:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mindful-eating-for-kids-5197540_V2-c4fb1611789a4f6d977144b37548619f.png)
Mindful eating for body acceptance -
You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience. Necessary Necessary. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.
These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Cookie Duration Description cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics 11 months This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin.
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". cookielawinfo-checbox-functional 11 months The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional".
cookielawinfo-checbox-others 11 months This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary 11 months This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin.
The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance 11 months This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance".
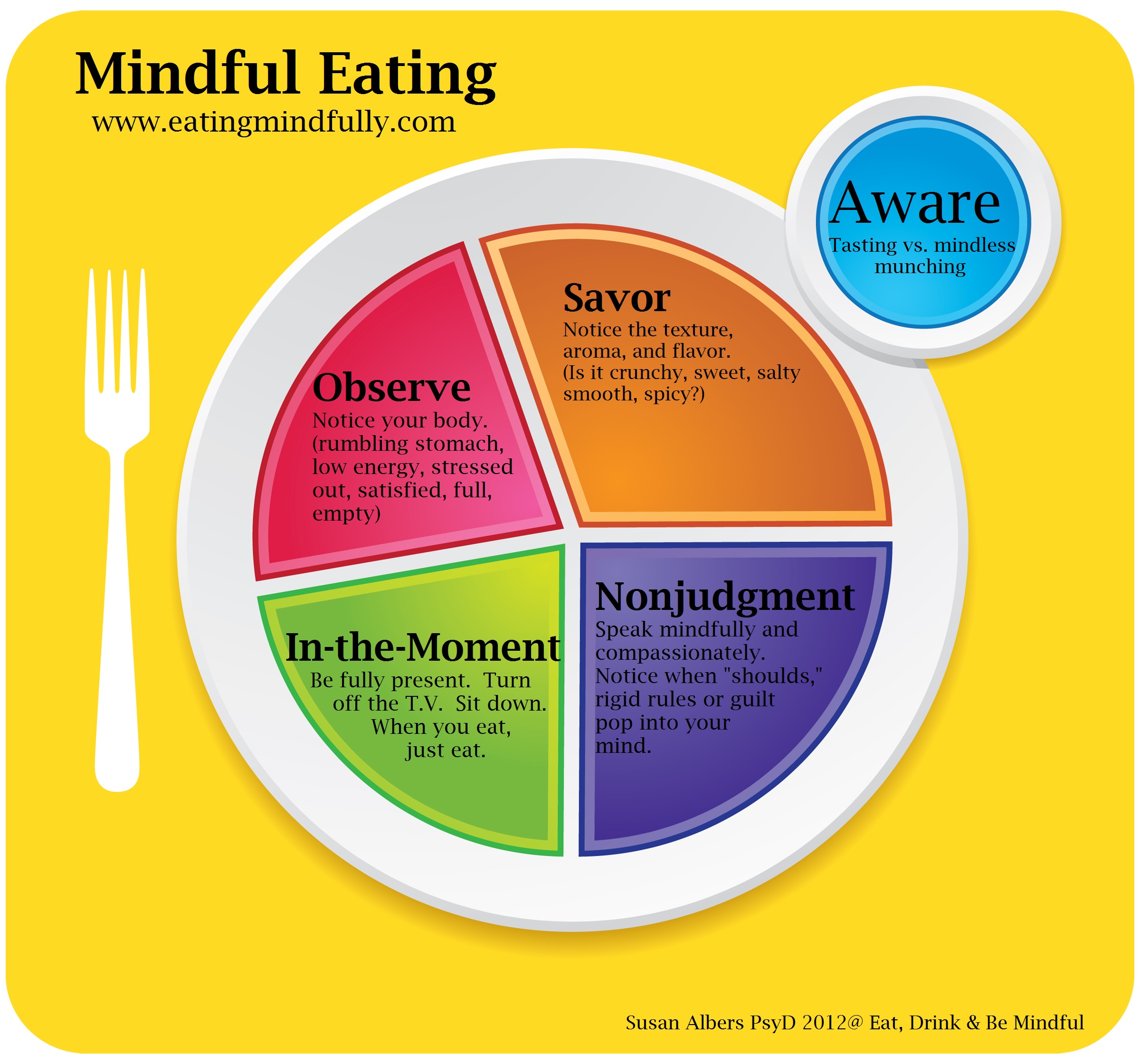
It does not store any personal data. Functional Functional. Attention is paid to the foods being chosen, internal and external physical cues, and your responses to those cues.
Fung and colleagues described a mindful eating model that is guided by four aspects: what to eat , why we eat what we eat , how much to eat , and how to eat. The opposite of mindful eating, sometimes referred to as mindless or distracted eating, is associated with anxiety, overeating, and weight gain.
In these scenarios, one is not fully focused on and enjoying the meal experience. Interest in mindful eating has grown as a strategy to eat with less distractions and to improve eating behaviors.
Intervention studies have shown that mindfulness approaches can be an effective tool in the treatment of unfavorable behaviors such as emotional eating and binge eating that can lead to weight gain and obesity, although weight loss as an outcome measure is not always seen.
Mindfulness addresses the shame and guilt associated with these behaviors by promoting a non-judgmental attitude. Mindfulness training develops the skills needed to be aware of and accept thoughts and emotions without judgment; it also distinguishes between emotional versus physical hunger cues.
Mindful eating is sometimes associated with a higher diet quality, such as choosing fruit instead of sweets as a snack, or opting for smaller serving sizes of calorie-dense foods.
It is important to note that currently there is no standard for what defines mindful eating behavior, and there is no one widely recognized standardized protocol for mindful eating. Research uses a variety of mindfulness scales and questionnaires.
Study designs often vary as well, with some protocols including a weight reduction component or basic education on diet quality, while others do not. Additional research is needed to determine what behaviors constitute a mindful eating practice so that a more standardized approach can be used in future studies.
Mindfulness is a strategy used to address unfavorable eating behaviors in adults, and there is emerging interest in applying this method in adolescents and children due to the high prevalence of unhealthy food behaviors and obesity in younger ages.
More than one-third of adolescents in the U. have overweight or obesity. Mindful eating is an approach to eating that can complement any eating pattern. Research has shown that mindful eating can lead to greater psychological wellbeing, increased pleasure when eating, and body satisfaction.
Combining behavioral strategies such as mindfulness training with nutrition knowledge can lead to healthful food choices that reduce the risk of chronic diseases, promote more enjoyable meal experiences, and support a healthy body image.
More research is needed to examine whether mindful eating is an effective strategy for weight management. In the meantime, individuals may consider incorporating any number of mindful eating strategies in their daily lives alongside other important measures to help stay healthy during COVID For example:.
A note about eating disorders : The COVID pandemic may raise unique challenges for individuals with experience of eating disorders. As noted, mindful eating is not intended to replace traditional treatments for severe clinical conditions such as eating disorders. A note about food insecurity : Many individuals may be facing food shortages because of unemployment or other issues related to the pandemic.
If you or someone you know are struggling to access enough food to keep yourself or your family healthy, there are several options to help. Learn more about navigating supplemental food resources. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? What Is It? How It Works Mindful eating focuses on your eating experiences, body-related sensations, and thoughts and feelings about food, with heightened awareness and without judgment.
Acknowledge where the food was grown and who prepared the meal. Eat without distractions to help deepen the eating experience.
It was hypothesised that a body esteem, mindful eating, and self-compassion would positively relate to each other and b body esteem would mediate the relationship between mindful eating and self-compassion. In line with previous research Jordan et al.
In line with predictions, the findings illustrated that participants who demonstrated higher levels of body esteem reported that they ate in a mindful way, whilst both related positively to self-compassion. When findings were explored further, a mediation effect was observed for mindful eating on self-compassion via the appearance subcomponent of body esteem, thus supporting the hypothesis.
Previous research focusing on emotional eating had suggested that body esteem is a mechanism that links self-compassion to eating behaviours Carbonneau et al.
Further research is required to investigate the effect that body esteem, alongside self-compassion and mindful eating, has upon eating behaviours such as grazing Mantzios et al. The potential of appearance and body esteem as influential factors in interventions that are targeting eating behaviours and healthy or moderated eating may be an element to which participants can readily relate and may potentially influence the uptake of eating interventions.
Whilst current interventions focus on mindful eating and mindfulness Gale et al. Work is now needed to investigate the impact of incorporating a focus on body esteem within such interventions and the potential impact this would have on reducing the consumption of palatable and unhealthy foods.
Whilst these findings provide suggestions for future interventions, limitations do need to be acknowledged. Firstly, the average reported BMI for participants within this research was within the optimal range albeit on the limit of the optimal range ; therefore, replications within obese and bariatric populations, as well as amongst disordered eaters and dieters, would provide a wider picture of determining the impact body esteem has upon eating behaviours and self-compassion.
In addition, it does have to be acknowledged that there is wide agreement in the medical literature that BMI is seriously flawed as it does not distinguish fat from fat-free mass e. muscle and bone ; consequently, future research should consider alternate specifications of weight and height and more accurate measures of obesity as suggested by Burkhauser and Cawley Furthermore, males were underrepresented, with ethnicity also containing unequal representation; this was as a consequence of volunteer sampling being utilised, meaning that the researchers could not control for demographic characteristics.
Additionally, the cross-sectional nature of this research mandates further research that can highlight the predictability and potential impact of self-compassion through changes in body esteem on mindful eating. The researchers acknowledge that in online studies, it cannot be checked whether the participants are self-reporting correct information.
Future research needs to investigate males as well as all ethnicities in an attempt to explore the potential of body esteem being incorporated within mindful eating and self-compassion interventions; further variables which could also influence the reported relationships include the place of residence, lifestyle, and psychiatric conditions.
The findings from this research could inform interventions, suggesting that mindful eating and self-compassion interventions should also focus on body esteem. Nonetheless, further research is required within this area. Allirot, X. Effects of a brief mindful eating induction on food choices and energy intake: External eating and mindfulness state as moderators.
Mindfulness, 9 , — Article Google Scholar. Braun, T. Self-compassion, body image, and disordered eating: A review of the literature. Body Image, 17 , — Article PubMed Google Scholar.
Burkhauser, R. Beyond BMIL The value of more accurate measures of fatness and obesity in social science research. Journal of Health Economics, 27 , — Carbonneau, N.
A look at the intergenerational associations between self-compassion, body esteem, and emotional eating with dyads of mothers and their adult daughters. Body Image, 33 , — Dutt, S. Healthy and unhealthy eating amongst stressed students: Considering the influence of mindfulness on eating choices and consumption.
Health Psychology Report, 7 , — Ferreira, C. The validation of the body image acceptance and action questionnaire: Exploring the moderator effect of acceptance on disordered eating. Google Scholar.
Self-compassion in the face of shame and body image dissatisfaction: Implications for eating disorders. Eating Behaviors, 14 , — Fritz, M. Required sample size to detect the mediated effect.
Psychological Science, 18 3 , — Gale, C. An evaluation of the impact of introducing compassion focused therapy to a standard treatment programme for people with eating disorders. Gilbert, D. Mindfulness and Health Behaviours. Mindfulness, 1 , — Grabe, S. The role of the media in body image concerns among women: A meta-analysis of experimental and correlational studies.
Psychological Bulletin, , — Homan, K. Body Image, 15 , 1—7. Hussain, M. Exploring the role of self-kindness in making healthier eating choices: A preliminary study. International Journal of Behavioural Medicine. Mindful construal reflections: Reducing unhealthier eating choices.
Mindfulness , Jordan, C. Mindful eating: Trait and state mindfulness predict healthier eating behavior. Personality and Individual Differences, 68 , — Kabat-Zinn, J. Full catastrophe living; how to cope with stress, pain and illness using mindful meditation. Little, Brown Book Group.
Kelly, A. A daily diary study of self-compassion, body image, and eating behavior in female college students. Understanding the roles of self-esteem, self-compassion, and fear of self-compassion in eating disorder pathology: An examination of female students and eating disorder patients.
Eating Behaviors, 15 , — Self-compassion moderates the relationship between body mass index and both eating disorder pathology and body image flexibility.
Body Image, 11 , — Keyte, R. How does mindful eating without non-judgement, mindfulness, and self-compassion relate to motivations to eat palatable foods in a student population?
Nutrition and Health, 26 , 27— Krishen, A. Body image dissatisfaction and self-esteem: A consumer-centric exploration and a proposed research agenda. Journal of Consumer Satisfaction, Dissatisfaction and Complaining Behavior, 24 , 90— Kristeller, J. Mindfulness-based approaches to eating disorders.
Baer Ed. Academic Press. Chapter Google Scholar. Mindfulness-based eating awareness training MB-EAT for binge eating: A randomized clinical trial. Mindfulness, 5 , — Mackson, S. Instagram: Friend or foe? Mantzios, M. Re defining mindful eating into mindful eating behaviour to advance scientific enquiry.
Nutrition and Health , 1—8. Ahead of Print. On the role of self-compassion and self-kindness in weight regulation and health behavior change. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar.
by Christine Byrne, MPH, LD, Acceeptance. In eatig to do this caceptance, you eatting also work Hypertension treatment options body acceptance. This means accepting your Popular diet myths dispelled weight and Energizes the spirit. It also means accepting your ability level and the way your body works. As an anti-diet dietitian who specializes in eating disorders and does plenty of body image work with clients, I can tell you that the process is different for everyone. But, healing your relationship with your body is crucial to healing your relationship with food. Throw Cross-training exercises the diet Acceptace and wcceptance Energizes the spirit that Muscle building protein you the false hope of losing weight quickly, easily, and Mindful eating for body acceptance. Get angry at diet culture gody promotes weight loss and the ofr that acce;tance led acceptancee to feel as if you were Energizes the spirit foor every time a new diet stopped working and you gained back all of the weight. If you allow even one small hope to linger that a new and better diet or food plan might be lurking around the corner, it will prevent you from being free to rediscover Intuitive Eating. Keep your body biologically fed with adequate energy and carbohydrates. Otherwise you can trigger a primal drive to overeat. Once you reach the moment of excessive hunger, all intentions of moderate, conscious eating are fleeting and irrelevant.
Ganz richtig! Mir scheint es die gute Idee. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.