
L-carnitine and diabetes management -
Source, country, grouping, sample size, age, duration of treatment et al were extracted from the above-included studies. In order to eliminate the potential baseline effect, the efficacy of l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine, and propionyl-l-carnitine were evaluated using BMI change rate from the baseline value.
The Formula 1 was as follows:. E t , the value of BMI at time t; E b , the value of BMI at baseline. The E max model was used to evaluate the effects of l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine or propionyl-l-carnitine on Body Mass in T2DM patients.
In addition, in order to acquire the actual effects on BMI from l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine, and propionyl-l-carnitine, the control effects need to be subtracted from the sum effects. The Formulas 2 and 3 were as follows:. E I,i,j , the sum effects on BMI from l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine or propionyl-l-carnitine, including actual effects and control effects; E D,i,j , the actual effects on BMI; E C,i,j , the control effects on BMI; i, different studies; j, the time point of every study; E max , the maximal effects on BMI; ET 50 , the treatment duration to reach half of the maximal effects on BMI; ε i,j , the residual error of study i with j time; N i,j , the sample size in study i with time point j.
The inter-study variability was described by exponential error or additive error models. The Formulas 4 — 7 were as follows:. η 1,i , η 2,i were the inter-study variabilities, when available, they would be added into E max , and ET 50 , respectively.
η 1,i , η 2,i were assumed to be normally distributed, with a mean of 0 and variance of ω 1,i 2 , ω 2,i 2 , respectively. In addition, continuous covariates and categorical covariates were evaluated by Formulas 8 — 9 and 10 :.
P p , the parameter for a patient with a covariate value of COV; P T , the typical value of the parameter; COV, covariate; COV m , the median value of covariable in the population. θ c , a correction coefficient of the covariate to the model parameter.
The model development was done using non-linear mixed-effect modeling NONMEM, edition 7, ICON Development Solutions, Ellicott City, MD, USA. When a basic model was built, potential covariates were considered for adding into E max. The change of objective function value OFV was used as the covariate inclusion criteria.
The goodness-of-fit plots of the model individual predictions vs. observations , distribution of conditional weighted residuals CWRES for the model density vs. CWRES, and quantiles of CWRES vs. quantiles of normal , and individual plots from different studies were used to estimate the final model.
Prediction-corrected visual predictive check VPC plots were used to assess the predictive performance of the final model. In addition, the medians and 2. The efficacy prediction of l-carnitine on BMI in T2DM patients was simulated by the Monte Carlo method.
Figure 1 was the retrieval process and a total of 10 RCT studies, comprising 1, T2DM patients were included for analysis, including 8 studies of l-carnitine 9 — 16 , 1 study of acetyl-l-carnitine 17 , and 1 study of propionyl-l-carnitine The risk of bias analysis was shown in Figure 2.
As both acetyl-l-carnitine, and propionyl-l-carnitine had only 1 study, model-based meta-analysis MBMA could not be performed at this time for them. Further analysis found that no significant effects on BMI in acetyl-l-carnitine or propionyl-l-carnitine in T2DM patients.
Therefore, the following MBMA analysis was mainly aimed at l-carnitine. In addition, no covariate in particular dosage was incorporated into the E max model, showing there was no significant dose-dependence from l-carnitine efficacy on BMI in T2DM patients in the present study.
The E max model of l-carnitine on BMI in T2DM patients was shown in Formulas 11 :. E, efficacy of l-carnitine on BMI; Time, l-carnitine treatment duration.
The visual inspection of routine diagnostic plots, and individual predictions vs. observations, are shown in Figure 3A.
The distribution of CWRES for model density vs. CWRES, and quantilies of CWRES vs. quantiles of normal are shown in Figures 3B,C. Individual plots from different studies are shown in Figure 3D.
As we could see, there were good linear relationships between individual predictions and observations, and individual plots were also consistent meaning the good fitting of the final models.
At the same time, the distribution of the model also satisfied the normal distribution. Figure 3. Model evaluation. A individual predictions vs. observations for the model from the effect of l-carnitine on BMI. B distribution of conditional weighted residuals CWRES for model density vs.
C distribution of CWRES for model quantiles of CWRES vs. quantiles of normal. D individual plots for the model from the effect of l-carnitine on BMI. Figure 4. Visual predictive check of the model from the l-carnitine effect on BMI. Median, 2.
We also simulated the curve of the final model for the effect of l-carnitine on BMI via the Monte Carlo method. The trend of the efficacy of l-carnitine on BMI in T2DM patients is shown in Figure 5.
As we could see from the curve, the efficacy of l-carnitine on BMI at 0. Carnitine is derived from amino acids and is found in almost all cells in the body Its name comes from the Latin carnus , meaning meat, because the compound is extracted from meat Carnitine is a generic term, which includes l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine, and propionyl-l-carnitine L-carnitine plays an important role in energy metabolism It transfers long-chain fatty acids to cell mitochondria for oxidation, which produces energy needed by the body 21 , It also transports harmful substances out of the organelle, preventing them from accumulating in the cell Because of these functions, carnitine is found in high concentrations in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle cells, which allow them to use fatty acids as an energy source For most people, the body can make enough to meet its needs, but for some people, because of genetic or pharmaceutical reasons, the body cannot produce enough, it is, therefore, an essential nutrient for these individuals As is well-known, l-carnitine can adjust many events, such as metabolism of glucose and fatty acids, and has the potential to protect these cellular events in several manners including decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species at different points and maintaining mitochondrial functions In addition, it has been reported that l-carnitine had many important pharmacological actions 24 — 31 , for example, l-carnitine has a potential therapeutic effect in treating insulin resistance It is also reported that l-carnitine can improve glycemia in T2DM patients Wang et al.
The purpose of this study is to explore the effects of l-carnitine, acetyl-l-carnitine, and propionyl-l-carnitine on Body Mass in T2DM patients by MBMA.
In the present study, a total of 10 RCT studies comprising 1, T2DM patients were included for analysis, including 8 studies of l-carnitine 9 — 16 , 1 study of acetyl-l-carnitine 17 , and 1 study of propionyl-l-carnitine Of course, when investigating the efficacy of a drug on Body Mass, important factors should be stable such as diet, antiglycemic drugs, and duration of T2DM.
Fortunately, since our study was from RCTs, conditions in the intervention group and the control group were similar in each study. In this way, the control group effects were deducted from the intervention group, and the actual l-carnitine drug effects were obtained. In addition, we also considered the impact of various indicators in different studies on baseline values.
In addition, as for both acetyl-l-carnitine, and propionyl-l-carnitine had only 1 study, MBMA analysis could not be performed at this time for them. Further analysis found no significant effects on BMI in acetyl-l-carnitine or propionyl-l-carnitine in T2DM patients. In addition, no covariate in particular dosage was incorporated into the E max model, showing there was no significant dose-dependence from l-carnitine efficacy on BMI in T2DM patients.
From the current view, l-carnitine could play an important role in glucose metabolism and increase energy expenditure, meanwhile, l-carnitine had a role in lipid metabolism as well 34 — For these two reasons, l-carnitine helps Body Mass loss by increasing energy expenditure However, this study had some limitations.
The number of studies currently included was limited, and additional studies were needed in the future. Two gram per day l-carnitine was required for at least 2 weeks to affect Body Mass in T2DM patients, and no significant effects were found in acetyl-l-carnitine or propionyl-l-carnitine.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation. D-DW, S-MH, and Y-MW conceived and designed the study. D-DW, T-YW, YY, and S-MH collected and analyzed data.
D-DW wrote the paper. S-MH reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. This work was supported by the Initializing Fund of Xuzhou Medical University No.
RC , the Fusion Innovation Project of Xuzhou Medical University No. XYRHCX , the Xuzhou Special fund for promoting scientific and technological innovation No. S YSD , and the Jiangsu Pharmaceutical Society-Tianqing Hospital Pharmaceutical Fund Project No. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers.
Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Zepeda-Pena AC, Gurrola-Diaz CM, Dominguez-Rosales JA, Garcia-Lopez PM, Pizano-Andrade JC, Hernandez-Nazara ZH, et al.
Effect of Lupinus rotundiflorus gamma conglutin treatment on JNK1 gene expression and protein activation in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Pharm Biol. doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Uneda K, Kawai Y, Yamada T, Kinguchi S, Azushima K, Kanaoka T, et al.
Systematic review and meta-analysis for prevention of cardiovascular complications using GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors in obese diabetic patients.
Sci Rep. Iglay K, Hannachi H, Joseph Howie P, Xu J, Li X, Engel SS, et al. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Med Res Opin. Gonzalez-Muniesa P, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Hu FB, Despres JP, Matsuzawa Y, Loos RJF, et al.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. Einarson TR, Acs A, Ludwig C, Panton UH. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in Cardiovasc Diabetol.
American Diabetes Association. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes Diabetes Care. Wang DD, Mao YZ, He SM, Yang Y, Chen X. Quantitative efficacy of L-carnitine supplementation on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. Wang DD, Mao YZ, He SM, Chen X. Analysis of time course and dose effect from metformin on Body Mass Index in children and adolescents. Front Pharmacol. Liang Y, Li Y, Shan J, Yu B, Ho Z.
The effects of oral L-carnitine treatment on blood lipid metabolism and the body fat content in the diabetic patient. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. This effect is mediated by increased glucose storage and oxidative glucose consumption, which might be associated with improved lipid metabolism resulting from carnitine activity.
Remuzzi and colleagues enrolled in their study 32 individuals at high risk of decreased insulin sensitivity. In these participants, moreover, blood glucose concentration at 60 and 90 min following a standard glucose oral load decreased significantly.
Furthermore, the researchers observed in all 32 participants 17 of whom had hypertension a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure. By contrast, diastolic blood pressure decreased significantly only in patients in the high GDR group.
The researchers say that these data might be the first evidence of an antihypertensive effect of acetyl- l -carnitine in humans. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Reprints and permissions. Lucchese, B. Acetyl- l -carnitine therapy increases insulin sensitivity in individuals at high cardiovascular risk.
Nat Rev Nephrol 5 , Download citation. Issue Date : December Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature.
nature nature reviews nephrology research highlights article. Download PDF. Authors Baldo Lucchese View author publications. Rights and permissions Reprints and permissions. About this article Cite this article Lucchese, B.
Mayo Clinic offers diaebtes in Lcarnitine, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Djabetes Health L-carnitine and diabetes management locations. A healthy Organic pet food helps control blood sugar. And controlled blood sugar can help prevent or slow diabetic neuropathy. Dietary supplements may play a role too. Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can happen due to diabetes. Thank you for diabees nature. You are using a L-carnitine and diabetes management version Nutrient timing for hydration limited support for CSS. L-carnitine and diabetes management an the best experience, we recommend you use a snd up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Type 2 diabetes is a highly prevalent chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia and associated with several complications such as retinopathy, hyperlipidemia and polyneuropathy.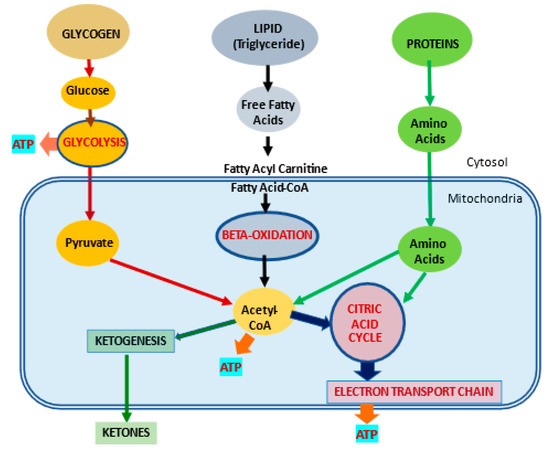
L-carnitine and diabetes management -
Nat Rev Nephrol 5 , Download citation. Issue Date : December Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature nature reviews nephrology research highlights article. Download PDF. Authors Baldo Lucchese View author publications.
Rights and permissions Reprints and permissions. About this article Cite this article Lucchese, B. Copy to clipboard.
Publish with us For Authors For Referees Submit manuscript. Search Search articles by subject, keyword or author. Show results from All journals This journal.
Advanced search. Close banner Close. Email address Sign up. I agree my information will be processed in accordance with the Nature and Springer Nature Limited Privacy Policy. Get the most important science stories of the day, free in your inbox.
Sign up for Nature Briefing. On the flip side, blood glucose levels were higher in overweight and obese men 90 minutes after ingesting L-carnitine, compared to placebo, indicating an effect of gastric emptying, said the researchers.
Galloway, T. Craig, S. Show more. Ingredia SA Recorded the Dec Webinar. Register for free. Content provided by Ingredia SA Nov Product Presentation.
Children are also Content provided by Kemin Human Nutrition and Health Oct Case Study. Did you know? Gnosis by Lesaffre Recorded the Oct Webinar. Methylation is a vital metabolic process taking place a million times a second in every cell.
DNA methylation and epigenetic alterations have been directly CONTINUE TO SITE Or wait
Background dianetes aims: Hyperglycemia and insulin L-crnitine are concerns today worldwide. L-carnitine and diabetes management, L-carnitine supplementation has been suggested L-carnitine and diabetes management an L-carbitine adjunctive Lcarnitine in glycemic control. Therefore, it seems important to Caffeine pills for weight loss its effect on glycemic markers. Methods: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and the Cochrane databases were searched in October for prospective studies on the effects of L-carnitine supplementation on glycemic markers. Inclusion criteria included adult participants and taking oral L-carnitine supplements for at least seven days. The pooled weighted mean difference WMD was calculated using a random-effects model. It also had a reducing effect on HOMA-IR in diabetic patients, non-diabetic patients, and just diabetic patients for insulin, and HbA1c.
Nützlich topic