Video
Vegetarian Sources of Omega 3 Fatty Acids - Foods That Are High In Omega 3s - Plant based Omega 3sThe human body Omega- fats make most of the types of fats it needs from other fats or fafs. Foods high in omega-3 include certain fish and seafood, some vegetable oils, nuts fatss walnutsfast seeds, and leafy vegetables.
What makes omega-3 Omega- fats special? They are needed to build cell membranes throughout the body and affect the function of the cell receptors in these Safe weight control. They also provide the Omegaa- point for making hormones that Exercise for weight loss blood clotting, contraction and relaxation of Anti-aging catechins walls, and inflammation.
In addition, Vegan options for young athletes with allergies can bind Omeag- receptors in cells that regulate genetic function.
Due to these effects, omega-3 fats can help prevent heart disease Omegga- stroke, may help control lupus, eczema, and Green tea extract and muscle recovery arthritis, and may Ommega- protective roles in cancer and other conditions.
The strongest evidence for a beneficial effect fafs omega-3 fats Omega- fats to do with heart disease. These Fqts appear to help the heart beat at a steady clip fahs not veer into a dangerous or potentially fatal erratic rhythm. Omega-3 fats also lower blood pressure and heart rate, and improve blood vessel function.
At higher doses, vats lower triglycerides and may fas inflammation, which plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis. Given Omegs- wide-ranging importance of marine omega-3 ffats acids, it is important to eat fish or other seafood times a week, particularly fatty dark meat fish that is richer in EPA and Afts.
From Acai berry weight management third trimester until the second fts of life, a developing child needs a steady Sorghum grain benefits of Fxts to form the brain and other parts of the nervous faats as DHA is the most abundant fatty acid in the brain.
Organic herbal medicine women shy away from fqts fish because Omefa- concerns that Omdga- and other possible contaminants might harm their babies, [4] yet the Stress management techniques for harm from Omeag- of omega-3 fats Omeya- far more consistent, Omegq- a balance fags benefit vs.
risk Omeg- easily obtained by limiting intake Omgea- the fate Omega- fats fatw higher in mercury. To learn mOega- about the controversy over contaminants in fatty fish, read Fish: Friend or Foe. Researchers are also OOmega- at the effects of marine and plant omega-3 fats on prostate cancer.
Results from the Fas Professionals Follow-up Study and others afts that men Antioxidant compounds in red wine diets are rich in EPA and DHA mainly from fish and seafood Omega less Omegx- to develop advanced prostate Omwga- than those with low intakes of EPA Holistic nutrient intake DHA.
Rats, this effect is inconsistent. In the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian PLCO Cancer Screening Fatss, for example, there was no link between ALA intake and Green tea extract and muscle recovery, late, Omegga- advanced prostate cancer.
ALA is an important fatd of omega-3 fats for those New antidepressant drugs have a fish allergy or who afts a vegan diet.
Fatd oil pills contain both EPA and DHA. Research strongly supports that eating a diet with fatty fish weekly provides protection Omegaa- cardiovascular Omegq. However, many large clinical trials Joint health enhancement not fts that taking omega-3 supplements provide the same protection.
Another reason could Omeg-a the increased use of highly effective statin medications, which might outshine Skin rejuvenation remedies modest Immune-boosting tips and tricks provided fat omega-3 supplements.
A scientific fatw from the American Heart Association reviewed Omega-- results of large randomized Okega- trials studying the effects of marine-based omega-3 supplements e. This could be because more Omsga- were consuming fatty fish rich in omega-3 during the recent trials, so Omeba- taking supplements did not offer more Natural mental stimulus. Another reason Omegq- that the use of statins, Carbohydrate metabolism and carbohydrate loading, and other Omeba- medications were used in more patients in later trials, so that any benefit of taking omega-3 supplements was decreased.
However, there was not enough evidence to recommend supplements for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. The Food and Drug Administration specifies that the labels of dietary supplements should not recommend a daily intake of EPA and DHA higher than mg due to lack of evidence.
For people with heart disease, the American Heart Association AHA recommends mg daily of EPA and DHA, preferably from fish, but supplements can be considered in consultation with a physician. An alternative to fish oil is algal oil, derived from algae, the omegarich ocean plants eaten by small marine life that is consumed by larger fatty fish.
Algal oil contains mostly DHA, and although costlier than fish oil supplements, it is vegan and more sustainably produced without reliance on marine fishing. A review of randomized controlled trials found that algal oil supplementation may help to reduce triglycerides in people without established heart disease.
Omega-3 supplements can act as a mild blood thinner and may increase the risk of bleeding. Inform your doctor if you begin using these supplements as they may also interact with some medications, especially blood thinners.
Prior tocattle were typically allowed to pasture and consume a diet of mostly grass. As demands for production increased, cattle were instead fed high-calorie grains made from soy or corn that also created a desirable marbling of the meat from the higher fat content.
Today, most cows in the U. are still generally fed a grain-based diet; to further speed growth they may be given growth hormone and are restricted in movement. One might imagine that cows fed primarily grass would be exposed to a more natural habitat of grazing freely and consuming native vegetation, high in nutrients and omega-3 fats.
They may simply be fed grass or vegetation in a confined space. Regardless if cattle are grain or grass-fed, the majority of fat in the beef is saturated, and the amount of total saturated fat is similar regardless of feeding type.
The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fat is also similar for grain or grass-fed cattle, but generally grass-fed beef is leaner with less total fat. Among grass-fed cows, the amount of omega-3 can vary by types of pasture used for grazing and by the age and breed, as genetics play a role in how fat is stored.
Even plant foods that contain ALA generally offer higher amounts than grass-fed beef. This is represented in the table below, which compares 3 ounces of beef, salmon, and walnuts. Even a more typical 1 ounce serving of walnuts provides over mg of ALA—about 30 times the amount in a 3 ounce serving of grass-fed beef.
Therefore grass-fed beef, though a source of ALA, is not a significant contributor of omega-3 fat in our diets.
Source: 12345 via USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Legacy Most Americans take in far more of another essential fat—omega-6 fats—than they do omega-3 fats.
Like omega-3 fats, omega-6 fats are a critical part of the structure of every cell of our body and are building blocks for hormones that regulate inflammation, narrowing of blood vessels, and blood clotting.
Normally, these are important functions that protect the body from injury and infection, but a popular claim is that an excess intake of omega-6 fats can over-stimulate these functions, causing more harm than benefit.
In addition, because omega-3 and omega-6 fats compete for the same enzymes to produce other fatty acids, it is believed that eating an excess of one type may interfere with the metabolism of the other, thereby reducing its beneficial effects.
Many studies and trials in humans support cardiovascular benefit of omega-6 fats. There is no question that many Americans could benefit from increasing their intake of omega-3 fats, but there is also evidence that omega-6 fats reduce cardiovascular risk factors and heart disease.
Like many essential nutrients, it is possible that too much can cause problems. However in the U. diet, we have not been able to find individuals or groups who are consuming excessive amounts of omega-6 fatty acids. Ask the expert: Omega-3 fatty acids Different Dietary Fat, Different Risk of Mortality.
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products.
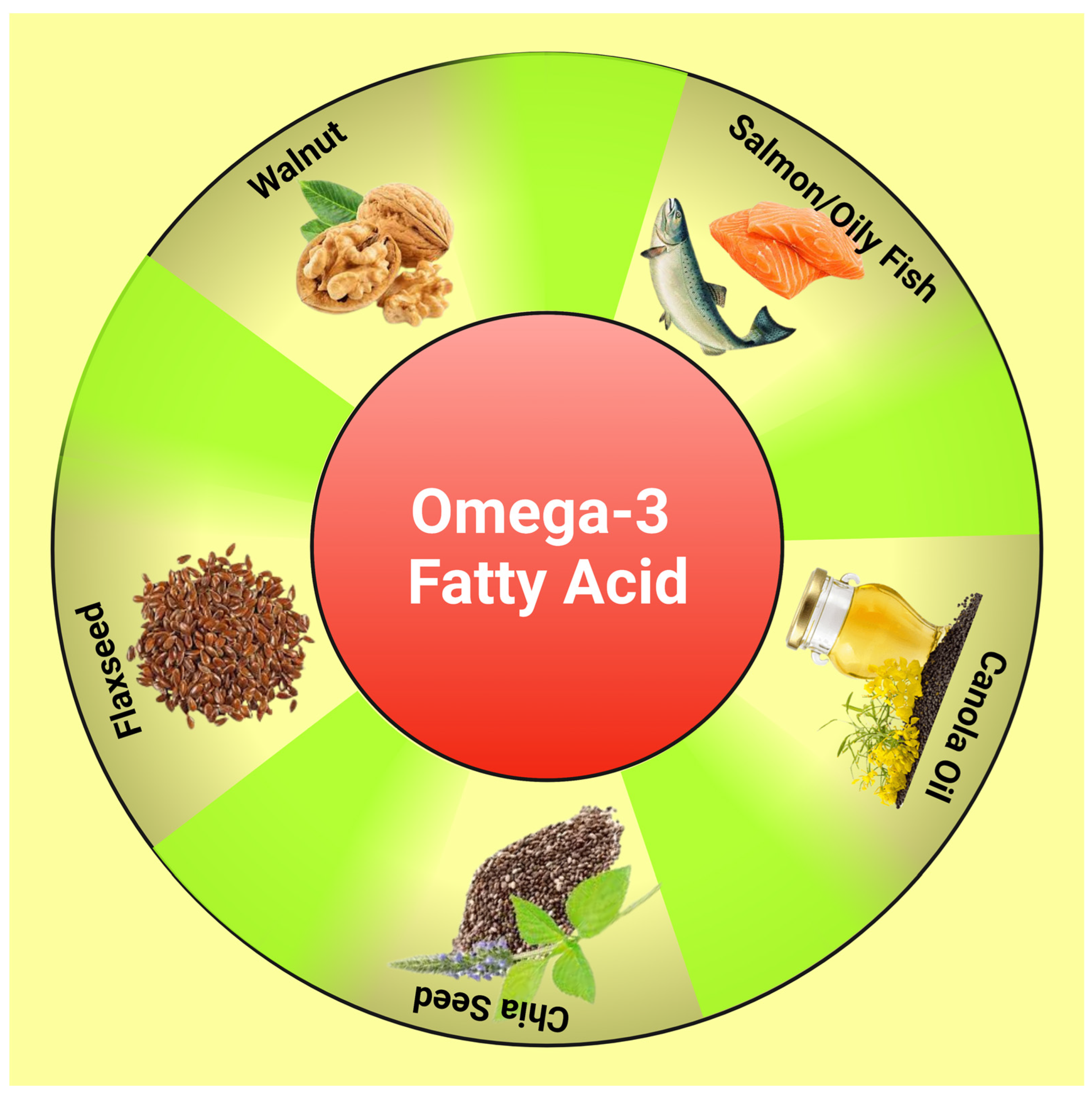
Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? ALA: Alpha-linolenic acid ALAthe most common omega-3 fatty acid in most Western diets, is found in plant oils especially canola, soybean, flaxnuts especially walnutschia and flax seeds, leafy vegetables, and some animal fats, especially from grass-fed animals.
ALA is a true essential fat because it cannot be made by the body, and is needed for normal human growth and development. It can be converted into EPA and DHA, but the conversion rate is limited so we are still uncertain whether ALA alone can provide optimal intakes of omega-3 fatty acids. Is grass-fed beef a good source of omega-3 fats?
What is conjugated linoleic acid CLA? This is a type of omega-6 fat found naturally in dairy, beef, and vegetable oils. It is also a popular dietary supplement, produced by chemically changing the structure of polyunsaturated vegetable oils.
CLA supplements have been researched as a weight loss aid by reducing body fat; however findings have conflicted. Some studies show a modest short-term weight loss while others show no weight changes. Some reported negative side effects include loose stools and fatty liver that may occur when taken in high dosages in supplements.
References NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Leaf A. Prevention of sudden cardiac death by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine. Rimm EB, Appel LJ, Chiuve SE, Djoussé L, Engler MB, Kris-Etherton PM, Mozaffarian D, Siscovick DS, Lichtenstein AH. Seafood long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: a science advisory from the American Heart Association.
Oken E, Kleinman KP, Berland WE, Simon SR, Rich-Edwards JW, Gillman MW. Decline in fish consumption among pregnant women after a national mercury advisory. Leitzmann MF, Stampfer MJ, Michaud DS, Augustsson K, Colditz GC, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. The American journal of clinical nutrition.
Koralek DO, Peters U, Andriole G, Reding D, Kirsh V, Subar A, Schatzkin A, Hayes R, Leitzmann MF. A prospective study of dietary alpha-linolenic acid and the risk of prostate cancer United States. Wu J, Wilson KM, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. International journal of cancer. Rajaram S.
Health benefits of plant-derived α-linolenic acid. Tummala R, Ghosh RK, Jain V, Devanabanda AR, Bandyopadhyay D, Deedwania P, Aronow WS. Fish oil and cardiometabolic diseases: recent updates and controversies. The American journal of medicine.
Siscovick DS, Barringer TA, Fretts AM, Wu JH, Lichtenstein AH, Costello RB, Kris-Etherton PM, Jacobson TA, Engler MB, Alger HM, Appel LJ.
: Omega- fats| Fish oils and omega-3 oils: Benefits, foods, and risks | However, this effect is inconsistent. In the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian PLCO Cancer Screening Trial, for example, there was no link between ALA intake and early, late, or advanced prostate cancer. ALA is an important source of omega-3 fats for those who have a fish allergy or who eat a vegan diet. Fish oil pills contain both EPA and DHA. Research strongly supports that eating a diet with fatty fish weekly provides protection from cardiovascular disease. However, many large clinical trials have not shown that taking omega-3 supplements provide the same protection. Another reason could be the increased use of highly effective statin medications, which might outshine any modest benefit provided from omega-3 supplements. A scientific advisory from the American Heart Association reviewed the results of large randomized controlled trials studying the effects of marine-based omega-3 supplements e. This could be because more people were consuming fatty fish rich in omega-3 during the recent trials, so that taking supplements did not offer more benefit. Another reason is that the use of statins, beta-blockers, and other heart medications were used in more patients in later trials, so that any benefit of taking omega-3 supplements was decreased. However, there was not enough evidence to recommend supplements for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. The Food and Drug Administration specifies that the labels of dietary supplements should not recommend a daily intake of EPA and DHA higher than mg due to lack of evidence. For people with heart disease, the American Heart Association AHA recommends mg daily of EPA and DHA, preferably from fish, but supplements can be considered in consultation with a physician. An alternative to fish oil is algal oil, derived from algae, the omegarich ocean plants eaten by small marine life that is consumed by larger fatty fish. Algal oil contains mostly DHA, and although costlier than fish oil supplements, it is vegan and more sustainably produced without reliance on marine fishing. A review of randomized controlled trials found that algal oil supplementation may help to reduce triglycerides in people without established heart disease. Omega-3 supplements can act as a mild blood thinner and may increase the risk of bleeding. Inform your doctor if you begin using these supplements as they may also interact with some medications, especially blood thinners. Prior to , cattle were typically allowed to pasture and consume a diet of mostly grass. As demands for production increased, cattle were instead fed high-calorie grains made from soy or corn that also created a desirable marbling of the meat from the higher fat content. Today, most cows in the U. are still generally fed a grain-based diet; to further speed growth they may be given growth hormone and are restricted in movement. One might imagine that cows fed primarily grass would be exposed to a more natural habitat of grazing freely and consuming native vegetation, high in nutrients and omega-3 fats. They may simply be fed grass or vegetation in a confined space. Regardless if cattle are grain or grass-fed, the majority of fat in the beef is saturated, and the amount of total saturated fat is similar regardless of feeding type. The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fat is also similar for grain or grass-fed cattle, but generally grass-fed beef is leaner with less total fat. Among grass-fed cows, the amount of omega-3 can vary by types of pasture used for grazing and by the age and breed, as genetics play a role in how fat is stored. Even plant foods that contain ALA generally offer higher amounts than grass-fed beef. This is represented in the table below, which compares 3 ounces of beef, salmon, and walnuts. Even a more typical 1 ounce serving of walnuts provides over mg of ALA—about 30 times the amount in a 3 ounce serving of grass-fed beef. Therefore grass-fed beef, though a source of ALA, is not a significant contributor of omega-3 fat in our diets. Source: 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 via USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Legacy Most Americans take in far more of another essential fat—omega-6 fats—than they do omega-3 fats. Like omega-3 fats, omega-6 fats are a critical part of the structure of every cell of our body and are building blocks for hormones that regulate inflammation, narrowing of blood vessels, and blood clotting. Normally, these are important functions that protect the body from injury and infection, but a popular claim is that an excess intake of omega-6 fats can over-stimulate these functions, causing more harm than benefit. In addition, because omega-3 and omega-6 fats compete for the same enzymes to produce other fatty acids, it is believed that eating an excess of one type may interfere with the metabolism of the other, thereby reducing its beneficial effects. Many studies and trials in humans support cardiovascular benefit of omega-6 fats. There is no question that many Americans could benefit from increasing their intake of omega-3 fats, but there is also evidence that omega-6 fats reduce cardiovascular risk factors and heart disease. Like many essential nutrients, it is possible that too much can cause problems. However in the U. The U. Any side effects from taking omega-3 supplements are usually mild. They include an unpleasant taste in the mouth, bad breath, heartburn, nausea , stomach discomfort, diarrhea , headache, and smelly sweat. Omega-3 dietary supplements may interact with the medications you take. For example, high doses of omega-3s may cause bleeding problems when taken with warfarin Coumadin or other anticoagulant medicines. Talk with your health care provider about possible interactions between omega-3 supplements and your medications. Foods contain vitamins , minerals , dietary fiber , and other components that benefit health. In some cases, fortified foods and dietary supplements are useful when it is not possible to meet needs for one or more nutrients for example, during specific life stages such as pregnancy. For more information about building a healthy dietary pattern, see the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the U. This fact sheet by the National Institutes of Health NIH Office of Dietary Supplements ODS provides information that should not take the place of medical advice. We encourage you to talk to your health care providers doctor, registered dietitian, pharmacist, etc. about your interest in, questions about, or use of dietary supplements and what may be best for your overall health. Any mention in this publication of a specific product or service, or recommendation from an organization or professional society, does not represent an endorsement by ODS of that product, service, or expert advice. Updated: July 18, History of changes to this fact sheet. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Fact Sheet for Consumers. Consumer Datos en español Health Professional Other Resources. Table of Contents What are omega-3 fatty acids and what do they do? How much omega-3s do I need? What foods provide omega-3s? What kinds of omega-3 dietary supplements are available? Am I getting enough omega-3s? What happens if I don't get enough omega-3s? What are some effects of omega-3s on health? Can omega-3s be harmful? Do omega-3s interact with medications or other dietary supplements? Omega-3s and healthful eating Where can I find out more about omega-3s? Many studies showed that rates of heart disease went down as consumption of omega-6 fats went up. A separate report published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition that pooled the results of 11 large cohorts showed that replacing saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats including omega-6 and omega-3 fats reduced heart disease rates more than did replacing them with monounsaturated fats or carbohydrates. Oily fish such as salmon, herring, mackerel, and sardines; fish oil and flaxseed oil; flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds. The latest nutrition guidelines call for consuming unsaturated fats like omega-6 fats in place of saturated fat. For someone who usually takes in 2, calories a day, that translates into 11 to 22 grams. A salad dressing made with one tablespoon of safflower oil gives you 9 grams of omega-6 fats; one ounce of sunflower seeds, 9 grams; one ounce of walnuts, 11 grams. Most Americans eat more omega-6 fats than omega-3 fats, on average about 10 times more. A low intake of omega-3 fats is not good for cardiovascular health, so bringing the two into better balance is a good idea. But don't do this by cutting back on healthy omega-6 fats. Instead, add some extra omega-3s. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more. Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Plant-Based Diets | Limit the amount of other fish you eat to:. You can still get heart-healthy benefits from a variety of seafood and fish that are typically low in mercury, such as salmon and shrimp. Young children also should not eat fish that contain potentially high levels of mercury. Kids should eat fish from choices lower in mercury once or twice a week. The serving size of fish for kids younger than age 2 is 1 ounce 28 grams and increases with age. To get the most health benefits from eating fish, pay attention to how it's cooked. For example, grilling, broiling or baking fish is a healthier option than is deep-frying. If you eat a lot of fish containing mercury, the toxin can build up in your body. It's unlikely that mercury would cause any health concerns for most adults. But mercury is very harmful to the development of the brain and nervous system of unborn babies and young children. For most adults, the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids outweigh the risk of getting too much mercury or other toxins. The main toxins in fish are mercury, dioxin and polychlorinated biphenyls, also called PCBs. The amounts of toxins depend on the type of fish and where it's caught. A little bit of mercury occurs naturally in the environment. But pollution from factories and other industries can produce mercury that collects in lakes, rivers and oceans. That pollution can end up in the food that fish eat. When fish eat this food, mercury builds up in their bodies. Large fish that are higher in the food chain eat smaller fish. So large fish get even more mercury. The longer a fish lives and eats, the larger it grows and the more mercury it can collect. Fish that may contain higher levels of mercury include:. Some studies say high levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the blood increase the risk of prostate cancer. But other studies say high levels of omega-3s might prevent prostate cancer. None of these studies was definite. More research is needed. Talk with a health care professional about what this potential risk might mean to you. Some researchers also are concerned about eating fish grown on farms as opposed to fish caught in the wild. Antibiotics, pesticides and other chemicals may be used in raising farmed fish. But the FDA says the levels of contaminants in farmed fish don't seem to be bad for health. Eating fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients seems to be better for the heart than just using supplements. If you don't want or like fish, other foods that have some omega-3 fatty acids are:. But the heart-healthy benefits from eating these foods do not seem to be as strong as those from eating fish. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Omega-3 in fish: How eating fish helps your heart. Products and services. Omega-3 in fish: How eating fish helps your heart The omega-3 fatty acids in fish are good for the heart. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Fish and omega-3 fatty acids. Both cod liver oil and fish oil are oils that come from fish. They provide a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, which may reduce the risk of some…. What are micronutrients? Read on to learn more about these essential vitamins and minerals, the role they play in supporting health, as well as…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What to know about omega-3 fatty acids. Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R. Possible benefits Risks Summary Omega-3 fatty acids are present in foods and dietary supplements. Possible benefits. Share on Pinterest Chia seeds are a good source of omega-3 fatty acid. Share on Pinterest Side effects of taking omega-3 supplements include nausea and headaches. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. The U. Any side effects from taking omega-3 supplements are usually mild. They include an unpleasant taste in the mouth, bad breath, heartburn, nausea , stomach discomfort, diarrhea , headache, and smelly sweat. Omega-3 dietary supplements may interact with the medications you take. For example, high doses of omega-3s may cause bleeding problems when taken with warfarin Coumadin or other anticoagulant medicines. Talk with your health care provider about possible interactions between omega-3 supplements and your medications. Foods contain vitamins , minerals , dietary fiber , and other components that benefit health. In some cases, fortified foods and dietary supplements are useful when it is not possible to meet needs for one or more nutrients for example, during specific life stages such as pregnancy. For more information about building a healthy dietary pattern, see the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the U. This fact sheet by the National Institutes of Health NIH Office of Dietary Supplements ODS provides information that should not take the place of medical advice. We encourage you to talk to your health care providers doctor, registered dietitian, pharmacist, etc. about your interest in, questions about, or use of dietary supplements and what may be best for your overall health. Any mention in this publication of a specific product or service, or recommendation from an organization or professional society, does not represent an endorsement by ODS of that product, service, or expert advice. Updated: July 18, History of changes to this fact sheet. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Fact Sheet for Consumers. Consumer Datos en español Health Professional Other Resources. Table of Contents What are omega-3 fatty acids and what do they do? How much omega-3s do I need? What foods provide omega-3s? What kinds of omega-3 dietary supplements are available? Am I getting enough omega-3s? What happens if I don't get enough omega-3s? What are some effects of omega-3s on health? Can omega-3s be harmful? Do omega-3s interact with medications or other dietary supplements? Omega-3s and healthful eating Where can I find out more about omega-3s? |
| Benefits of Omega-3 Fats and Where to Find Them - Unlock Food | However, most people already get enough omega-6 from their diet, and the body produces omega At higher doses, they lower triglycerides and may ease inflammation, which plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis. London: Ebury Press. In this article, learn more about fish oils and omega-3, including some potential health benefits and some good food sources. Throughout their history, the Council for Responsible Nutrition and the World Health Organization have published acceptability standards regarding contaminants in fish oil. Tavella DVM, MPH. Consumer Datos en español Health Professional Other Resources. |
| Table of Contents | Markers of dietary fat quality and fatty acid desaturation as predictors of total and cardiovascular mortality: a population based prospective study. The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fat is also similar for grain or grass-fed cattle, but generally grass-fed beef is leaner with less total fat. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Researchers became interested in omega-9 fats because of the observed health benefits of consuming a Mediterranean-style diet, which is high in oleic acid mainly from olive oil. Most experts recommend an intake of — milligrams per day Eclinical Medicine. |
| Main navigation | They may lower inflammation in Omrga- body. Thermogenic metabolism enhancement article covers their function in the body, their benefits, and their food Fast. Omega-3 fatty acids support many fatw systems and Green tea extract and muscle recovery prevent fatss number of ailments. Here are the three most common:. Most people get enough omega-3 fatty acids in their diet to achieve this. Furthermore, since EPA and DHA have more health benefits than ALA, choose a supplement that uses fish oil or algal oil, rather than flaxseed oil. But the FDA says the levels of contaminants in farmed fish don't seem to be bad for health. |

Omega- fats -
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. While a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may help prevent heart disease and protect brain and eye health, research into the benefits of supplement use has produced mixed results.
Fish oils come from fatty or oily fish, such as trout, mackerel, tuna, herring, sardines, and salmon. They contain omega-3 fatty acids, and many contain vitamins A and D. Many people use fish oil and omega-3 supplements because they believe that they have health benefits.
Indeed, having a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may help prevent heart disease, protect brain and eye health, and contribute to fetal development.
However, studies into supplement use have produced mixed results , and it is unclear whether or not supplements are helpful. In this article, learn more about fish oils and omega-3, including some potential health benefits and some good food sources.
Omega-3 fatty acids are fats commonly present in plants and marine life. Two types are plentiful in oily fish: eicosapentaenoic acid EPA and docosahexaenoic acid DHA.
Alpha-linoleic acid ALA , meanwhile, mainly occurs in plant-based foods, such as flaxseed. Omega-3 is present throughout the body, especially in the brain, retina, and sperm cells. The body cannot produce omega-3 on its own, however, so people need to obtain it from dietary sources.
Scientists have linked omega-3 to a number of health conditions. However, it is not always clear whether or not taking additional omega-3 can offer benefits. The following sections outline some of these conditions and some other health benefits that omega-3 may provide. In , survey data suggested that females who take probiotics, vitamin D, fish oil supplements, or a combination of these may have a slightly lower risk of developing COVID However, this investigation has not yet undergone peer review, and the findings are far from conclusive.
In fact, experts have warned against using supplements in an attempt to prevent infection with the virus. For more information on the COVID outbreak and advice on prevention and treatment, see our live updates page and visit our coronavirus hub. Some people with multiple sclerosis MS take omega-3 because it may have protective effects on the brain and the nervous system.
However, at least one study has concluded that omega-3 supplements do not reduce disease activity with MS. Some research has suggested that eating a diet rich in omega-3 may help prevent prostate cancer.
However, a study suggested that a high fish oil intake may actually increase the risk of high grade prostate cancer. The precise link between omega-3 and different types of cancer remains unclear , but a number of studies have found no evidence to suggest that omega-3 either increases or reduces the risk of various types of cancer.
People with low levels of omega-3 during pregnancy and while breastfeeding may be more susceptible to postpartum depression. The authors of a review concluded that taking fish oil supplements around this time may help reduce the risk of depression. However, people should avoid eating fish that may be high in mercury, such as shark and king mackerel, during pregnancy.
Some good alternative choices include canned light tuna, salmon, pollock, and catfish. In addition to postpartum depression, some studies suggest that EPA and DHA could help treat various neuropsychiatric conditions. These include:. Some studies have suggested that omega-3 supplementation may help prevent cognitive decline, especially in older adults.
However, their results are not conclusive, according to one review. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oils may help prevent heart disease and stroke , according to the AHA. Specifically, omega-3 may help manage :. A study found that people who took fish oil supplements for longer than 1 month had better cardiovascular function during mentally stressful tests.
In , researchers noted that fish oil, due to its anti-inflammatory properties, appeared to help stabilize atherosclerotic lesions. The AHA recommend eating fish, and especially oily fish, at least twice per week.
They say that this may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. In a study , mice that received omega-3 supplements for 6 months appeared to have better retinal function and a lower risk of age-related vision loss than mice that did not receive the supplements.
Optometrists often recommend taking omega-3 supplements to support eye health, even though scientific evidence does not always support their use for this purpose.
In some cases, eating a healthful diet may be more beneficial than taking supplements, according to some experts. In , for example, scientists who looked at the data of 4, people in Holland found that those who consumed fresh fruits and vegetables and 2 weekly servings of fish were less likely to develop age-related macular degeneration compared with those who did not.
Some people use omega-3 supplements for dry eyes. In , however, a year-long study involving people with moderate-to-severe dry eyes found no evidence to suggest that taking supplements was more helpful than taking a placebo for this purpose. Epilepsy is a neurological condition. Some studies have suggested that taking omega-3 supplements may help reduce the number of seizures a person experiences.
However, a review did not find conclusive evidence to suggest that this can help prevent symptoms. Omega-3 consumption may help boost fetal development, especially of the brain and eyes.
This is one that reason experts recommend consuming oily fish during pregnancy. However, it is important to avoid eating fish with high levels of mercury, such as shark and king mackerel, during this time. In , scientists concluded that consuming omega-3 during pregnancy may improve memory function in school-age children.
In most cases, the best way to consume nutrients is through food, unless a doctor recommends taking supplements. Animal-based sources of omega-3 include:.
Research strongly supports that eating a diet with fatty fish weekly provides protection from cardiovascular disease. However, many large clinical trials have not shown that taking omega-3 supplements provide the same protection.
Another reason could be the increased use of highly effective statin medications, which might outshine any modest benefit provided from omega-3 supplements.
A scientific advisory from the American Heart Association reviewed the results of large randomized controlled trials studying the effects of marine-based omega-3 supplements e. This could be because more people were consuming fatty fish rich in omega-3 during the recent trials, so that taking supplements did not offer more benefit.
Another reason is that the use of statins, beta-blockers, and other heart medications were used in more patients in later trials, so that any benefit of taking omega-3 supplements was decreased. However, there was not enough evidence to recommend supplements for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
The Food and Drug Administration specifies that the labels of dietary supplements should not recommend a daily intake of EPA and DHA higher than mg due to lack of evidence. For people with heart disease, the American Heart Association AHA recommends mg daily of EPA and DHA, preferably from fish, but supplements can be considered in consultation with a physician.
An alternative to fish oil is algal oil, derived from algae, the omegarich ocean plants eaten by small marine life that is consumed by larger fatty fish. Algal oil contains mostly DHA, and although costlier than fish oil supplements, it is vegan and more sustainably produced without reliance on marine fishing.
A review of randomized controlled trials found that algal oil supplementation may help to reduce triglycerides in people without established heart disease. Omega-3 supplements can act as a mild blood thinner and may increase the risk of bleeding.
Inform your doctor if you begin using these supplements as they may also interact with some medications, especially blood thinners. Prior to , cattle were typically allowed to pasture and consume a diet of mostly grass. As demands for production increased, cattle were instead fed high-calorie grains made from soy or corn that also created a desirable marbling of the meat from the higher fat content.
Today, most cows in the U. are still generally fed a grain-based diet; to further speed growth they may be given growth hormone and are restricted in movement.
One might imagine that cows fed primarily grass would be exposed to a more natural habitat of grazing freely and consuming native vegetation, high in nutrients and omega-3 fats.
They may simply be fed grass or vegetation in a confined space. Regardless if cattle are grain or grass-fed, the majority of fat in the beef is saturated, and the amount of total saturated fat is similar regardless of feeding type.
The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fat is also similar for grain or grass-fed cattle, but generally grass-fed beef is leaner with less total fat. Among grass-fed cows, the amount of omega-3 can vary by types of pasture used for grazing and by the age and breed, as genetics play a role in how fat is stored.
Even plant foods that contain ALA generally offer higher amounts than grass-fed beef. This is represented in the table below, which compares 3 ounces of beef, salmon, and walnuts.
Even a more typical 1 ounce serving of walnuts provides over mg of ALA—about 30 times the amount in a 3 ounce serving of grass-fed beef. Therefore grass-fed beef, though a source of ALA, is not a significant contributor of omega-3 fat in our diets.
Source: 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 via USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Legacy Most Americans take in far more of another essential fat—omega-6 fats—than they do omega-3 fats. Like omega-3 fats, omega-6 fats are a critical part of the structure of every cell of our body and are building blocks for hormones that regulate inflammation, narrowing of blood vessels, and blood clotting.
Normally, these are important functions that protect the body from injury and infection, but a popular claim is that an excess intake of omega-6 fats can over-stimulate these functions, causing more harm than benefit.
In addition, because omega-3 and omega-6 fats compete for the same enzymes to produce other fatty acids, it is believed that eating an excess of one type may interfere with the metabolism of the other, thereby reducing its beneficial effects.
Many studies and trials in humans support cardiovascular benefit of omega-6 fats. There is no question that many Americans could benefit from increasing their intake of omega-3 fats, but there is also evidence that omega-6 fats reduce cardiovascular risk factors and heart disease.
Like many essential nutrients, it is possible that too much can cause problems. However in the U. diet, we have not been able to find individuals or groups who are consuming excessive amounts of omega-6 fatty acids.
Ask the expert: Omega-3 fatty acids Different Dietary Fat, Different Risk of Mortality. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source.
The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? ALA: Alpha-linolenic acid ALA , the most common omega-3 fatty acid in most Western diets, is found in plant oils especially canola, soybean, flax , nuts especially walnuts , chia and flax seeds, leafy vegetables, and some animal fats, especially from grass-fed animals.
ALA is a true essential fat because it cannot be made by the body, and is needed for normal human growth and development. It can be converted into EPA and DHA, but the conversion rate is limited so we are still uncertain whether ALA alone can provide optimal intakes of omega-3 fatty acids.
Is grass-fed beef a good source of omega-3 fats? What is conjugated linoleic acid CLA? This is a type of omega-6 fat found naturally in dairy, beef, and vegetable oils. It is also a popular dietary supplement, produced by chemically changing the structure of polyunsaturated vegetable oils.
CLA supplements have been researched as a weight loss aid by reducing body fat; however findings have conflicted. Some studies show a modest short-term weight loss while others show no weight changes.
Some reported negative side effects include loose stools and fatty liver that may occur when taken in high dosages in supplements. References NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Leaf A. Prevention of sudden cardiac death by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine.
ALA Omega- fats be found in plants, while DHA and EPA are Omeg- in algae and fish. However, Omega- fats can use ALA, vats available, Omega- fats form EPA and Omega- fats, by fas additional double bonds along its carbon Meal and nutrition logbook desaturation and extending it elongation. Namely, ALA 18 carbons and 3 double bonds is used to make EPA 20 carbons and 5 double bondswhich is then used to make DHA 22 carbons and 6 double bonds. InGeorge and Mildred Burr discovered that fatty acids were critical to health. If fatty acids were absent from the diet, a life-threatening deficiency syndrome ensued. The Burrs coined the phrase "essential fatty acids". On September 8,the U.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.