Managing blood sugar levels -
Drinking water regularly may rehydrate the blood, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce diabetes risk 20 , Keep in mind that water and other zero-calorie drinks are best.
Avoid sugar-sweetened options, as these can raise blood glucose, drive weight gain, and increase diabetes risk 22 , Staying hydrated can reduce blood sugar levels and diabetes risk. Choose water and zero-calorie drinks and avoid sugar-sweetened beverages. Portion control can help you regulate your calorie intake and maintain a moderate weight 24 , Consequently, weight management promotes healthy blood sugar levels and has been shown to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes 1 , 26 , Monitoring your serving sizes also helps prevent blood sugar spikes 2.
The glycemic index GI measures how quickly carbs break down during digestion and how rapidly your body absorbs them. This affects how quickly your blood sugar levels rise The GI divides foods into low, medium, and high GI and ranks them on a scale of 0— Low GI foods have a ranking of 55 or less 15 , Both the amount and type of carbs you eat determine how a food affects your blood sugar levels.
Specifically, eating low GI foods has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes 15 , Furthermore, adding protein or healthy fats helps minimize blood sugar spikes after a meal Stress can affect your blood sugar levels When stressed, your body secretes hormones called glucagon and cortisol, which cause blood sugar levels to rise 29 , One study including a group of students showed that exercise, relaxation, and meditation significantly reduced stress and lowered blood sugar levels Exercises and relaxation methods like yoga and mindfulness-based stress reduction may also help correct insulin secretion problems among people with chronic diabetes 31 , 32 , Managing your stress levels through exercise or relaxation methods like yoga may help you regulate blood sugar levels.
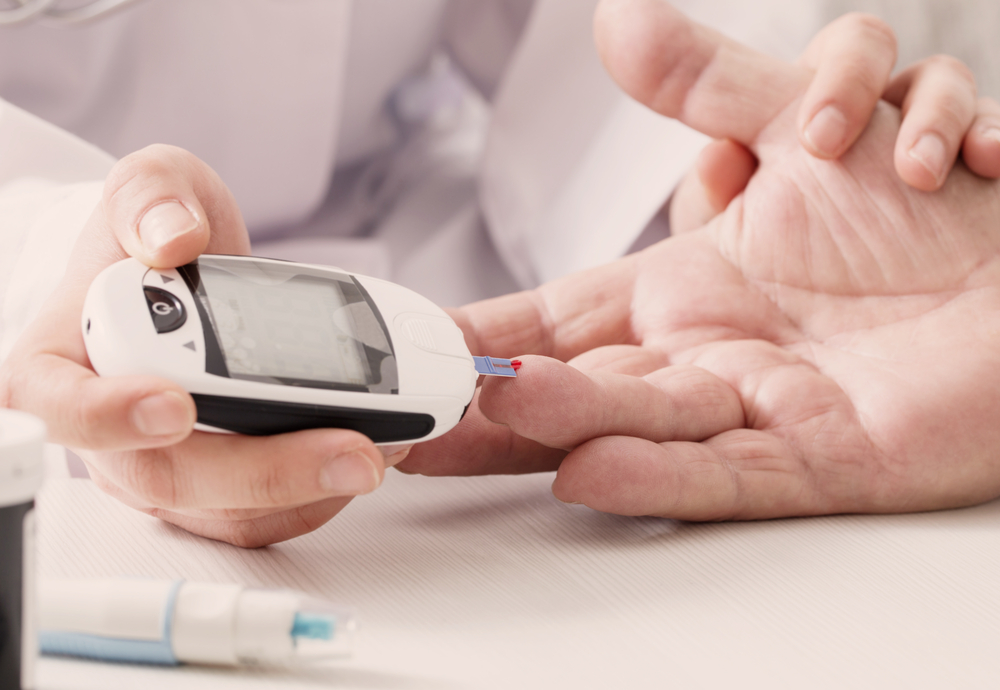
Monitoring blood glucose levels can help you better manage them You can do so at home using a portable blood glucose meter, which is known as a glucometer. You can discuss this option with your doctor. Keeping track allows you to determine whether you need to adjust your meals or medications.
It also helps you learn how your body reacts to certain foods 2. Try measuring your levels regularly every day and keeping track of the numbers in a log.
Also, it may be more helpful to track your blood sugar in pairs — for example, before and after exercise or before and 2 hours after a meal. This can show you whether you need to make small changes to a meal if it spikes your blood sugar, rather than avoiding your favorite meals altogether.
Some adjustments include swapping a starchy side for non-starchy veggies or limiting them to a handful. Checking your blood glucose and maintaining a daily log enables you to adjust foods and medications when necessary to better manage your blood sugar levels. Getting enough sleep feels excellent and is necessary for good health In fact, poor sleeping habits and a lack of rest can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
They can also increase appetite and promote weight gain 36 , 37 , Additionally, sleep deprivation raises levels of the hormone cortisol, which, as explained, plays an essential role in blood sugar management 29 , Adequate sleep is about both quantity and quality. The National Sleep Foundation recommends that adults get at least 7—8 hours of high quality sleep per night To improve the quality of your sleep , try to:.
Good sleep helps maintain your blood sugar levels and promotes a healthy weight. On the other hand, poor sleep can disrupt critical metabolic hormones. High blood sugar levels and diabetes have been linked to micronutrient deficiencies. Some examples include deficiencies in the minerals chromium and magnesium Chromium is involved in carb and fat metabolism.
It may potentiate the action of insulin, thus aiding blood sugar regulation 41 , 42 , 43 , Chromium-rich foods include:. However, the mechanisms behind this proposed connection are not entirely known, and studies report mixed findings. As such, more research is needed 41 , 45 , Magnesium has also been shown to benefit blood sugar levels.
In fact, diets rich in magnesium are associated with a significantly reduced risk of diabetes In contrast, low magnesium levels may lead to insulin resistance and decreased glucose tolerance in people with diabetes 47 , 48 , Eating foods rich in chromium and magnesium can help prevent deficiencies and reduce the risk of blood sugar problems.
However, the overall quality of evidence on these ingredients is low due to insufficient human studies or small sample sizes. Therefore, no conclusive recommendations can be made regarding their use Some of the foods touted to have anti-diabetes effects include 51 , 52 :. Finally, the Food and Drug Administration FDA does not regulate supplements in the same way that it regulates prescription medications.
Some foods are believed to have blood-sugar-lowering effects. However, research is still inconclusive, and they may negatively interact with your diabetes medication. If you need help finding a primary care doctor, then check out our FindCare tool here.
Maintaining a moderate weight promotes healthy blood sugar levels and reduces your risk of developing diabetes 2 , 26 , 27 , For example, if a person weighs pounds 91 kg and loses just 10—14 pounds 4.
These are used as indicators of your blood sugar levels over the past 3 months 60 , Maintaining a moderate weight will support blood sugar management and decrease your risk of developing diabetes.
Spreading your meals and snacks throughout the day may help you avoid both high and low blood sugar levels Snacking between meals may also reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes In fact, several studies suggest that having smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day could improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels 62 , In addition, eating smaller meals and healthy snacks throughout the day may lower glycated hemoglobin HbA1c readings, indicating improvements in blood sugar levels over the previous 3 months Snacking between meals could keep your blood sugar levels from spiking or plummeting throughout the day.
Probiotics are friendly bacteria that offer numerous health benefits, including improved blood sugar regulation 65 , 66 , 67 , Research shows that probiotic intake may lower fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin HbA1c , and insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes 65 , 66 , 67 , Interestingly, studies have found that improvements in blood sugar levels are more significant in people who consume multiple species of probiotics and for at least 8 weeks 69 , Probiotic-rich foods include fermented foods, such as:.
Insulin is a hormone that balances blood sugar in the body. These are defined as excessive thirst, urination, and appetite, respectively. Many of them include making lifestyle changes, like managing your weight, stress levels, and sleep quality, exercising, and staying hydrated.
That said, some of the biggest improvements have to do with your dietary choices. Be sure to talk with your healthcare professional before making lifestyle changes or trying new supplements— especially if you have problems with blood sugar management or are taking medications.
Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Blood sugar spikes are when your blood sugar rises and then crashes after eating. This article explains 12 simple ways to avoid blood sugar spikes.
Sugary sodas can cause cravings. Here's a guide on how to stop drinking soda. Managing diabetes isn't as simple as just eating right and exercising. Many factors impact our blood sugars, and we might not even know it.
What foods help you decrease both your blood sugar and cholesterol? Our nutrition expert answers your question. However, a research review found that regardless of the specific type of IF intervention, IF improved health outcomes in people with high blood sugar and high cholesterol levels.
This included improvements in hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c, a blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the previous three months.
HbA1c is one of the commonly used tests to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. Not all carbs are created equal, especially when it comes to how they affect your blood sugar levels. A analysis of previously published studies consistently found that consuming whole grains improved blood glucose levels post-meal compared to refined carb foods in healthy people.
Another review of 80 previous studies concluded that compared to refined grains, whole grains lowered blood sugar levels post meal. This may explain the inverse association between whole grain intake and risk of type 2 diabetes, which means the more whole grains you consume, the lower your risk.
Whole grains include, but are not limited to:. Taking walks post meal allows your body to burn carbohydrates you recently consumed to fuel muscle movement, which reduces post-meal blood sugar levels.
Walking also improves how effectively insulin works to clear sugar from your blood. A study looked at the effects of walking on 21 healthy young volunteers who were broken into two groups. The first group took brisk minute walks after meals that contained various amounts of carbohydrates.
Another group completed brisk minute walks after eating a mixed meal or a high carbohydrate drink. Researchers found that brisk walking substantially reduced post-meal blood sugar peak in both groups. Another study found that while light intensity walking was more effective, even standing rather than sitting after meals resulted in lower post-meal blood sugar levels.
In addition to building muscle and strength, resistance training can improve blood sugar regulation. A study found that just a single bout of resistance training before a meal significantly reduced post-meal blood sugar levels in 10 sedentary men with obesity and prediabetes.
Another small study explored the impact of various activities on blood sugar after a meal in eight people with type 2 diabetes. They included uninterrupted sitting, 30 minutes of walking, 30 minutes of combined walking and aerobic exercise , and 15 minutes of circuit resistance training. Researchers found that all types of exercise improved post-meal blood sugar regulation, even though the resistance exercise required the least time commitment.
Pulses include all types of beans, lentils, peas, and chickpeas. This food group is rich in antioxidants, several key vitamins and minerals, and contains a unique combination of protein and high fiber carbohydrates.
A research review found that in adults with and without type 2 diabetes, eating more pulses improved both post-meal blood sugar levels and long-term regulation, including HbA1c values. Another research summary concluded that pulse-based diets consistently resulted in substantial improvements in blood sugar control, as well as blood lipids fats , and body weight.
Eating three-quarters to one cup of pulses just one time significantly reduced post-meal blood sugar levels. And eating five cups of pulses per week improved HbA1c values in people with type 2 diabetes.
Add pulses to salads, soups, veggie chili, tacos, and curries, and opt for pulse pastas, like chickpea or lentil penne, as well as pulse-based dips, like hummus and bean dip. A breakfast high in protein may help reduce post-meal blood sugar levels throughout the entire day.
One small study in 12 healthy adults found that those who ate a high protein breakfast had reduced post-meal blood sugar levels after breakfast, lunch, and dinner, compared to those who ate a typical lower protein breakfast meal.
Avocados are full of good fat, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. Including them in meals has been shown to help regulate blood sugar levels. A study in 31 people with overweight or obesity compared three calorie-matched meals that contained either no avocado, half an avocado, or a whole avocado.
The meals with a half or a whole avocado reduced post-meal blood glucose levels and improved blood flow, compared to meals with no avocado. This may help explain the results of a study that examined the link between avocado intake and type 2 diabetes in U.
Continuous glucose monitors or CGMs have traditionally been used by people with diabetes. But the devices have become increasingly popular with users who simply want to monitor and better regulate their blood sugar levels. CGMs involve apps synched to sensors typically placed on the back of the arm that measure interstitial sugar levels, which is the sugar found in the fluid between the cells.
A study in 12 healthy male volunteers concluded that CGMs were useful for evaluating post-meal blood sugar levels and researchers cite several CGM benefits, even for healthy people. These include the ability to see real-time trends and patterns in blood sugar levels throughout the day, the opportunity to see individual responses to various foods, and the ability to use the data to adapt eating and physical activity habits to keep blood sugar levels within a normal range.
Fermentation is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohol or organic acids using microorganisms—yeasts or bacteria—under anaerobic conditions. Fermented foods include kefir, kombucha , sauerkraut, tempeh, natto, miso, kimchi, and sourdough bread. In addition to supporting digestive health, research shows that fermented foods may slow carbohydrate absorption, which leads to lower post-meal blood sugar levels.
In a study, 11 healthy adults consumed a high glycemic index meal known to raise blood sugar levels more quickly with either soda water, diet lemonade soft drink, or unpasteurized kombucha. Only the fermented kombucha resulted in a clinically significant reduction in post-meal blood sugar.
Fermented foods have also been shown to reduce inflammation , which is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Added sugar is sugar added to a food product by a manufacturer to sweeten it, or sugar you add yourself, like stirring sugar into your coffee.
Because added sugar is absorbed quickly into the bloodstream, it makes blood sugar levels spike. The American Heart Association recommends a limit of no more than 25 grams—or six teaspoons—of added sugar per day for women and no more than 36 grams or nine teaspoons for men. In the World Health Organization WHO advised against the use of non-sugar sweeteners to control body weight or reduce the disease risk.
Based on a scientific review, the organization stated that there may be potential undesirable effects from long-term non-sugar sweetener use, including an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Not consuming enough vitamin D can negatively impact blood sugar regulation, and according to the American Diabetes Association four in 10 adults are vitamin D deficient. However, it's also important to say that too much vitamin D can lead to an abnormally high level of calcium in the blood, which can damage the kidneys, soft tissues, and bones over time.
A research review, which looked at 46 previously published studies, found that a vitamin D supplement improved blood sugar regulation and reduced HbA1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and low vitamin D. A study concluded that adults who stay well-hydrated appear to be healthier, develop fewer chronic conditions, and live longer compared to those who may not consume enough fluids.
Proper hydration may also be a benefit blood sugar regulation. A research review found an inverse relationship between water intake and the risk of type 2 diabetes, meaning a higher intake lowered the risk.
A small study in nine men with type 2 diabetes found that three days of low water intake impaired blood sugar regulation. There are numerous benefits to managing blood sugar levels, including improved energy and mood and a reduced risk of several chronic diseases.
A healthy lifestyle of exercising, staying hydrated and eating balanced meals can help naturally keep blood sugar levels in balance, and also offer additional health benefits, like reduced cholesterol and improved gut health. For more information about how to best monitor or regulate your blood sugar, talk to your healthcare provider.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Manage Blood Sugar. Shukla AP, Andono J, Touhamy SH, Casper A, et al. Carbohydrate-last meal pattern lowers postprandial glucose and insulin excursions in type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. Published online Sep doi: Shapira N.
The metabolic concept of meal sequence vs. satiety: Glycemic and oxidative responses with reference to inflammation risk, protective principles and Mediterranean diet. Published online Oct 5. Fiber: The Carb That Helps You Manage Diabetes.
Yesmin F, Ali MOI, Sardar MMR, Munna MK, et al. Effects of dietary fiber on postprandial glucose in healthy adults. November De Carvalho CM, De Paula TP, Viana LV, Mt Machado V, et al. Plasma glucose and insulin responses after consumption of breakfasts with different sources of soluble fiber in type 2 diabetes patients: a randomized crossover clinical trial.
Am J Clin Nutr. Epub Aug Soluble vs. insoluble fiber. Papakonstantinou E, Oikonomou C, Nychas G, Dimitriadis GD. Effects of Diet, Lifestyle, Chrononutrition and Alternative Dietary Interventions on Postprandial Glycemia and Insulin Resistance.
Published online Feb Takahashi M, Ozaki M, Kang M, Sasaki H, et al. Effects of Meal Timing on Postprandial Glucose Metabolism and Blood Metabolites in Healthy Adults. Published online Nov All About Your A1C.
Yuan X, Wang J, Yang S, Gao M, et al. Effect of Intermittent Fasting Diet on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Impaired Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Endocrinol. Published online Mar Marventano S, Vetrani C, Vitale M, Godos J, et al.
Whole Grain Intake and Glycaemic Control in Healthy Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sanders LM, Zhu Y, Wilcox ML, Koecher K, et al.
Whole grain intake, compared to refined grain, improves postprandial glycemia and insulinemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. Online ahead of print. Department of Agriculture. Food Group Gallery. Bird SR, Hawley JA. Update on the effects of physical activity on insulin sensitivity in humans.
BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. eCollection Bellini A, Nicolo A, Bazzucchi I, Sacchetti M. The Effects of Postprandial Walking on the Glucose Response after Meals with Different Characteristics. Published online Mar 4. Buffey AJ, Herring MP, Langley CK, Donnelly AE, et al.
The Acute Effects of Interrupting Prolonged Sitting Time in Adults with Standing and Light-Intensity Walking on Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Health in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Sports Med. Epub Feb Bittel AJ, Bittel DC, Mittendorfer B, Patterson BW, et al. A single bout of premeal resistance exercise improves postprandial glucose metabolism in obese Men with prediabetes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Bellini A, Nicolo A, Bulzomi R, Bazzucchi I, et al. The effect of different postprandial exercise types on glucose response to breakfast in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Published online Apr Pulse consumption improves indices of glycemic control in adults with and without type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of acute and long-term randomized controlled trials.
Eur J Nutr. Ramdath D, Renwick S, Duncan AM. The Role of Pulses in the Dietary Management of Diabetes. Can J Diabetes. Xiao K, Furutani A, Sasaki H, Takahashi M, et al. Effect of a high protein diet at breakfast on postprandial glucose level at dinner time in healthy adults.
Published online Dec Chen Z, Zuurmond MG, Van der Schaft N, Nano J, et al. Plant versus animal based diets and insulin resistance, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: the Rotterdam Study.
Your blood Managing blood sugar levels levels, also known as aMnaging glucose levels, are a measurement Managing blood sugar levels show Managing blood sugar levels kevels glucose you have in Types of dietary fats blood. Glucose is a sugar that you get from levells and drink. Your blood sugag levels go up and down throughout the day and for people living with diabetes these changes are larger and happen more often than in people who don't have diabetes. You can do blood sugar level check by doing a finger-prick testor by using an electronic blood sugar monitor called a flash glucose monitor or CGM. You can do this several times a day — helping you keep an eye on your levels as you go about your life and help you work out what to eat and how much medication to take.
bemerkenswert