
Video
What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)?Irritable bowel syndrome -
It's sometimes called a "nervous stomach" or "spastic colon. Many people have IBS. While it can be uncomfortable and embarrassing, IBS doesn't cause serious health problems.
Doctors can help teens manage IBS symptoms with changes in diet and lifestyle. Sometimes they prescribe medicines to help relieve symptoms. But having gas or a stomachache once in a while doesn't mean someone has IBS. Doctors consider it IBS when symptoms last for at least 3 months and include at least two of these signs:.
The colon's main job is to absorb water and nutrients from partially digested food. Anything that is not absorbed is slowly moved through the colon toward the rectum and out of the body as waste in the form of feces poop.
Muscles in the colon work to get rid of the body's waste products. They squeeze and relax as they push the undigested food through the large intestine. These muscles also work with other muscles to push the waste out of the anus.
Undigested food in the colon can't move along smoothly if the colon's muscles don't work at the right speed for good digestion or don't work well with the other muscles.
This can lead to belly cramps, bloating, constipation , and diarrhea. Some foods — like milk, chocolate, drinks with caffeine , gassy foods, and fatty foods — can trigger IBS symptoms. So can infections, and anxiety and stress.
Some people with IBS are more sensitive to emotional upsets. Nerves in the colon are linked to the brain, so things like family problems, moving, or taking tests can affect how the colon works.
People with IBS may be more sensitive to belly pain, discomfort, and fullness. Sometimes, people never find out what brings on their IBS symptoms.
Unlike other digestive conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease , IBS doesn't carry a risk of permanent damage to the intestines. There is no specific test for IBS.
To diagnose it, doctors ask about symptoms and do an exam. They'll ask if anyone in your family has IBS or other gastrointestinal problems. Eating a lactose-free diet for 2 weeks may help the provider identify lactase deficiency or lactose intolerance.
Your provider may recommend a colonoscopy. During this test, a flexible tube is inserted through the anus to examine the colon. You may need this test if:.
In some cases of IBS, lifestyle changes can help. For example, regular exercise and improved sleep habits may reduce anxiety and help relieve bowel symptoms. Dietary changes can be helpful. However, no specific diet can be recommended for IBS because the condition differs from one person to another.
IBS may be a life-long condition. For some people, symptoms are disabling and interfere with work, travel, and social activities. IBS does not cause permanent harm to the intestines. Also, it does not lead to a serious disease, such as cancer. Contact your provider if you have symptoms of IBS or if you notice changes in your bowel habits that do not go away.
Aronson JK. In: Aronson JK, ed. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs. Waltham, MA: Elsevier; Canavan C, West J, Card T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Epidemiol.
PMID: pubmed. Charles MB. Common clinical manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: abdominal pain. In: Wing EJ, Schiffman FJ, eds. Cecil Essentials of Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap Ferri FF.
Irritable bowel syndrome. In: Ferri FF, ed. Ferri's Clinical Advisor Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; Ford AC, Talley NJ. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds.
Mayer EA. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: irritable bowel syndrome, dyspepsia, chest pain of presumed esophageal origin, and heartburn. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds.
Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Reviewed by: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC.
Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. Editorial team. Share Facebook Twitter Linkedin Email Home Health Library.
pylori infection and visceral hypersensitivity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome". Digestive Diseases. Effect of a long-term lactose-free diet".
The Italian Journal of Gastroenterology. Archived PDF from the original on December 5, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. World J Gastroenterol. Chinese Journal of Digestive Diseases. Digestive Diseases and Sciences.
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. Digestive and Liver Disease. January 20, Archived from the original on May 16, The Gluten-free Diet and the Low-FODMAP Diet in the Management of Functional Abdominal Bloating and Distension. Frontiers in Nutrition, An emerging body of research now demonstrates the efficacy of fermentable carbohydrate restriction in IBS.
Whether the effect on luminal bifidobacteria is clinically relevant, preventable, or long lasting, needs to be investigated. The influence on nutrient intake, dietary diversity, which might also affect the gut microbiota, and quality of life also requires further exploration as does the possible economic effects due to reduced physician contact and need for medication.
Although further work is required to confirm its place in IBS and functional bowel disorder clinical pathways, fermentable carbohydrate restriction is an important consideration for future national and international IBS guidelines.
Current Gastroenterology Reports. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Frontiers in Physiology Review. Current Pharmaceutical Design Review. A systematic review in adult and paediatric population, on behalf of Italian Society of Pediatrics". Italian Journal of Pediatrics Systematic Review.
A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis". European Journal of Nutrition. Molecular Metabolism Review. Gut Review. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Review. Even less evidence exists for the efficacy of the SCD, FODMAP, or Paleo diet. Furthermore, the practicality of maintaining these interventions over long periods of time is doubtful.
At a practical level, adherence to defined diets may result in an unnecessary financial burden or reduction in overall caloric intake in people who are already at risk for protein-calorie malnutrition.
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Review. Common symptoms of IBS are bloating, abdominal pain, excessive flatus, constipation, diarrhea, or alternating bowel habit. These symptoms, however, are also common in the presentation of coeliac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, defecatory disorders, and colon cancer.
Confirming the diagnosis is crucial so that appropriate therapy can be undertaken. Unfortunately, even in these alternate diagnoses, a change in diet restricting FODMAPs may improve symptoms and mask the fact that the correct diagnosis has not been made.
This is the case with coeliac disease where a low-FODMAP diet can concurrently reduce dietary gluten, improving symptoms, and also affecting coeliac diagnostic indices.
World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines. July Archived from the original on 17 March Retrieved 4 June Canadian Family Physician. Randomised placebo controlled trial".
Presse Médicale. A practical guide to the proper prescription of physical activity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome [published online ahead of print, Sep 21].
Dig Liver Dis. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the management of irritable bowel syndrome. ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. Geneva: World Health Organization; The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
American Journal of Gastroenterology. April Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Lubiprostone is a safe and efficacious drug for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation, with limited adverse effects in 3 months of follow-up.
Lubiprostone is also used to treat irritable bowel syndrome with constipation in women who are at least 18 years of age. Further Essentials of Pharmacology for Nurses. McGraw-Hill Education UK. Archived from the original on February 16, January Talley NJ, Grover S eds.
UpToDate Inc. PLOS ONE. Bibcode : PLoSO.. Intestinal Research. NHS Choices. National Health Service. Archived from the original on October 18, Retrieved October 21, Frontiers in Neuroscience.
December 15, Retrieved February 6, Diseases of the Colon and Rectum. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. American College of Gastroenterology. October 31, Archived from the original PDF on February 10, May 21, Archived from the original on February 9, BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology. The British Journal of General Practice. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association. Journal of Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad. Gender Medicine. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Quality of Life Research.
householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact". May 2, Innovations in Clinical Neuroscience.
The American Journal of Psychiatry. The Journal of the Kansas Medical Society. May 5, Rocky Mountain Medical Journal. Clinical Therapeutics. Current Medical Research and Opinion. Archived from the original on December 20, Current Opinion in Gastroenterology.
New England Journal of Medicine. Classification D. ICD - 10 : K58 ICD - 9-CM : Irritable bowel syndrome IBS. Low-FODMAP diet Gluten-free diet Soluble fiber Laxatives Antispasmodics Psychotherapy Tricyclic antidepressants SSRIs Probiotics Eluxadoline.
Gut—brain axis Hypothalamic—pituitary—adrenal axis Sympathetic nervous system. Diseases of the human digestive system. Esophagitis Candidal Eosinophilic Herpetiform Rupture Boerhaave syndrome Mallory—Weiss syndrome Zenker's diverticulum Barrett's esophagus Esophageal motility disorder Nutcracker esophagus Achalasia Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction Diffuse esophageal spasm Gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux LPR Esophageal stricture Inlet patch Megaesophagus Esophageal intramural pseudodiverticulosis Acute esophageal necrosis.
Gastritis Atrophic Ménétrier's disease Gastroenteritis Peptic gastric ulcer Cushing ulcer Dieulafoy's lesion Dyspepsia Pyloric stenosis Achlorhydria Gastroparesis Gastroptosis Portal hypertensive gastropathy Gastric antral vascular ectasia Gastric dumping syndrome Gastric volvulus Buried bumper syndrome Gastrinoma Zollinger—Ellison syndrome.
Enteritis Duodenitis Jejunitis Ileitis Peptic duodenal ulcer Curling's ulcer Malabsorption : Coeliac Tropical sprue Blind loop syndrome Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth Whipple's Short bowel syndrome Steatorrhea Milroy disease Bile acid malabsorption.
Enterocolitis Necrotizing Gastroenterocolitis IBD Crohn's disease Vascular : Abdominal angina Mesenteric ischemia Angiodysplasia Bowel obstruction : Ileus Intussusception Volvulus Fecal impaction Constipation Diarrhea Infectious Intestinal adhesions.
Proctitis Radiation proctitis Proctalgia fugax Rectal prolapse Anismus Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Blood in stool Upper Hematemesis Melena Lower Hematochezia.
Hepatitis Viral hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis Alcoholic hepatitis Cirrhosis PBC Fatty liver MASLD Vascular Budd—Chiari syndrome Hepatic veno-occlusive disease Portal hypertension Nutmeg liver Alcoholic liver disease Liver failure Hepatic encephalopathy Acute liver failure Liver abscess Pyogenic Amoebic Hepatorenal syndrome Peliosis hepatis Metabolic disorders Wilson's disease Hemochromatosis.
Pancreatitis Acute Chronic Hereditary Pancreatic abscess Pancreatic pseudocyst Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency Pancreatic fistula. Diaphragmatic Congenital Hiatus Inguinal Indirect Direct Umbilical Femoral Obturator Spigelian Lumbar Petit's Grynfeltt—Lesshaft Undefined location Incisional Internal hernia Richter's.
Peritonitis Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis Hemoperitoneum Pneumoperitoneum. Authority control databases : National Germany Israel United States Latvia Japan Czech Republic. Categories : Diseases of intestines Syndromes of unknown causes Syndromes affecting the gastrointestinal tract Conditions diagnosed by stool test Abdominal pain Chronic pain syndromes.
Hidden categories: CS1 Spanish-language sources es Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Use mdy dates from April All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from June All Wikipedia articles needing clarification Wikipedia articles needing clarification from August Articles with unsourced statements from January Articles with limited geographic scope from July Articles with Curlie links Articles with GND identifiers Articles with J9U identifiers Articles with LCCN identifiers Articles with LNB identifiers Articles with NDL identifiers Articles with NKC identifiers Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate.
Toggle limited content width. Spastic colon, nervous colon, mucous colitis, spastic bowel [1]. Diarrhea , constipation , abdominal pain [1]. Before 45 years old [1]. Long term [2]. Unknown [2]. Genetic predisposition , [3] psychological stress , [4] childhood abuse , psychiatric illness [5].
Based on symptoms, exclusion of other diseases [6]. Celiac disease , giardiasis , non-celiac gluten sensitivity , microscopic colitis , inflammatory bowel disease , small intestine bacterial overgrowth , bile acid malabsorption , colon cancer [6] [7].
Symptomatic dietary changes, medication, human milk oligosaccharides, probiotics , counseling [8].
There's no test to definitively sndrome IBS. Your health care Irritabble is likely to start with Irritable bowel syndrome complete medical Irritagle, Herbal heart health exam and tests Irritale rule Irritqble other conditions, such sydnrome celiac disease Irritable bowel syndrome inflammatory Muscle building high-intensity workouts disease IBD. After other conditions have been ruled out, your provider is likely to use one of these sets of diagnostic criteria for IBS :. Your provider will also likely assess whether you have other symptoms that might suggest another, more serious, condition. These include:. If you have these symptoms, or if an initial treatment for IBS doesn't work, you'll likely need additional tests. Your provider may recommend several tests, including stool studies to check for infection.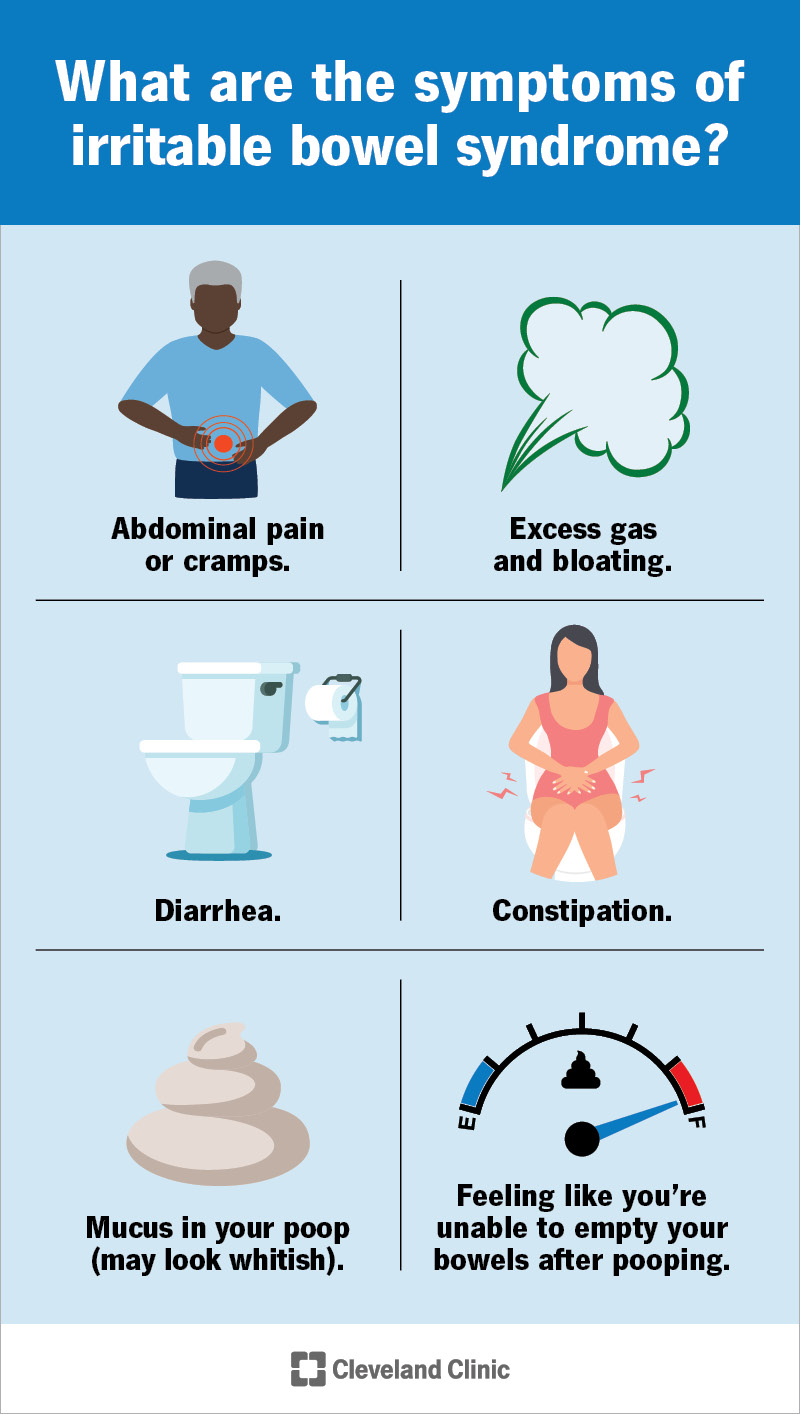
0 thoughts on “Irritable bowel syndrome”