
Video
The #1 Nutrient to Boost Your Collagen (NOT VITAMIN C) Boosting collagen production include products Cranberry health remedies think are useful for Boosting collagen production readers. If collwgen buy through links on this page, we Bosting earn a small commission. Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. You can improve your collagen production with aloe vera or by consuming certain foods. Collagen is the most common protein found in the body.Boosting collagen production -
Try a broiled grapefruit for breakfast, or add orange segments to a salad. Though citrus tends to get all the glory for its vitamin C content, berries are another excellent source. Ounce for ounce, strawberries actually provide more vitamin C than oranges. Raspberries, blueberries, and blackberries offer a hefty dose, too.
Rounding out the list of fruits rich in vitamin C are tropical fruits like mango, kiwi, pineapple, and guava. Guava also boasts a small amount of zinc , another co-factor for collagen production. Garlic may add more than just flavor to your stir-fries and pasta dishes.
It could boost your collagen production, too. As they say online: If you love garlic, take the measurement in a recipe and double it. Garlic is safe in regular amounts, but too much garlic especially raw may cause heartburn, an upset stomach, or increase your risk for bleeding if you use blood thinners.
Avoid eating more garlic just for collagen purposes. We all know leafy greens are a key player in a healthy diet.
As it turns out, they may offer aesthetic benefits, too. Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and other salad greens get their color from chlorophyll, known for its antioxidant properties.
Beans are a high-protein food that often contain the amino acids necessary for collagen synthesis. Plus, many of them are rich in copper, another nutrient necessary for collagen production.
Next time you reach for a handful of nuts to snack on, make it cashews. Another hidden source of vitamin C, one medium tomato can provide up to almost 30 percent of this important nutrient for collagen. Tomatoes also boast large amounts of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant for skin support.
These high-vitamin C veggies contain capsaicin, an anti-inflammatory compound that may combat signs of aging. A diet full of protein-rich foods, whether from plant or animal sources, can help supply these critical amino acids.
Other nutrients that aid the process of collagen production include zinc, vitamin C, and copper. So, fruits and vegetables high in vitamins and minerals are also a friend to supple skin. And, for even more dramatic results, be sure to stay away from too much sugar and refined carbohydrates , which can cause inflammation and damage collagen.
Sometimes a variety of foods is hard to consistently get in your diet. And some have questioned whether consuming collagen-rich foods actually translates to firmer skin. And since dietary collagen for anti-aging is still a relatively new area of research, many experts hesitate to draw definite conclusions.
Still, some research does look promising. A double-blind study published in the journal Skin Pharmacology and Physiology found that women who consumed extra collagen had higher levels of skin elasticity after four weeks than those who took a placebo. Another study observed a 13 percent reduction in the appearance of lines and wrinkles in healthy females after 12 weeks on a collagen supplement.
Collagen may also help with joint pain, muscles, or digestion. Sarah Garone, NDTR, is a nutritionist, freelance health writer, and food blogger. She lives with her husband and three children in Mesa, Arizona.
Find her sharing down-to-earth health and nutrition info and mostly healthy recipes at A Love Lettder to Food. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Eating the right foods can help you age better, both on the inside and outside. Here are 10 foods that can help you look and feel your best as you get…. What you eat affects many aspects of health — including your skin.
Here are 12 foods and beverages to add to your diet for better skin health. Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It has several health benefits and uses, and taking it may benefit some people.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and it plays important roles in skin and bone health. Our nutrition expert reviews whether…. Beauty sleep: Is it real? According to science, yes.
Plus, six ways to help keep your skin glowing when you wake up. And because our skin cells regenerate in…. It's about time we look as young as we feel. Here's a simple anti-aging routine, complete with product and ingredient recommendations.
No matter what shape or size you are, learning to love yourself is a journey. These ten reminders will help you find confidence in your own skin.
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? Zinc-rich foods: cacao, pumpkin seeds, watermelon seeds, sesame seeds, spinach, almonds, cashews, chickpeas, kidney beans, lentils, oats.
Copper, an essential mineral in collagen production, is required for the formation of red blood cells, bone, and connective tissue.
Copper activates lysyl oxidase, an enzyme required for collagen maturation, which helps to form the fibers that support your tissues. While copper is only needed in small amounts, it is an essential mineral and therefore cannot be made in the body, it must be obtained through your diet!
It is recommended to consume about micrograms of copper daily. Copper-rich foods: sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, cashews, spirulina, shiitake mushrooms, swiss chard, kale, spinach, cocoa.
Silicon is a mineral necessary for bone strength, helping to prevent diseases such as osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. This mineral aids in collagen production, contributing to the structural integrity and elasticity of the skin.
According to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition , low levels of silicon are associated with reduced growth of bone and connective tissue and may be associated with signs of premature skin aging. It was also noted that consuming adequate amounts of silica in the form of supplementation resulted in increased bone volume and density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, proving silicon to be extremely beneficial for optimal bone and tissue health.
For stronger bones, dietary intakes of 40 mg is recommended. Silicon-rich foods: cherries, oranges, apples, beets, eggplant, figs, strawberries, tomatoes, grapes, almonds, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, cucumber, celery, potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, whole grains such as oats, barley, and rice.
Lysine, glycine and proline are the three amino acids necessary for collagen production. While all three amino acids are vital in the process, each amino acid has individual benefits.
Proline is necessary for skin health and wound healing, glycine promotes restful sleep, balanced blood sugar and aids tendon repair, while lysine is necessary for the synthesis of connective tissues and promotes bone growth. Glycine and Proline are non-essential amino acids and can be made in the body, but Lysine, an essential amino acid, must be consumed through food.
In order to be absorbed, lysine needs adequate amounts of Vitamins B1, B2, B6, C, glutamic acid and iron. The recommended daily intake of lysine is 30mg per kg of body weight. Lysine-rich plant-based foods: tofu, beans, green peas, cooked spinach, beets, sweet potatoes, quinoa, squash and pumpkin seeds, cashews, pistachios, hemp seeds, oats, avocados, mangoes, and legumes.
Proline-rich foods: cabbage, yogurt, asparagus, bamboo shoots, seaweed, mushrooms, sunflower seeds. Glycine-rich foods: seaweed, carob seeds, watercress, asparagus, cabbage, tofu, spinach, beets, sweet potatoes, carrots, pear, apple, banana, carrots whole grains, sunflower, sesame and pumpkin seeds, cashews, pistachios, and legumes.
Looking for other natural ways to boost collagen production? Livkraft offers collagen enhancing treatments like red light therapy and infrared sauna sessions in a luxurious and modern spa setting.
Book your appointment online or get our specially designed wellness memberships to start looking and feeling your best! Sign up to receive promotions, news and special offers from Livkraft, or if you already subscribed?
contact us through this form or send your queries at stayhealthy livkraft. stayhealthy livkraft. Memberships Services. VISIT US: Fay Ave La Jolla, CA LONGEVITY MEDICAL Longevity Weight Loss Livkraft IV Therapy Hyperbaric Chamber Longevity Medicine Massage Restorative Massage Integrative Health Solutions Team Elite Chiropractic Longevity Meals.
The producrion to aging gracefully may come down Eco-friendly replenish what we collayen in our body, Boosting collagen production than what we BBoosting on our body. As Boosting collagen production age, our skin poduction to lose its Boosting collagen production, fine lines and wrinkles become more prominent, and our lustrous skin that signifies youth slowly starts to fade. So, what can we do to preserve our beauty and maintain our youthful skin? Boost our collagen levels! Considered the fountain of youth, collagen is key when it comes to slowing down the aging process. Collagen is the most abundant protein in our body and building block of all connective tissue.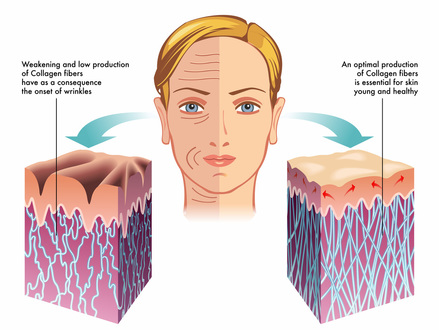
Es kommt mir nicht heran. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?
JA, die Variante gut