduce stress.
Try slow, deep breathing. Practice taking deep, slow breaths to help relax. Some research shows that slow, paced breathing 5 to 7 deep breaths per minute combined with mindfulness techniques can reduce blood pressure. There are devices available to promote slow, deep breathing.
According to the American Heart Association, device-guided breathing may be a reasonable nondrug option for lowering blood pressure.
It may be an good option if you have anxiety with high blood pressure or can't tolerate standard treatments. High blood pressure and exercise.
Medication-free hypertension control. Stress and high blood pressure. Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe?
Resperate: Can it help reduce blood pressure? How to measure blood pressure using a manual monitor. How to measure blood pressure using an automatic monitor.
What is blood pressure? These supplements include: Fiber, such as blond psyllium and wheat bran Minerals, such as magnesium, calcium and potassium Folic acid Supplements or products that increase nitric oxide or widen blood vessels — called vasodilators — such as cocoa, coenzyme Q10, L-arginine and garlic Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, high-dose fish oil supplements and flaxseed Researchers are also studying whether vitamin D can reduce blood pressure, but evidence is conflicting.
L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure? Some things you can do to help manage the condition are: Take medicines as directed. If side effects or costs pose problems, ask your provider about other options. Don't stop taking your medicines without first talking to a care provider.
Schedule regular health checkups. It takes a team effort to treat high blood pressure successfully. Work with your provider to bring your blood pressure to a safe level and keep it there. Know your goal blood pressure level. Choose healthy habits. Eat healthy foods, lose excess weight and get regular physical activity.
If you smoke, quit. Say no to extra tasks, release negative thoughts, and remain patient and optimistic. Ask for help. Sticking to lifestyle changes can be difficult, especially if you don't see or feel any symptoms of high blood pressure.
It may help to ask your friends and family to help you meet your goals. Join a support group. You may find that talking about any concerns with others in similar situations can help.
What you can do Write down any symptoms that you're having. High blood pressure rarely has symptoms, but it's a risk factor for heart disease.
Let your care provider know if you have symptoms such as chest pains or shortness of breath. Doing so can help your provider decide how aggressively to treat your high blood pressure.
Write down important medical information, including a family history of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart disease, stroke, kidney disease or diabetes, and any major stresses or recent life changes.
Make a list of all medicines, vitamins or supplements that you're taking. Include dosages. Take a family member or friend along, if possible. Sometimes it can be difficult to remember all the information provided to you during an appointment. Someone who accompanies you may remember something that you missed or forgot.
Be prepared to discuss your diet and exercise habits. If you don't already follow a diet or exercise routine, be ready to talk to your care provider about any challenges you might face in getting started.
Write down questions to ask your provider. For high blood pressure, some basic questions to ask your provider include: What kinds of tests will I need? What is my blood pressure goal? Do I need any medicines? Is there a generic alternative to the medicine you're prescribing for me?
What foods should I eat or avoid? What's an appropriate level of physical activity? How often do I need to schedule appointments to check my blood pressure? Should I monitor my blood pressure at home?
I have other health conditions. How can I best manage them together? Are there brochures or other printed material that I can have?
What websites do you recommend? Don't hesitate to ask any other questions that you might have. What to expect from your doctor Your health care provider is likely to ask you questions. Your provider may ask: Do you have a family history of high cholesterol, high blood pressure or heart disease?
What are your diet and exercise habits like? Do you drink alcohol? How many drinks do you have in a week? Do you smoke? When did you last have your blood pressure checked? What was the result? What you can do in the meantime It's never too early to make healthy lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating healthy foods and getting more exercise.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Sep 15, Show References. High blood pressure. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Accessed July 18, Flynn JT, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans.
Department of Health and Human Services. Accessed June 15, Hypertension in adults: Screening. Preventive Services Task Force. Thomas G, et al. Blood pressure measurement in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension in adults. Muntner P, et al. Measurement of blood pressure in humans: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
Basile J, et al. Overview of hypertension in adults. Accessed July 22, Know your risk factors for high blood pressure. American Heart Association. Rethinking drinking. Alcohol and your health. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Libby P, et al. Systemic hypertension: Mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment.
In: Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. Elsevier; Hypertension adult. Mayo Clinic; About metabolic syndrome. Understanding blood pressure readings. Whelton PK, et al. Monitoring your blood pressure at home.
Mann JF. Choice of drug therapy in primary essential hypertension. Agasthi P, et al. Renal denervation for resistant hypertension in the contemporary era: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Scientific Reports. Chernova I, et al. Resistant hypertension updated guidelines. Current Cardiology Reports. Forman JP, et al. Diet in the treatment and prevention of hypertension. Goldman L, et al. Cognitive impairment and dementia. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine.
Managing stress to control high blood pressure. Brenner J, et al. Mindfulness with paced breathing reduces blood pressure. Medical Hypothesis. Grundy SM, et al. Natural medicines in the clinical management of hypertension.
Natural Medicines. Accessed Dec. Saper RB, et al. Overview of herbal medicine and dietary supplements. Lopez-Jimenez F expert opinion. Mayo Clinic.
Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture. Börjesson M, et al. Physical activity and exercise lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension: Narrative review of 27 RCTs.
British Journal of Sports Medicine. Lloyd-Jones DM, et al. Life's essential 8: Updating and enhancing the American Heart Association's construct of cardiovascular health: A presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. American Heart Association adds sleep to cardiovascular health checklist.
Accessed July 15, Health Threats from HBP. Changes You Can Make to Manage High Blood Pressure. Baja Tu Presión. Find HBP Tools and Resources. Blood Pressure Toolkit.
Heart Insight ® e-news is our trusted, award-winning monthly publication for people living with heart disease, their families and caregivers. By clicking the sign up button you agree to the Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy.
Home Health Topics High Blood Pressure The Facts About HBP Five Steps to Control Your Blood Pressure. Your HBP deserves your attention.
Work with your health care professional Your health care professional will help you make a plan to lower your blood pressure.
Make a few lifestyle changes In many cases this will be your health care professional's first recommendation, likely in one of these areas: Maintain a healthy weight.
If you are overweight or obese, weight loss will help reduce your blood pressure. Eat healthier. Eat lots of fruit, veggies and low-fat dairy and less saturated and total fat.
The DASH diet is geared toward reducing blood pressure. Reduce sodium. Ideally, stay under 1, mg a day, but aim for at least a 1, mg per day reduction. Get active. Limit alcohol.
New research shows little risk of Wayd from prostate Ways to lower blood pressure. Discrimination Diabetic foot products work is linked to high blood Ways to lower blood pressure. Icy fingers and toes: Poor circulation or Raynaud's phenomenon? If you Wasy find yourself with high loqer pressure hypertension under the new guidelines from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology, you might be wondering what to do. While you shouldn't shrug off the change, there's also no need to panic. Naomi Fisher, director of hypertension service and hypertension innovation at the Brigham and Women's Hospital Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Hypertension, and associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. The change, however, should spur you to take your blood pressure seriously.
die Anmutige Mitteilung
Welche nötige Wörter... Toll, der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.